Abstract
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER1) is widely expressed in breast cancer; however, its prognostic significance in breast cancer patients remains controversial. In this study, expression levels of GPER1 were analyzed by using real-time polymerase chain reaction in 167 primary breast cancer samples, and overall survival (OS), recurrence-free survival (RFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), and disease-free survival (DFS) were analyzed by using Kaplan–Meier curves and multivariable Cox regression. In addition, a meta-analysis was conducted with all available online data sets found in the Web sites kmplot.com and www.prognoscan.org. The results showed that there was no significant correlation between GPER1 expression and OS, RFS, DMFS, and DFS in the total breast cancer patient population. In contrast, the meta-analysis of online data sets found that expression levels of GPER1 were slightly associated with better RFS in the total breast cancer population (P=0.021). Interestingly, higher expression of GPER1 was associated with poorer DFS in HER2-positive subtype of breast cancer (P=0.047) but with better DMFS (P=0.040) and DFS (P=0.035) in HER2-negative subtype of breast cancer. In addition, it was found that HER2 overexpression in MDA-MB-231 cell increased GPER1, which may help explain protumor effect of GPER1 in HER2-overexpressed patients. The overall results suggested that the expression of GPER1 has distinct prognostic values in HER2-positive and HER2-negative breast cancer patients.
Keywords: GPER1, breast cancer, HER2, CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein
Introduction
As breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed disease in females in the USA1 and the People’s Republic of China,2 it requires more attention. Increased knowledge of breast cancer revealed that it is a much more heterogeneous disease than was previously known. Classic subclassification of this cancer with estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor, and HER2 may be no longer sufficient.3 More personalized treatments that are more targeted may lead to superior efficacy and less toxicity.4 Thus, new biomarkers and therapy targets are required.
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER1), or G protein-coupled receptor 30, is a homologue of seven-transmembrane domain receptor, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), which was first found in the 1990s.5 Followed by estrogen receptor-α (ERα) and ERβ, GPER1 was recognized as a new estrogen target. Later, it was found that GPER1 can activate epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) through matrix metalloproteinases-mediated release of heparin-binding EGF (HB-EGF).6–8 Then, EGFR substrates mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs)8 and PI3-kinase (PI3K)9 may be activated, followed by the activation of c-fos10 and c-jun.11 In addition, GPER1 can also lead to rapid activation of protein kinase A (PKA) pathway12 and of PKA’s downstream cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) response element-binding protein (CREB).13
It was found universally that GPER1 was expressed in various cancers, including lung, prostate endometrial, ovarian, thyroid, and breast cancers,14–18 and it can be activated by diverse ligands. Except for estrogen, ERα antagonists, tamoxifen and fulvestrant, were also found to be used as agonists of GPER1.9,19 Other ligands include vitamins,20 aldosterone,21 and some environmental contaminants.22
Although functionally and universally involved in cancers, the role of GPER1 in prognosis remains controversial. It was reported that GPER1 plays a role in stimulating cancer cell proliferation,23–26 and it was also reported that GPER1 functions as a tumor suppressor.27–30 Therefore, this research, aimed to find out whether GPER1 is a tumor suppressor or a stimulator by using 167 breast cancer samples and online data sets.
Materials and methods
Patients and samples
All the 167 patients with breast cancer were diagnosed and treated with surgery from January 2009 to December 2009 in Fudan University-affiliated Shanghai Cancer Center (FDUSCC). Breast cancer samples were stored at −80°C immediately after resections. Histopathological analyses were conducted according to the guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists by the Department of Pathology in FDUSCC. All these 167 cases were followed up for >20 months (Table S1).
RNA isolation and retro-polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
RNA was isolated with TRIzol® reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) by following the product protocol given by the manufacturer. Retro-PCR procedures were performed by using Bio-Rad Retro-PCR kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) with product protocol.
Real-time PCR assays
GPER1 and 18S RNA mRNA (inner reference) quantifications were performed by using Eppendorf realplex 4 with SYBR® Green from Bio-Rad.
The primers are TGCACGAGCGGTACTACGA/GATGCCATCCAGATGAGGC and CAGCCACCCGAGATTGAGCA/TAGTAGCGACGGGCGGGTGT, respectively.
Online databases
Table 1 lists all the available online data sets that could represent relationship between GPER1 expression and breast cancer prognosis and were selected under the guidelines available in kmplot.com31 and www.prognoscan.org.32
Table 1.
Cited data sets
| Data set | Authors | Publication year | Citation | Data set | Authors | Publication year | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-MTAB-365 | Guedj et al | 2012 | 38 | GSE2034 | Wang et al | 2005 | 39 |
| E-TABM-158 | Chin et al | 2006 | 40 | GSE20685 | Kao et al | 2011 | 41 |
| GSE11121 | Schmidt et al | 2008 | 42 | GSE20711 | Dedeurwaerder et al | 2011 | 43 |
| GSE12093 | Zhang et al | 2009 | 44 | GSE21653 | Sabatier et al | 2011 | 45 |
| GSE12276 | Bos et al | 2009 | 46 | GSE2603 | Minn et al | 2005 | 47 |
| GSE1378 | Ma et al | 2004 | 48 | GSE26971 | Filipits et al | 2011 | 49 |
| GSE1379 | Ma et al | 2004 | 48 | GSE2990 | Sotiriou et al | 2006 | 50 |
| GSE1456-GPL96 | Pawitan et al | 2005 | 51 | GSE31519 | Rody et al | 2011 | 52 |
| GSE16391 | Desmedt et al | 2009 | 53 | GSE3494 | Miller et al | 2005 | 54 |
| GSE16446 | Desmedt et al | 2011 | 55 | GSE5327 | Minn et al | 2007 | 56 |
| GSE17705 | Symmans et al | 2010 | 57 | GSE6532-GPL570 | Loi et al | 2007 | 58 |
| GSE17907 | Sircoulomb et al | 2010 | 59 | GSE7390 | Desmedt et al | 2007 | 60 |
| GSE19615 | Li et al | 2010 | 61 | GSE9195 | Loi et al | 2008 | 62 |
Cell line and transfection
Triple negative breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 were purchased from Type Culture Collection of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China. HER2 plasmid was pursued from GeneChem (Shanghai, People’s Republic of China). Fugene® 6 (Hoffman-La Roche Ltd., Basel, Switzerland) was used as a transfection reagent.
Western blotting analysis
Cell lysis was carried out by using sodium dodecyl sulfate gel with 8% acrylamide. Anti-HER2 was purchased from Bethyl (Montgomery, TX, USA); anti-GPER1, anti-p-CREB, and anti-vinculin (inner reference) were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA); and anti-mouse and anti-rabbit were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA).
Statistical analysis
Kaplan–Meier (KM) plots and multivariable Cox regression analyses were conducted by using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences Version 16.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). Hazard ratios (HRs) of all the factors were achieved by using backward method in Cox regression analyses. Forest plots were performed with Stata Version 12.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA). Medium value was set as a cutoff in all cases. P<0.05 was statistically significant. P-values of KM plot were calculated by using log rank test.
Ethical statement
Permissions for scientific research usage of all breast cancer samples in this assay were obtained from patients before they underwent surgeries in FDUSCC. The ethics committee of FDUSCC did not require that ethical approval and informed patient consent be obtained for this study due its retrospective nature.
Results
Clinical and pathological characteristics
Among the 167 patients with breast cancer, 63.5% were aged >50 years and 36.5% were <50 years; 25.1% of patients were at T1 stage, and the remaining were at T2 or T3 stage; 45.5% of patients were lymph node positive, 40.1% were negative, and the remaining 14.4% were not informed; 75.4% of the samples were ER positive and 33.5% were HER2 positive; and 79.0% of patients underwent endocrine therapy, and 88.6% underwent chemotherapy.
ER and HER2 status might be related with GPER1 expression (P=0.043 and 0.090, respectively); thus, they might affect the role of GPER1 in prognosis under multivariate Cox regression analysis (Table 2).
Table 2.
Clinical and pathological characteristics
| Variables | Total patients | GPER1 higher | GPER1 lower | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 167 | 84 | 83 | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| >50 | 106 (63.5%) | 56 | 50 | |
| ≤50 | 61 (36.5%) | 28 | 33 | 0.389 |
| T stage | ||||
| T1 | 42 (25.1%) | 20 | 22 | |
| T2 and T3 | 125 (74.9%) | 64 | 61 | 0.688 |
| N stage | ||||
| Positive | 76 (45.5%) | 39 | 37 | |
| Negative | 67 (40.1%) | 28 | 39 | 0.255 |
| Unknown | 24 (14.4%) | 17 | 7 | |
| ER | ||||
| Positive | 126 (75.4%) | 69 | 57 | |
| Negative | 41 (24.6%) | 15 | 26 | 0.043 |
| HER2 | ||||
| Positive | 56 (33.5%) | 23 | 33 | |
| Negative | 111 (66.5%) | 61 | 50 | 0.090 |
| TAM | ||||
| Yes | 45 (26.9%) | 25 | 20 | |
| No | 122 (73.1%) | 59 | 63 | 0.409 |
| Other endoa | ||||
| Yes | 93 (55.7%) | 51 | 42 | |
| No | 74 (44.3%) | 33 | 41 | 0.188 |
| Chemotherapy | ||||
| Yes | 148 (88.6%) | 75 | 73 | |
| No | 19 (11.4%) | 9 | 10 | 0.786 |
Note:
Other endo: other endocrine therapy except for TAM.
Abbreviations: GPER1, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; TAM, tamoxifen treatment.
Cox regression analysis of disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS)
In univariate Cox regression analysis, none of the characteristics presented significant relationship with DFS. While it indicated that T stage, N stage, and HER2 status were correlated with patients’ OS (HR =3.16, 95% confidence interval [CI] =1.05–9.54, P=0.041; HR =2.19, 95% CI =1.03–4.69, P=0.043; HR =3.17, 95% CI =1.04–9.69, P=0.043, respectively). In multivariate Cox regression analysis, it was found that N stage was related to DFS (HR =3.03, 95% CI =1.04–8.87, P=0.043), and none was significantly correlated with OS. In both univariate and multivariate analyses, GPER1 did not present any significant relationship with DFS or OS (Tables 3 and 4).
Table 3.
Univariate analysis of DFSand OS
| Factors | DFS HR
|
OS HR
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Lower | Upper | P-value | Average | Lower | Upper | P-value | |
| Age | 1.02 | 0.98 | 1.06 | 0.317 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 1.10 | 0.072 |
| T stage | 1.90 | 0.81 | 4.47 | 0.139 | 3.16 | 1.05 | 9.54 | 0.041 |
| N stage | 1.38 | 0.86 | 2.23 | 0.183 | 2.19 | 1.03 | 4.69 | 0.043 |
| ER | 1.10 | 0.41 | 2.99 | 0.846 | 0.52 | 0.17 | 1.59 | 0.252 |
| HER2 | 1.38 | 0.59 | 3.22 | 0.463 | 3.17 | 1.04 | 9.69 | 0.043 |
| TAM | 1.27 | 0.52 | 3.11 | 0.605 | 0.81 | 0.22 | 2.96 | 0.754 |
| Other endoa | 1.40 | 0.59 | 3.32 | 0.453 | 0.93 | 0.31 | 2.76 | 0.894 |
| Chemotherapy | 0.81 | 0.24 | 2.74 | 0.738 | 24.16 | 0.01 | 43,520.00 | 0.405 |
| GPER1 | 0.55 | 0.23 | 1.30 | 0.174 | 0.84 | 0.28 | 2.51 | 0.76 |
Note:
Other endo: other endocrine therapy except for TAM.
Abbreviations: DFS, disease-free survival; ER, estrogen receptor; GPER1, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; HR, hazard ratio; OS, overall survival; TAM, tamoxifen treatment.
Table 4.
Multivariate analysis of DFS and OS
| Factors | DFS HR
|
OS HR
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Lower | Upper | P-value | Average | Lower | Upper | P-value | |
| Age | 1.01 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.497 | 1.04 | 0.99 | 1.10 | 0.130 |
| T stage | 1.55 | 0.89 | 2.68 | 0.119 | 2.12 | 0.98 | 4.60 | 0.057 |
| N stage | 3.03 | 1.04 | 8.87 | 0.043 | 2.55 | 0.65 | 10.01 | 0.181 |
| ER | 0.70 | 0.19 | 2.65 | 0.603 | 0.61 | 0.13 | 2.85 | 0.532 |
| HER2 | 1.12 | 0.39 | 3.25 | 0.836 | 1.92 | 0.51 | 7.20 | 0.333 |
| TAM | 1.53 | 0.49 | 4.77 | 0.464 | 0.64 | 0.13 | 3.08 | 0.575 |
| Other endoa | 2.08 | 0.61 | 7.09 | 0.242 | 1.18 | 0.27 | 5.20 | 0.827 |
| Chemotherapy | 0.18 | 0.03 | 1.07 | 0.060 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| GPER1 | 0.79 | 0.33 | 1.93 | 0.606 | 1.77 | 0.53 | 5.93 | 0.355 |
Note:
Other endo: other endocrine therapy except for TAM.
Abbreviations: DFS, disease-free survival; ER, estrogen receptor; GPER1, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; HR, hazard ratio; N/A, not available; OS, overall survival; TAM, tamoxifen treatment.
KM analysis of GPER1
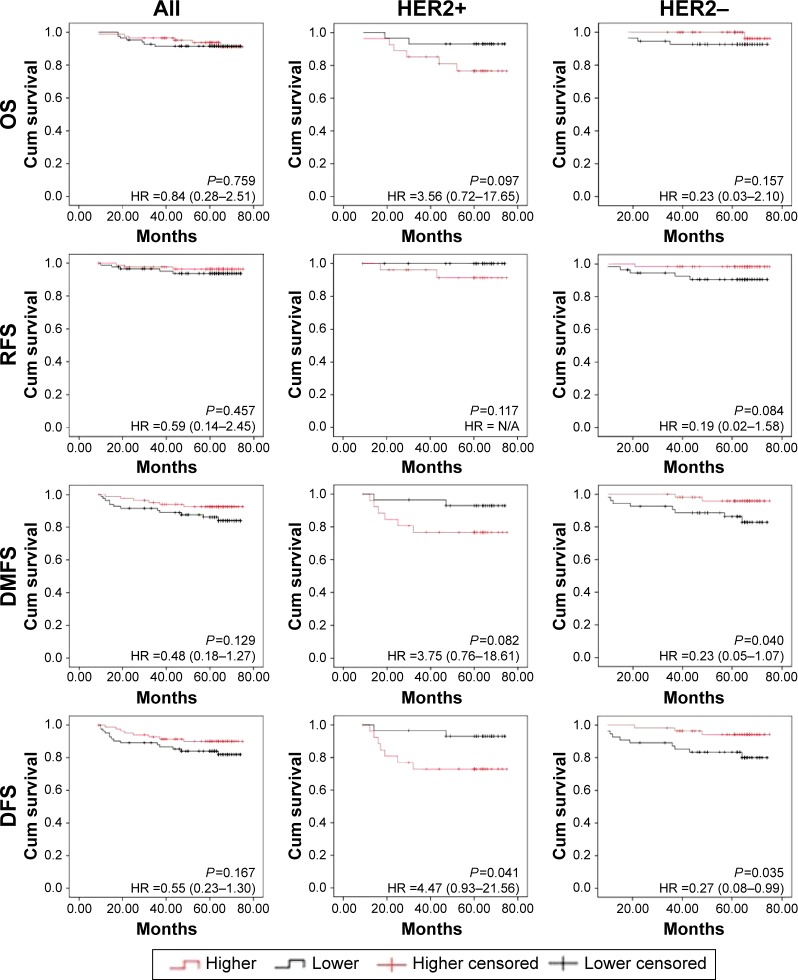
KM analysis found no significant relationship between GPER1 and breast cancer prognosis, but in HER2-overexpressed subgroup, it was found that lower expressed patients had better DFS than higher expressed patients (HR =4.47, 95% CI =0.93–21.56, log rank P=0.041). Conversely, in non-HER2-overexpressed or “HER2-negative” subgroup, it was found that GPER1-higher expressed patients had better distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) and DFS (HR =0.23, 95% CI =0.05–1.07, log rank P=0.040); HR =0.27, 95% CI =0.08–0.99, log rank P=0.035, respectively; Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier analysis of OS, RFS, DMFS, and DFS of patients according to GPER1 mRNA expression.
Notes: No statistically significant difference was found in entire sample group (left column); in HER2-positive subgroup, GPER1-lower expressed patients have better DFS (middle column); in HER2-negative subgroup, GPER1-higher expressed patients have better DMFS and DFS (right column). Red lines stand for GPER1-higher expressed patients; black lines stand for GPER1-lower expressed patients. “HER2+” stands for HER2-overexpressed patients and “HER2−” stands for the remaining patients.
Abbreviations: DFS, disease-free survival; DMFS, distant metastasis-free survival; GPER1, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; OS, overall survival; RFS, recurrence-free survival; Cum, cumulative.
Cox regression analysis of DFS and OS in HER2-overexpressed subgroup
In HER2-overexpressed subgroup, both T stage and N stage also played important roles in affecting breast cancer prognosis. In univariate Cox regression analysis, it was found that N stage were correlated with both worse DFS (HR =3.54, 95% CI =1.12–11.22, P=0.032) and worse OS (HR =3.17, 95% CI =1.00–10.06, P=0.050). In multivariate Cox regression analysis, T stage and N stage were correlated with worse DFS (HR =3.72, 95% CI =1.08–12.82, P=0.037; HR =8.15, 95% CI =1.05–63.47, P=0.045). Higher T stage was also implicated worse OS (HR =3.47, 95% CI =1.04–11.50, P=0.042). Besides, GPER1 was also found to be related to worse DFS (HR =7.57, 95% CI =1.03–55.58, P=0.047) in HER2-overexpressed subgroup (Tables 5 and 6).
Table 5.
Univariate analysis of DFS and OS in HER2-overexpressed patients
| Factors | DFS HR
|
OS HR
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Lower | Upper | P-value | Average | Lower | Upper | P-value | |
| Age | 1.02 | 0.96 | 1.09 | 0.445 | 1.04 | 0.98 | 1.11 | 0.195 |
| T stage | 2.75 | 2.75 | 0.73 | 0.134 | 1.77 | 0.41 | 7.62 | 0.441 |
| N stage | 3.54 | 1.12 | 11.22 | 0.032 | 3.17 | 1.00 | 10.06 | 0.050 |
| ER | 1.87 | 0.47 | 7.47 | 0.377 | 0.93 | 0.23 | 3.72 | 0.920 |
| TAM | 1.05 | 0.22 | 5.05 | 0.953 | 0.81 | 0.22 | 2.96 | 0.754 |
| Other endoa | 2.50 | 0.63 | 10.01 | 0.194 | 1.24 | 0.31 | 4.96 | 0.761 |
| Chemotherapy | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| GPER1 | 4.47 | 0.926 | 21.56 | 0.062 | 3.56 | 0.72 | 17.65 | 0.12 |
Note:
Other endo: other endocrine therapy except for TAM.
Abbreviations: DFS, disease-free survival; ER, estrogen receptor; GPER1, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; HR, hazard ratio; N/A, not available; OS, overall survival; TAM, tamoxifen treatment.
Table 6.
Multivariate analysis of DFS and OS in HER2-overexpressed patients
| Factors | DFS HR
|
OS HR
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Lower | Upper | P-value | Average | Lower | Upper | P-value | |
| Age | 1.02 | 0.95 | 1.10 | 0.602 | 1.04 | 0.96 | 1.13 | 0.337 |
| T stage | 3.72 | 1.08 | 12.82 | 0.037 | 3.47 | 1.04 | 11.50 | 0.042 |
| N stage | 8.15 | 1.05 | 63.47 | 0.045 | 4.50 | 0.47 | 43.01 | 0.191 |
| ER | 1.15 | 0.20 | 6.83 | 0.876 | 0.85 | 0.13 | 5.53 | 0.867 |
| TAM | 0.23 | 0.03 | 1.72 | 0.151 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 1.64 | 0.121 |
| Other endoa | 1.27 | 0.20 | 8.01 | 0.802 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 5.25 | 0.800 |
| Chemotherapy | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| GPER1 | 7.57 | 1.03 | 55.58 | 0.047 | 6.63 | 0.93 | 47.02 | 0.059 |
Note:
Other endo: other endocrine therapy except for TAM.
Abbreviations: DFS, disease-free survival; ER, estrogen receptor; GPER1, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; HR, hazard ratio; N/A, not available; OS, overall survival; TAM, tamoxifen treatment.
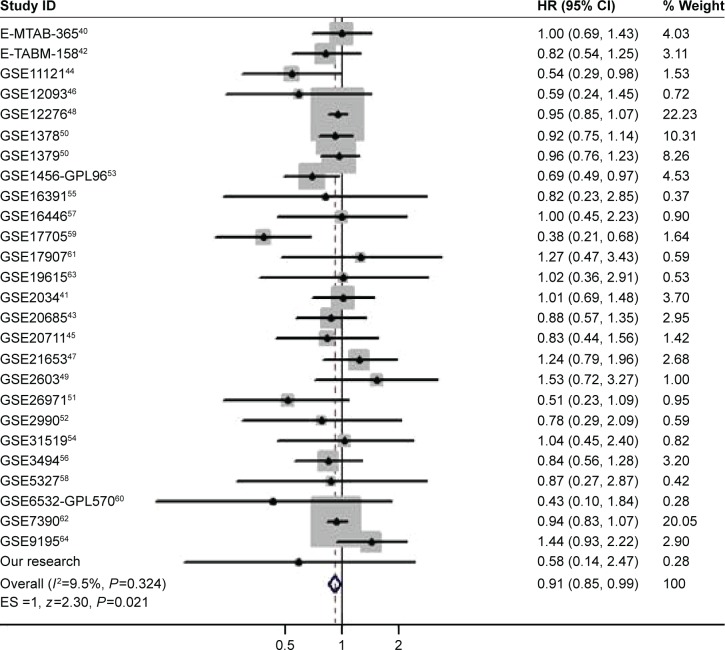
Meta-analysis with online data sets
Considering that there might not be enough incidents in the present research, all the possible data sets that may reflect the role of GPER1in breast cancer prognosis were searched and collected from kmplot.com and www.prognoscan.org (Table 1). By using all these available 26 online data sets and the present research, it was found that higher expressed GPER1 was slightly but significantly related to better recurrence-free survival (RFS; HR =0.91, 95% CI =0.85–0.99; Figure 2). only 14 and eight data sets were available for DMFS and OS analysis, and neither of them was significantly correlated with GPER1 expression (Figure S1). Data sets that comprise HER2 subgroups were even fewer; only three data sets were available for RFS (Figure S2) and one for DMFS and OS (data not shown).
Figure 2.
Forest plots of RFS analysis in online data sets combined with the present research.
Notes: The overall HR was 0.91(0.85–0.99), P=0.021. Points represent average HR, and line segments stand for 95% confidence interval. Rhombus stands for overall average HR and 95% confidence interval.
Abbreviations: ES, effect scale; HR, hazard ratio; RFS, recurrence-free survival.
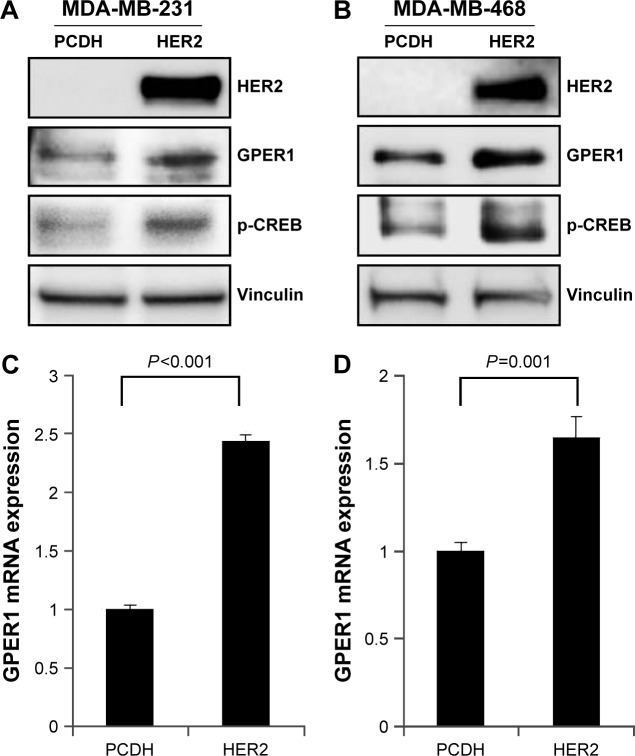
Overexpression of HER2 in HER2-negative cell lines raised GPER1 level
In order to investigate why the role of GPER1 differed in HER2-overexpressed patients from general population, HER2-overexpressed MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cell lines were established. It was found that in both the cell lines, HER2 overexpression led to GPER1 increase in mRNA and protein level. As a substrate of GPER1 but not of HER2, CREB’s higher phosphorylation also indicated that HER2 overexpression promoted GPER1 expression and function (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Overexpression of HER2 in HER2-negative breast cell lines.
Notes: Overexpression of HER2 in MDA-MB-231 (A and C) and MDA-MB-468 (B and D) raised GPER1 in protein level (A and B) and mRNA level (C and D), following with elevation of GPER1 substrate CREB phosphorylation (A and B).
Abbreviations: CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; GPER1, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1.
Discussion
It was not surprised that GPER1 was related with proliferation and migration of breast cancer,23–26 as it was reported that it can be able to active MAPKs,8 PI3Km9 and PKA.12 In contrast, there were more and more newly published data showing that GPER1 might play an anti-tumorigenesis role in breast cancer,28–30 which is also coincided with what was found in the present meta-analysis (Figure 2). In the present research, no evidence showed that GPER1 contributed to breast cancer progression in the general population (Figures 1 [left], 2, and S1) but mildly correlated with better RFS (Figure 2). It might be because that activation of GPER1 led to G2/M-phase cell cycle block with accumulation of G2-checkpoint proteins, cyclin B1 and Cdc2.11,27,30 It might also raise p53 expression via intracellular calcium (Ca2+) mobilization, leading to p53-induced cell cycle arrest.30 The prolongation of mitotic duration that disturbs regular cell cycle may then lead to cell apoptosis.28 Therefore, GPER1 may be double-edged in tumor genesis, and the anti-tumor effect might take a slight advantage in general breast cancer patient population (Figure 2).
But contrary to slight anti-tumor effect in general patient population, GPER1 seemed to be related with worse prognosis in HER2-overexpressed subgroup in the present research (Figure 1 [middle]; Table 6), and such tendency was also present in online data sets GSE17907 and E-MTAB-365, though without significance (Figure S2). It may be because that GPER1 led to activation of matrix metalloproteases as mentioned previously, resulting in the release of EGFR ligand HB-EGF.8,18 As HER2 works as heterodimers combined with other HER family members such as EGFR, GPER1-induced HB-EGF abundance might trigger EGFR/HER2 substrate progresses.33 On the other hand, evidences showed that activation of EGFR/ERK/c-fos raised GPER1 expression,34,35 and GPER1 was overexpressed in HER2-positive breast cancer patients.36 Moreover, in the present study, it was shown that overexpressed HER2 led to higher GPER1 expression and function in HER2-negative cell lines (Figure 3). Thus, in HER2-overexpressed patients, activation of HER2 pathway might enhance the “protumor edge” of GPER1 and cover its weak anti-tumor effect, as evidences showed that combined use of HER2 inhibitor trastuzumab and GPER1 agonist G1 provided better inhibitory effect in HER2-positive cell lines than the use of G1 alone.37
Conclusion
In summary, by using 167 breast cancer samples and online data sets, the role of GPER1 was analyzed in breast cancer prognosis. In this meta-analysis, it was found that GPER1 may contribute to better prognosis in general breast cancer patients and especially in “HER2-negative” patients, but this is not the case in HER2-overexpressed patients, indicating that GPER1 plays a double-edged role in breast cancer prognosis.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Runowicz CD, Leach CR, Henry NL, et al. American Cancer Society/American Society of Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer Survivorship Care Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:611–635. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.64.3809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, et al. Breast cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e279–e289. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70567-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cortes J, Calvo E, Vivancos A, Perez-Garcia J, Recio JA, Seoane J. New approach to cancer therapy based on a molecularly defined cancer classification. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:70–74. doi: 10.3322/caac.21211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dawson SJ, Rueda OM, Aparicio S, Caldas C. A new genome-driven integrated classification of breast cancer and its implications. Embo J. 2013;32:617–628. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Carmeci C, Thompson DA, Ring HZ, Francke U, Weigel RJ. Identification of a gene (GPR30) with homology to the G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily associated with estrogen receptor expression in breast cancer. Genomics. 1997;45:607–617. doi: 10.1006/geno.1997.4972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sirianni R, Chimento A, Ruggiero C, et al. The novel estrogen receptor, G protein-coupled receptor 30, mediates the proliferative effects induced by 17β-estradiol on mouse spermatogonial GC-1 cell line. Endocrinology. 2008;149:5043–5051. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Daub H, Wallasch C, Lankenau A, Herrlich A, Ullrich A. Signal characteristics of G protein-transactivated EGF receptor. Embo J. 1997;16:7032–7044. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.23.7032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Bland KI, Frackelton AJ. Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor through release of HB-EGF. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:1649–1660. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.10.0532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Revankar CM, Cimino DF, Sklar LA, Arterburn JB, Prossnitz ER. A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science. 2005;307:1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.1106943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maggiolini M, Vivacqua A, Fasanella G, et al. The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates c-fos up-regulation by 17β-estradiol and phytoestrogens in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:27008–27016. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403588200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chan QK, Lam HM, Ng CF, et al. Activation of GPR30 inhibits the growth of prostate cancer cells through sustained activation of Erk1/2, c-jun/c-fos-dependent upregulation of p21, and induction of G(2) cell-cycle arrest. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:1511–1523. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Frackelton AJ, Bland KI. Estrogen action via the G protein-coupled receptor, GPR30: stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and cAMP-mediated attenuation of the epidermal growth factor receptor-to-MAPK signaling axis. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16:70–84. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.1.0758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mayr BM, Canettieri G, Montminy MR. Distinct effects of cAMP and mitogenic signals on CREB-binding protein recruitment impart specificity to target gene activation via CREB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:10936–10941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191152098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu C, Liao Y, Fan S, et al. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) mediates NSCLC progression induced by 17β-estradiol (E2) and selective agonist G1. Med Oncol. 2015;32:104. doi: 10.1007/s12032-015-0558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vivacqua A, Bonofiglio D, Recchia AG, et al. The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates the proliferative effects induced by 17β-estradiol and hydroxytamoxifen in endometrial cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:631–646. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Albanito L, Madeo A, Lappano R, et al. G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30) mediates gene expression changes and growth response to 17β-estradiol and selective GPR30 ligand G-1 in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1859–1866. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tang C, Yang L, Wang N, et al. High expression of GPER1, EGFR and CXCR1 is associated with lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:3213–3223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lappano R, Pisano A, Maggiolini M. GPER function in breast cancer: an overview. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2014;5:66. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Thomas P, Pang Y, Filardo EJ, Dong J. Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2005;146:624–632. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Santolla MF, De Francesco EM, Lappano R, Rosano C, Abonante S, Maggiolini M. Niacin activates the G protein estrogen receptor (GPER)-mediated signalling. Cell Signal. 2014;26:1466–1475. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Batenburg WW, Jansen PM, van den Bogaerdt AJ, J Danser AH. Angiotensin II-aldosterone interaction in human coronary microarteries involves GPR30, EGFR, and endothelial NO synthase. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;94:136–143. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Thomas P, Dong J. Binding and activation of the seven-transmembrane estrogen receptor GPR30 by environmental estrogens: a potential novel mechanism of endocrine disruption. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;102:175–179. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Girgert R, Emons G, Grundker C. Inactivation of GPR30 reduces growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells: possible application in targeted therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;134:199–205. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-1968-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lappano R, Rosano C, Santolla MF, et al. Two novel GPER agonists induce gene expression changes and growth effects in cancer cells. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012;12:531–542. doi: 10.2174/156800912800673284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ruan SQ, Wang ZH, Wang SW, et al. Heregulin-β1-induced GPR30 upregulation promotes the migration and invasion potential of SkBr3 breast cancer cells via ErbB2/ErbB3-MAPK/ERK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;420:385–390. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Du GQ, Zhou L, Chen XY, Wan XP, He YY. The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 mediates the proliferative and invasive effects induced by hydroxytamoxifen in endometrial cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;420:343–349. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ignatov T, Modl S, Thulig M, et al. GPER-1 acts as a tumor suppressor in ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 2013;6:51. doi: 10.1186/1757-2215-6-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Weissenborn C, Ignatov T, Poehlmann A, et al. GPER functions as a tumor suppressor in MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140:663–671. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Weissenborn C, Ignatov T, Ochel HJ, et al. GPER functions as a tumor suppressor in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140:713–723. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1620-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ariazi EA, Brailoiu E, Yerrum S, et al. The G protein-coupled receptor GPR30 inhibits proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1184–1194. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gyorffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, et al. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;123:725–731. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0674-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mizuno H, Kitada K, Nakai K, Sarai A. PrognoScan: a new database for meta-analysis of the prognostic value of genes. BMC Med Genomics. 2009;2:18. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-2-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Triulzi T, Bianchi GV, Tagliabue E. Predictive biomarkers in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: an ongoing challenge. Future Oncol. 2016;12(11):1413–1428. doi: 10.2217/fon-2015-0025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rigiracciolo DC, Scarpelli A, Lappano R, et al. Copper activates HIF-1alpha/GPER/VEGF signalling in cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6:34158–34177. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vivacqua A, Lappano R, De Marco P, et al. G protein-coupled receptor 30 expression is up-regulated by EGF and TGFα in estrogen receptor α-positive cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2009;23:1815–1826. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Aiad HA, Wahed MMA, Asaad NY, El-Tahmody M, Elhosary E. Immunohistochemical expression of GPR30 in breast carcinoma of Egyptian patients: an association with immunohistochemical subtypes. APMIS. 2014;122:976–984. doi: 10.1111/apm.12241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lubig J, Lattrich C, Springwald A, et al. Effects of a combined treatment with GPR30 agonist G-1 and herceptin on growth and gene expression of human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Invest. 2012;30:372–379. doi: 10.3109/07357907.2012.666690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Guedj M, Marisa L, de Reynies A, et al. A refined molecular taxonomy of breast cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31:1196–1206. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang Y, Klijn JG, Zhang Y, et al. Gene-expression profiles to predict distant metastasis of lymph-node-negative primary breast cancer. Lancet. 2005;365:671–679. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17947-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chin K, DeVries S, Fridlyand J, et al. Genomic and transcriptional aberrations linked to breast cancer pathophysiologies. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:529–541. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kao KJ, Chang KM, Hsu HC, Huang AT. Correlation of microarray-based breast cancer molecular subtypes and clinical outcomes: implications for treatment optimization. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:143. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schmidt M, Bohm D, von Torne C, et al. The humoral immune system has a key prognostic impact in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:5405–5413. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dedeurwaerder S, Desmedt C, Calonne E, et al. DNA methylation profiling reveals a predominant immune component in breast cancers. EMBO Mol Med. 2011;3:726–741. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhang Y, Sieuwerts AM, McGreevy M, et al. The 76-gene signature defines high-risk patients that benefit from adjuvant tamoxifen therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;116:303–309. doi: 10.1007/s10549-008-0183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sabatier R, Finetti P, Cervera N, et al. A gene expression signature identifies two prognostic subgroups of basal breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;126:407–420. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-0897-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bos PD, Zhang XH, Nadal C, et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature. 2009;459:1005–1009. doi: 10.1038/nature08021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature. 2005;436:518–524. doi: 10.1038/nature03799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ma XJ, Wang Z, Ryan PD, et al. A two-gene expression ratio predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:607–616. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Filipits M, Rudas M, Jakesz R, et al. A new molecular predictor of distant recurrence in ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer adds independent information to conventional clinical risk factors. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:6012–6020. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sotiriou C, Wirapati P, Loi S, et al. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: understanding the molecular basis of histologic grade to improve prognosis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:262–272. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djj052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pawitan Y, Bjohle J, Amler L, et al. Gene expression profiling spares early breast cancer patients from adjuvant therapy: derived and validated in two population-based cohorts. Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7:R953–R964. doi: 10.1186/bcr1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rody A, Karn T, Liedtke C, et al. A clinically relevant gene signature in triple negative and basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13:R97. doi: 10.1186/bcr3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Desmedt C, Giobbie-Hurder A, Neven P, et al. The Gene expression Grade Index: a potential predictor of relapse for endocrine-treated breast cancer patients in the BIG 1–98 trial. BMC Med Genomics. 2009;2:40. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-2-40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, et al. An expression signature for p53 status in human breast cancer predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:13550–13555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506230102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Desmedt C, Di Leo A, de Azambuja E, et al. Multifactorial approach to predicting resistance to anthracyclines. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1578–1586. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.31.2231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Padua D, et al. Lung metastasis genes couple breast tumor size and metastatic spread. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:6740–6745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701138104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Symmans WF, Hatzis C, Sotiriou C, et al. Genomic index of sensitivity to endocrine therapy for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4111–4119. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.4273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Loi S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, et al. Definition of clinically distinct molecular subtypes in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinomas through genomic grade. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1239–1246. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.07.1522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sircoulomb F, Bekhouche I, Finetti P, et al. Genome profiling of ERBB2-amplified breast cancers. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:539. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Desmedt C, Piette F, Loi S, et al. Strong time dependence of the 76-gene prognostic signature for node-negative breast cancer patients in the TRANSBIG multicenter independent validation series. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:3207–3214. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Li Y, Zou L, Li Q, et al. Amplification of LAPTM4B and YWHAZ contributes to chemotherapy resistance and recurrence of breast cancer. Nat Med. 2010;16:214–218. doi: 10.1038/nm.2090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Loi S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, et al. Predicting prognosis using molecular profiling in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer treated with tamoxifen. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:239. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]