Abstract
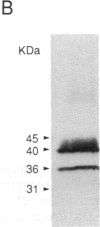
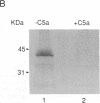
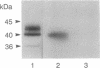
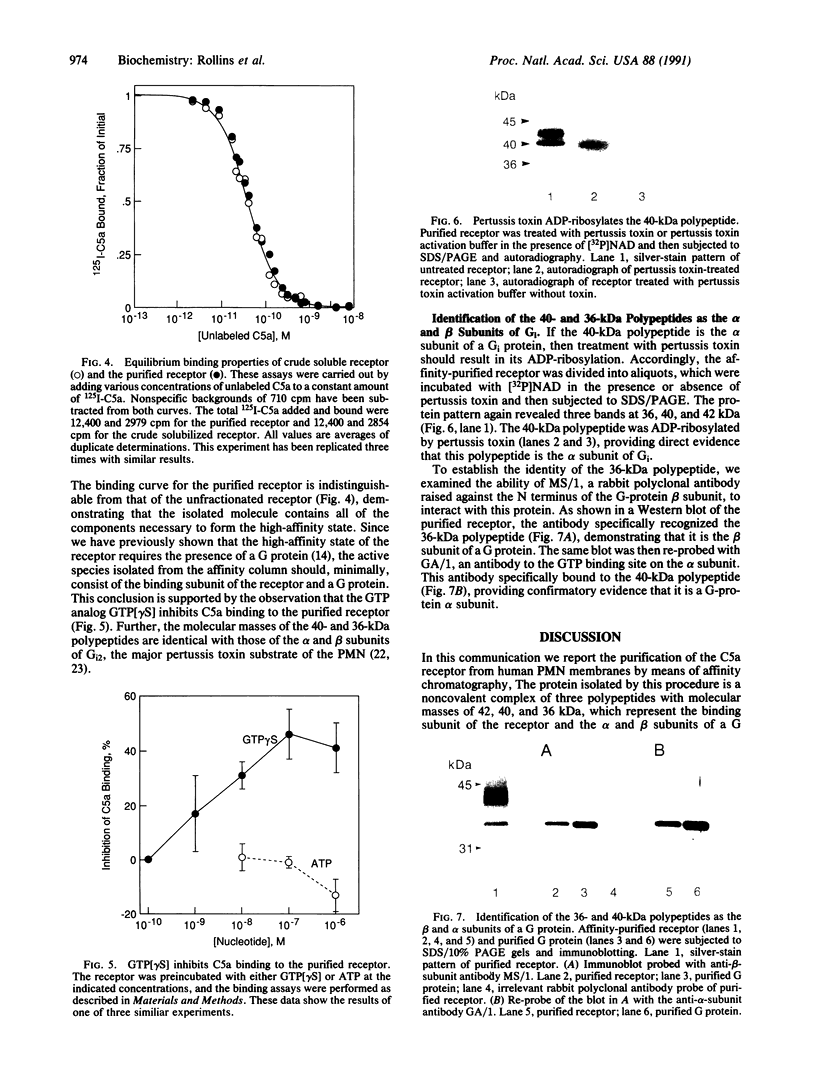
We have isolated, in an active state, the C5a receptor from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. The purification was achieved in a single step using a C5a affinity column in which the C5a molecule was coupled to the resin through its N terminus. The purified receptor, like the crude solubilized molecule, exhibited a single class of high-affinity binding sites with a Kd of 30 pM. Further, the binding of C5a retained its sensitivity to guanine nucleotides, implying that the purified receptor contained a guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein). SDS/PAGE revealed the presence of three polypeptides with molecular masses of 42, 40, and 36 kDa, which were determined to be the C5a-binding subunit and the alpha and beta subunits of Gi, respectively. The 36- and 40-kDa polypeptides were identified by immunoblotting and by the ability of pertussis toxin to ADP-ribosylate the 40-kDa molecule. These results confirm our earlier hypothesis that the receptor exists as a complex with a G protein in the presence or absence of C5a. The tight coupling between the receptor and G protein should make possible the identification of the G protein(s) involved in the transduction pathways used by C5a to produce its many biological effects.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker E. L., Kermode J. C., Naccache P. H., Yassin R., Marsh M. L., Munoz J. J., Sha'afi R. I. The inhibition of neutrophil granule enzyme secretion and chemotaxis by pertussis toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1641–1646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Harris J. I., Hartley B. S., Lebeman R. The use of maleic anhydride for the reversible blocking of amino groups in polypeptide chains. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):679–689. doi: 10.1042/bj1120679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltner D. E., Smith R. H., Marasco W. A. Characterization of the plasma membrane bound GTPase from rabbit neutrophils. I. Evidence for an Ni-like protein coupled to the formyl peptide, C5a, and leukotriene B4 chemotaxis receptors. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1961–1970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I., Schachman H. K. A method for the separation of hybrids of chromatographically identical oligomeric proteins. Use of 3,4,5,6-tetrahydrophthaloyl groups as a reversible "chromatographic handle". Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):52–60. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Falloon J., Milligan G., Pines M., Gallin J. I., Spiegel A. Immunochemical evidence for a novel pertussis toxin substrate in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8058–8062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Chang F. H., Gifford L. A., Goetzl E. J., Bourne H. R. Pertussis toxin inhibition of chemotactic factor-induced calcium mobilization and function in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):145–156. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huey R., Hugli T. E. Characterization of a C5a receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2063–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. Structure and function of the anaphylatoxins. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):193–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01893020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. The structural basis for anaphylatoxin and chemotactic functions of C3a, C4a, and C5a. Crit Rev Immunol. 1981 Feb;1(4):321–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Chenoweth D. E. Labeling the granulocyte C5a receptor with a unique photoreactive probe. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7161–7164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Toyama R., Tsukamoto T., Matsuoka M., Nakafuku M., Obara T., Takagi T., Hernandez R. Structures of the genes coding for G-protein alpha subunits from mammalian and yeast cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):209–220. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Olson C. V., Smiley P. A. Association of the N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe receptor in human neutrophils with a GTP-binding protein sensitive to pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):869–873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura Y., Kitamura Y., Segawa T. Decrease of clonidine binding affinity to alpha 2-adrenoceptor by ADP-ribosylation of 41,000-dalton proteins in rat cerebral cortical membranes by islet-activating protein. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):364–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins T. E., Siciliano S., Springer M. S. Solubilization of the functional C5a receptor from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins T. E., Springer M. S. Identification of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte C5a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7157–7160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirato M., Takahashi K., Nagasawa S., Koyama J. Different sensitivities of the responses of human neutrophils stimulated with immune complex and C5a anaphylatoxin to pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano S. J., Rollins T. E., Springer M. S. Interaction between the C5a receptor and Gi in both the membrane-bound and detergent-solubilized states. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19568–19574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde M. W., Carlson K. E., Manning D. R., Zigmond S. H. Chemoattractant-stimulated GTPase activity is decreased on membranes from polymorphonuclear leukocytes incubated in chemoattractant. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):190–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]