Abstract
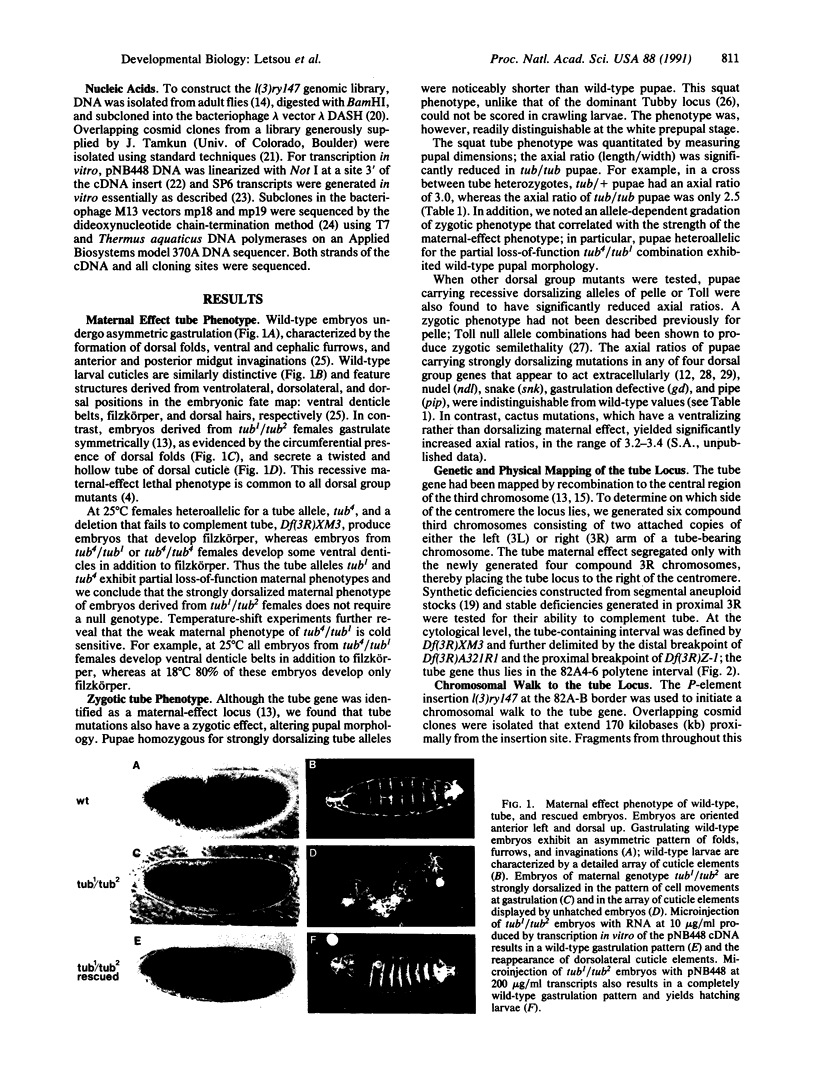
Loss of maternal function of the tube gene disrupts a signaling pathway required for pattern formation in Drosophila, causing cells throughout the embryo to adopt the fate normally reserved for those at the dorsal surface. Here we demonstrate that tube mutations also have a zygotic effect on pupal morphology and that this phenotype is shared by mutations in Toll and pelle, two genes with apparent intracellular roles in determining dorsoventral polarity. We then describe the isolation of a functionally full-length tube cDNA identified in a phenotypic rescue assay. The tube mRNA is expressed maximally early in embryogenesis and again late in larval development, corresponding to required periods of tube activity as defined by distinct maternal and zygotic loss-of-function phenotypes in tube mutants. Sequence analysis of the cDNA indicates that the tube protein contains five copies of an eight-residue motif and shares no significant sequence similarity with known proteins. These results suggest that tube represents a class of protein active in signal transduction at two stages of development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. V., Jürgens G., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Establishment of dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo: genetic studies on the role of the Toll gene product. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):779–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. V., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Information for the dorsal--ventral pattern of the Drosophila embryo is stored as maternal mRNA. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):223–227. doi: 10.1038/311223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., Kafatos F. C. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasan R., Anderson K. V. The role of easter, an apparent serine protease, in organizing the dorsal-ventral pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLotto R., Spierer P. A gene required for the specification of dorsal-ventral pattern in Drosophila appears to encode a serine protease. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):688–692. doi: 10.1038/323688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerttula S., Jin Y. S., Anderson K. V. Zygotic expression and activity of the Drosophila Toll gene, a gene required maternally for embryonic dorsal-ventral pattern formation. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):123–133. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Hudson K. L., Anderson K. V. The Toll gene of Drosophila, required for dorsal-ventral embryonic polarity, appears to encode a transmembrane protein. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalfayan L., Wensink P. C. Developmental regulation of Drosophila alpha-tubulin genes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:397–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. Molecular analysis of dorsal-ventral polarity in Drosophila. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):785–786. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley D. L., Sandler L., Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T., Denell R. E., Hall J. C., Jacobs P. A., Miklos G. L., Davis B. K., Gethmann R. C. Segmental aneuploidy and the genetic gross structure of the Drosophila genome. Genetics. 1972 May;71(1):157–184. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchant G. E., Holm D. G. Genetic analysis of the heterochromatin of chromosome 3 in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Products of compound-autosome detachment. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):503–517. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Holtkamp F., Knipple D. C., Seifert E., Jäckle H. An early role of maternal mRNA in establishing the dorsoventral pattern in pelle mutant Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):238–246. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria P., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Partial rescue of dorsal, a maternal effect mutation affecting the dorso-ventral pattern of the Drosophila embryo, by the injection of wild-type cytoplasm. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1695–1699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüpbach T., Wieschaus E. Female sterile mutations on the second chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Maternal effect mutations. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):101–117. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strynadka N. C., James M. N. Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:951–998. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]