Abstract
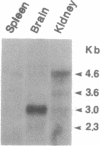
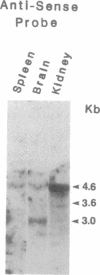
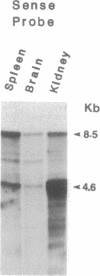
We have isolated a cDNA clone (RB alpha 2B) and its homologous gene (GR alpha 2B) encoding an alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor subtype by screening a rat brain cDNA and a rat genomic library. Nucleotide sequence analysis showed that both clones code for a protein of 458 amino acids, which is 87% homologous to the human kidney glycosylated adrenergic receptor (alpha 2-C4) and divergent from the rat kidney nonglycosylated alpha 2B subtype (RNG alpha 2). Transient expression of RB alpha 2B in COS-7 cells resulted in high-affinity saturable binding (Kd = 0.25 nM) for [3H]rauwolscine and a high receptor number (Bmax = 7.7 pmol/mg of protein) in the membranes of transfected COS-7 cells. Pharmacological analysis demonstrated that the expressed receptor bound adrenergic ligands with the following order of potency: rauwolscine greater than yohimbine greater than prazosin greater than oxymetazoline, with a prazosin-to-oxymetazoline Ki ratio of 0.34. This profile is characteristic of the alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor subtype. Blotting analysis of rat brain mRNA gave one major (3.0-kilobase) and two minor (4.6- and 2.3-kilobase) mRNA species, and hybridization with strand-specific probes showed that both DNA strands of GR alpha 2B may be transcriptionally active. These findings show that rat brain expresses an alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor subtype that is structurally different from the rat kidney nonglycosylated alpha 2B subtype. Thus the rat expresses at least two divergent alpha 2B-adrenergic receptors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Bond C. T., Douglass J., Herbert E. Two mammalian genes transcribed from opposite strands of the same DNA locus. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1514–1517. doi: 10.1126/science.3547652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan M. R., Flordellis C. S., Vassilatis D. K., Makrides S. C., Zannis V. I., Gavras H. High level of expression of functional human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in a stable mouse C127 cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Heterogeneity of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Toso R., Sommer B., Ewert M., Herb A., Pritchett D. B., Bach A., Shivers B. D., Seeburg P. H. The dopamine D2 receptor: two molecular forms generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4025–4034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Rands E., Register R. B., Candelore M. R., Blake A. D., Strader C. D. Ligand binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor involves its rhodopsin-like core. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):73–77. doi: 10.1038/326073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flordellis C. S., Castellano M., Franco R., Zannis V. I., Gavras H. Expression of multiple alpha 2-adrenergic receptor messenger RNA species in rat tissues. Hypertension. 1990 Jun;15(6 Pt 2):881–887. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.6.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. M., Arakawa S., McCombie W. R., Venter J. C. Cloning, sequence analysis, and permanent expression of a human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Evidence for independent pathways of receptor coupling to adenylate cyclase attenuation and activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11754–11761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Kobilka T. S., Daniel K., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Chimeric alpha 2-,beta 2-adrenergic receptors: delineation of domains involved in effector coupling and ligand binding specificity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1310–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.2836950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier S. M., Homcy C. J., Patenaude C., Graham R. M. Identification of structurally distinct alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14491–14496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. A novel member of the thyroid/steroid hormone receptor family is encoded by the opposite strand of the rat c-erbA alpha transcriptional unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1128–1136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Adrenergic receptors. Models for the study of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):4993–4996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Allen L. F., King K., Regan J. W., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Expansion of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor family: cloning and characterization of a human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype, the gene for which is located on chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5094–5098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makrides S. C., Mulinari R., Zannis V. I., Gavras H. Regulation of renin gene expression in hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1988 Oct;12(4):405–410. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.12.4.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Regan J. W., Leader W. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cytoplasmic domains of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Localization of regions involved in G protein-receptor coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15985–15992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrash A. C., Bylund D. B. Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes indicated by [3H]yohimbine binding in human brain. Life Sci. 1986 Jun 9;38(23):2129–2137. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. E. A graphic method for the determination and presentation of binding parameters in a complex system. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Gietz R. D., Hodgetts R. B. Overlapping transcription units in the dopa decarboxylase region of Drosophila. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):279–281. doi: 10.1038/322279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Dixon R. A., Cheung A. H., Candelore M. R., Blake A. D., Sigal I. S. Mutations that uncouple the beta-adrenergic receptor from Gs and increase agonist affinity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16439–16443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E., Akers M., Caron M. G., Hagen P. O. Norepinephrine-induced down regulation of alpha 1 adrenergic receptors in cultured rabbit aorta smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. 1983 Oct 3;33(14):1409–1417. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90824-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng D. W., Harrison J. K., D'Angelo D. D., Barber C. M., Tucker A. L., Lu Z. H., Lynch K. R. Molecular characterization of a rat alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3102–3106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]