Abstract
Human exposures to bisphenol A (BPA) has attained considerable global health attention and represents one of the leading environmental contaminants with potential adverse health effects including endocrine disruption. Current practice of measuring of exposure to BPA includes the measurement of unconjugated BPA (aglycone) and total (both conjugated and unconjugated) BPA; the difference between the two measurements leads to estimation of conjugated forms. However, the measurement of BPA as the end analyte leads to inaccurate estimates from potential interferences from background sources during sample collection and analysis. BPA glucuronides (BPAG) and sulfates (BPAS) represent better candidates for biomarkers of BPA exposure, since they require in vivo metabolism and are not prone to external contamination. In this work, the primary focus was to review the current state of the art in analytical methods available to quantitate BPA conjugates. The entire analytical procedure for the simultaneous extraction and detection of aglycone BPA and conjugates is covered, from sample pre-treatment, extraction, separation, ionization, and detection. Solid phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatograph and tandem mass spectrometer analysis provides the most sensitive detection and quantification of BPA conjugates. Discussed herein are the applications of BPA conjugates analysis in human exposure assessment studies. Measuring these potential biomarkers of BPA exposure has only recently become analytically feasible and there are limitations and challenges to overcome in biomonitoring studies.
Keywords: Biomarkers of exposure, Bisphenol conjugates, Chromatography, Human biomonitoring, Mass spectrometry
Graphical Abstract
1. Background
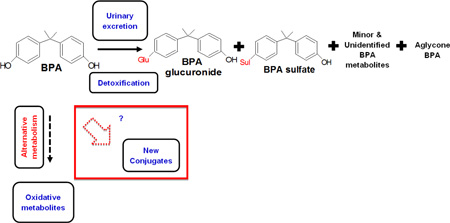
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a phenolic compound in wide use with innumerable industrial, commercial, consumer, and domestic applications. It is a monomer used in polycarbonate and epoxy resins that are used in the production of food, water and beverage packaging material [1–3]. Human exposure to BPA primarily occurs from oral ingestion and dietary sources such as canned foods, water bottles and other food contact material [4–17], and through inhalation and dermal routes as well [2, 18–24]. The bioavailability of BPA is dependent on the exposure route and is therefore an important factor for assessing BPA exposure risks in humans [25, 26]. A schematic for the general exposure sources and routes in humans are presented in Figure SI–1. Upon oral ingestion in humans, BPA is mostly absorbed and undergoes fast and almost complete conversion to conjugates by uridine diphosphate and glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoforms, and sulfotransferase in the gastrointestinal track and liver [27]. Within 24h BPA is almost completely eliminated via urine with 84–97% of absorbed BPA excreted there within the first 5–7h following ingestion [27, 28]. The major fraction of BPA gets excreted in conjugated forms namely bisphenol A glucuronide (BPAG) and bisphenol A sulfate (BPAS). A minor fraction, usually less than 1% of total (aglycone and conjugated forms) BPA measured, circulates as the aglycone [27–29], and absolute bioavailability is less than 0.1–0.2% [30]. BPA pharmacokinetics and bioavailability vary by route of exposure in humans [31]. For example, BPA exposure via dermal absorption [19] resulted in a longer half-life and increased bioavailability [32, 33]. Associations between human exposures to BPA and several health outcomes were reviewed [34–45].
2. Conventional practice of BPA exposure assessment: measuring total and aglycone BPA
Biomonitoring of BPA in various human matrices was recently reviewed [46]. Urine has traditionally been the most preferred matrix to study because BPA is extensively conjugated via glucuronidation and excreted in urine and sampling is minimally invasive. However given the short half-life of BPA in humans (~6 hr), the observed levels in urine can only reflect recent exposure to BPA, limiting its scope as a biomarker [47–49]. An overview of the common analytical workflow for the determination of total and aglycone BPA in human matrices is outlined in Figure SI–2. Details of the analytical steps followed for the determination of total BPA, and BPA structural analogs and chlorinated derivatives in human matrices were recently reviewed [50]. Current analytical methods determine the total concentration of BPA after enzymatic hydrolysis preferably at 37°C for a few hours and in some cases overnight. Typically only the β-glucuronidase enzyme is used for the deconjugation step because of the predominant presence of the glucuronide conjugate form of BPA, while few have additionally used sulfatase enzyme for the release of BPA from the sulfate conjugate that occurs as a very minor fraction. In addition to the glucuronide form, sulfatase is also deconjugated if the source of β-glucuronidase is from Helix pomatia-H1 compared to Escherichia coli-K12 [51]. Some issues that lead to inaccurate measurement or underestimation due to suboptimal conditions of total BPA arises from insufficient enzyme concentrations, inappropriate choice of enzymes, incomplete deconjugation, unfavorable hydrolysis conditions and overall suboptimal deconjugation protocol. In cases where only aglycone BPA was measured the enzymatic deconjugation step was skipped. Representative sample preparation, analyte separation and detection approaches for the analysis of total and aglycone BPA in human matrices are presented in Table SI–1.
3. Rationale to study BPA conjugates
A major concern in using BPA concentrations in bio-matrices for assessing human exposure is the potential post-exposure specimen contamination from external sources. Such contaminations result in elevation of aglycone BPA that subsequently contributes to inflated total BPA concentrations. High blood levels of aglycone BPA in some studies [52–54] was questioned because (i) deconjugation can happen during the sample collection, storage, or analysis, and (ii) measuring aglycone BPA but not its conjugated forms could reflect external contamination rather than blood levels [55]. However, a recent review overrules the occurrence of external contamination in the current studies [31]. Unlike aglycone BPA, conjugates are not prone to external contamination [56].
Aglycone BPA was shown to passively cross the placenta in a bi-directional fashion between maternal and fetal compartments, while BPAG has limited permeability in either direction [57]. Moreover, the authors concluded that given the limited clearance of BPAG via placenta, it is likely that BPA conjugates form and accumulate in fetal compartments. If this is the case, then the presence of BPA conjugates in maternal-fetal matrices such as amniotic fluid, meconium and first urine at birth is likely attributed to fetal, not maternal, metabolism. Though conjugated forms of BPA are widely considered as biologically inactive and lacking estrogenicity, [58] it is speculated that they could interfere with certain physiological and metabolic pathways during windows of susceptibility in certain life stages such as fetal and early infancy. In support of this are the findings from recent in vitro studies that showed BPA conjugates altered mechanisms in prolactemia cells [59] and induced adipocyte differentiation in human and 3T3L1 murine pre-adipocytes [60]. The authors concluded that BPA conjugates might interact with membrane estrogen receptor alpha (ER-α) that mediates cellular signaling [59] and BPAG was biologically active. BPAG has no estrogen receptor transcriptional activation function but induced adipogenesis via a different biological pathway yet to be determined [60]. In addition, other minor and secondary conjugated forms such as hydroxylated- and carboxylated-BPA [61–64] have shown some estrogenic activity [65, 66].
A growing concern is the reversion of glucuronide (BPAG) and sulfate forms (bisphenol A monosulfate – BPAS and bisphenol A disulfate – BPADS) to BPA by deconjugation with β-glucuronidase [67] and arylsulfatase C [68], which occur at high levels in human tissues such as liver, kidney, intestine and placenta. This phenomenon is particularly important for pregnant women and their fetuses because of the presence of de-conjugating enzymes in the placenta and fetal tissues during pregnancy [68–70]. However, the deconjugation of BPAG to BPA was not observed in population-based human studies [71]. This is because circulating BPA levels are very low in human tissues [67] and not applicable to whole body exposure scenario in humans [71]. Moreover, the inter-species differences in BPA metabolism observed in human versus non-human primates due to differences in exposure routes could lead to differential interpretation on fate of BPA conjugates [71]. Lower uridine 5’-diphospho glucurontosyltransferase and higher sulfotransferase activities in fetal placenta and fetal liver could result in differential conjugation efficiency and outcomes of BPA exposure [72–75]. Moreover difference in BPA exposure levels will dictate the amount of conjugation depending on saturation of BPA metabolism [69, 76, 77].
In summary, the additional monitoring of BPA conjugates is recommended to (i) avoid misinterpretation due to external contamination and/or biological sample degradation during handling in the field or laboratory [78] contributing to aglycone BPA concentrations, (ii) determine the exposure route with higher levels of conjugates arising from oral versus dermal exposure [79], and (iii) understand the inter-individual, inter-life stage and excretion compartment (e.g. breast milk vs urine) variability in BPA metabolism [67, 80]. As emphasized, it is very important to measure both aglycone and conjugated forms of BPA for assessing human exposures and to reduce external contamination issues. However, to date, the most commonly practiced approach is to measure total BPA and aglycone and infer the conjugated levels based on these measurements. More recently advances in analytical methods and commercial availability of analytical standards for BPA conjugates has enabled quantitation of specific BPA conjugates feasible.
4. Novel approach for BPA exposure assessment: simultaneous measurement of aglycone BPA and conjugates
Glucuronide and sulfate conjugates are the most common metabolites of xenobiotics and exogenous chemicals that undergo phase II metabolism in humans as a detoxification measure. Such conjugates are detected and measured preferentially with LC-MS based methods. The following section presents the analytical approaches taken by studies for the simultaneous analysis of BPA and its conjugates.
Only ten studies are available as of April 2016 that have developed and reported analytical methods for the simultaneous determination of aglycone BPA and its primary conjugates BPAG, BPAS, and BPADS. Research was limited by the lack of both commercial or custom-synthesized BPA conjugates and respective labelled internal standards until very recently. Though some studies reported analyzing conjugated BPA in bio-specimens, the information was derived from taking the difference between total and free BPA but not a measurement of BPAG and BPAS directly (for example, see reported concentrations of conjugated BPA in adult and fetal liver tissues [81]). Studies that made direct measurement of individual BPA conjugates in bio-matrices used (i) urine [28, 82–88], (ii) plasma [28, 88, 89], (iii) serum[82, 90], and (iv) cord serum [91]. More than 50% of these studies were reported in the last couple of years (Figure SI–3A). The majority of these studies used human matrices (84%) (Figure SI℃3B) with almost equal preference for urine (44%) and blood serum (37%) (Figure SI–3C). All the reported assays have used LC coupled with MS measurement. Extraction and satisfactory recovery of BPA and its conjugates from the biological sample is critical, followed by their best separation from matrix ions that yields optimal ionization, detection and quantitation by the MS platform. Analytical steps at each stage of the sample preparation and analysis for BPAG in human serum by the four laboratories that participated in the round robin trial was presented to the finest detail [90]. However, the rest of the studies that analyzed BPAG and BPAS do not provide information to comparable detail (Table SI–2). We attempt to present and discuss the analytical steps reported in literature in the following sub-sections.
4.1. Sample preparation
Sample preparation is a key step of bio-analysis that impacts the later steps during analysis and results. Sample volume for extraction was lab-dependent and for urine ranged between 0.1mL [28, 88] and 1.5 mL [86], and serum or plasma between 0.1 mL [28, 88, 89] and 1.0 mL [90]. Enzymatic deconjugation was not performed to recover glucuronide and sulfate forms along with aglycone BPA from the sample. Protein precipitation was performed as a pre-cleanup step using acetonitrile or methanol [85, 88, 90]. This step helps to minimize matrix effects and interferences on both hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules but analyte loss induced by co-precipitation is possible. Recoveries of BPA and its conjugates were above 90% in studies that used a protein removal step [85, 88]. Derivatization of BPA and conjugates was performed only in a minor fraction of the studies (14%) (Figure SI–3D). Derivatizations with dansyl chloride was proposed to overcome the need for any further sample extraction steps and yet achieve desirable recoveries and detection limits for free and total BPA [56]. This approach was extended to analyze BPAG in addition to measuring free BPA in neonates’ urine [83, 84]. No reports were found that used gas chromatography after derivatization of BPA conjugates. Further, isolation and pre-concentration of BPA and its conjugates in biological samples was achieved with either liquid-liquid extraction [28, 85, 86, 88, 90] or solid phase extraction [82, 86, 89–91]. Application of SPE was a popular choice (57%) compared to LLE (36%) in the reported studies (Figure SI–3E). LLE or SPE steps not only enhance analyte recovery but also minimize matrix effects and prolong the life of the chromatography column and minimize the matrix residues deposit in the ionization source and on the mass spectrometer detector. Though SPE offers greater selectivity and cleaner extracts than LLE procedures, BPA aglycone and conjugates recoveries were similar and typically in an acceptable range of 80%-120% (Table SI–2).
Use of different SPE phase materials was reported for the extraction of BPA and conjugates in various biological matrices. The most common SPE materials were a conventional C18 [89] and polymeric reversed-phase sorbent such as Oasis HLB [82, 91]. Due the differences in polarity of BPA and its conjugates, some studies used a combination of extraction techniques such as (i) SPE with reversed-phase (C18) for aglycone BPA, and amino (NH2) phase for BPAG and BPADS in human urine [82], (ii) sequential use of SPE phases such as amino and a mixed-mode (reversed-phase / strong cation-exchange) for human serum [82], and (iii) LLE for aglycone BPA and SPE with weak anion-exchange polymeric sorbent for BPG, BPAS, and BPADS in human urine [86]. Details of the extraction solutions used in LLE and elution mixtures for SPE are presented in Table SI–2.
4.2. Chromatographic separation and mass spectrometry detection
Separation of the aglycone BPA and its conjugates has been performed using liquid chromatography in all the available studies (Figure SI–3F). Reversed-phase LC was applied in all the studies (Table 1). A C18 column was the most popular choice (67%). Other columns included C8 [84, 89], PFP [85], HSS T3 [86], and BEH amide [87] (Figure SI–3G). All the reported methods used a gradient elution of concentrated and unaltered solvent made of acetonitrile [28, 88, 89] or methanol [82] or either one with some modifiers [84, 86, 87, 91] as the mobile phase. Run length and retention times of aglycone BPA and its conjugates are dependent on the chromatographic conditions used in the individual study. The run times ranged between <5.0 min [88] and 22.0 min [28]. BPA conjugates eluted prior to aglycone BPA and hence had shorter retention times compared to the latter (Table SI–2).
Table 1.
Summary of the novel analytical approaches for the determination of BPA aglycone form and its glucuronide and sulfate conjugates in bio-matrices.
| Study # |
Sample (i) Subject (ii) Matrix (iii) Analysis volume |
Sample preparation: key steps (i) Enzymatic deconjugation (Yes/No) (ii) Internal standards |
Analytical method: key parameters (i) Injection volume (ii) LC column (iii) Mobile phase (iv) Ionization source (v) Mass transitions (m/z) |
Analytical performance: key features (i) LOD, LOQ definition (ii) LOD (iii) LOQ |
Reference (chronological) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (i) Humans (ii) Urine and Plasma (iii) Urine: 100 µL; plasma: 100 µL |
(i) No enzymatic deconjugation for the analysis of aglycone BPA and BPAG. For total BPA, an enzymatic hydrolysis was performed with glucuronidase/ sulfatase from Helix pomatia (EC 3.2.1.31). (ii) BPA-d16; BPAG-d16 |
(i) Urine: 10 µL; plasma: 20 µL (ii) ReproSil-Pur ODS-3 column (150 mm × 4.6 mm × 5 µm) (Maisch, Ammerbuch, Germany) (iii) Mobile phase: Solvent A: water; and Solvent B: acetonitrile (iv) ESI, negative ion mode (TurbolonSpray was also operated in negative ion mode) (v) BPAG: 403.2 → 113.1, 227.0; BPAG-d16 417.2 → 113.0, 241.1; BPA: 227.0 → 212.0, 133.0; BPA-d16 241.1 → 223.3), 142.1. |
(i) NA (ii) BPA (1.14 ng/mL); BPAG (10.1 ng/mL). (iii) BPA (3.42 ng/mL); BPAG (26.26 ng/mL). |
[28] |
| 2 | (i) Rats (ii) Plasma (iii) 0.1 mL |
(i) No enzymatic hydrolysis (ii) NA |
(i) 10 µL (ii) Two columns were tested: Kinetex C18 column (100 mm × 4.6 mm × 2.6 µm, Phenomenex, CA, USA); and Discovery C8 column (50 mm × 4.6 mm × 5 µm, Supelco, MO, USA). Guard column: Krud Katcher Ultra In-Line Filter guard column (0.5 µm, Phenomenex, CA, USA). (iii) Mobile phase: Solvent A: ammonium acetate (2 mM, pH 9) and Solvent B: acetonitrile. (iv) ESI, negative ion mode (v) BPAG: 403 → 227; BPA: 227 → 212. |
(i) NA (ii) BPA (0.1 ng); BPAG (0.25 ng). (iii) NA |
[89] |
| 3 | (i) Sheep (ii) Urine and plasma (iii) Urine: 100 µL; plasma: 100 µL |
(i) No enzymatic hydrolysis for simultaneous analysis of aglycone BPA and BPAG. However, β-hydrolysis was also performed for comparison between direct assay and after enzymatic deconjugation. (ii)BPA-d16 |
(i) NA (ii) Acquity BEH C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm × 1.7 µm; Waters, MA, USA) (iii) Mobile phase: Solvent A: water in acetonitrile; and Solvent B: acetonitrile. (iv) ESI, negative ion mode (v) BPAG: 403 → 227; BPA: 227 → 212; BPA-d16 241 → 142. |
(i) LOD: concentration that has a signal to noise ratio greater than three times the mean noise of six blanks. LOQ: lowest concentration with a precision <20% and accuracy within 80–120%. (ii) Urine: BPA (2 ng/mL); BPAG (10 ng/mL). Plasma: BPA (0.6 ng/mL); BPAG (2 ng/mL). (iii) Urine: BPA (25 ng/mL); BPAG (1000 ng/mL). Plasma: BPA (1 ng/mL); BPAG (20 ng/mL). |
[88] |
| 4 | (i) Humans (ii) Urine and serum (iii) Urine: 0.5 mL; serum: 0.5 mL |
(i) (a) Yes for analyzing total BPA (aglycone + conjugated); and (b) No for the analysis of aglycone BPA, BPAG, and BPADS. (ii) 13C12-BPA |
(i) 10 µL (ii) Betasil C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm i.d. × 5 µm particle size; Thermo Electron Corp., MA, USA) and Javelin Betasil C18 guard column (20 mm × 2.1 mm i.d. × 5 µm particle size; Thermo Electron Corp., MA, USA) (iii) Mobile phase: Solvent A: Methanol and 10 mM ammonium acetate; Solvent B: Methanol. (iv) ESI, negative ion mode (v) BPA: 227 → 212; BPAG: 403 → 113; BPADS: 387 →307. |
(i) LOD: three times the standard deviation of five replicates of 0.01 ng/mL standard. LOQ: ten times the standard deviation of five replicates of 0.01 ng/mL standard. (ii) BPA (aglycone): 0.003 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.02 ng/mL; and BPADS: 0.02 ng/mL (iii) BPA (aglycone): 0.01 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.05 ng/mL; and BPADS: 0.05 ng/mL |
[82] |
| 5 | (i) Humans (ii) Umbilical cord serum (iii) 0.25 mL |
(i) No enzymatic hydrolysis for simultaneous analysis of aglycone BPA and BPAG. (ii)BPA-d16 (Note: internal standards for BPAG and BPAS were unavailable at the time of analysis). |
(i) 25 µL (ii) Agilent Extend-C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm × 1.8 µm). Temperature at 50°C. (iii) Mobile phase: Solvent A: Water with 0.05% ammonium acetetate (pH 7.8) Solvent B: Methanol with 0.05% ammonium acetetate (pH 7.8). (iv) ESI, negative ion mode (v) BPA: 227.0 → 133.1, 212.1; BPA-d16 241.0 → 142.2, 222.1; BPAG: 402.9 → 112.9, 226.9; BPADS: 307.0 → 227.0, 212.1. |
(i) LOD: lowest concentration that has a signal to noise ratio ≥3. LOQ: lowest concentration that has a signal to noise ratio ≥10 and yield ≥ 0.95 regression coefficient for the calibration curve. (ii) BPA: 0.05 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.05 ng/mL; BPAS: 0.025 ng/mL (iii) BPA: 0.1 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.1 ng/mL; BPAS: 0.1 ng/mL |
[91] |
| 6 | (i) Humans (ii) Urine (iii) 0.5 mL |
(i) No enzymatic hydrolysis for simultaneous analysis of aglycone BPA and BPAG. (ii) 13C12-BPA |
(i) 20 µL (ii) Agilent Pursuit 3 penta floura-phenyl propyl (PFP) column (100 mm × 3.0 mm internal i.d. × 3 µm particle size; Agilent Technologies). Column temperature at 20°C (iii) Mobile phase: Solvent A: 2 mM ammonium acetate in water; and Solvent B: Methanol. (iv) ESI, negative ion mode (v) BPA: 227.0 → 132.8; BPA: 227.0 → 212.1; BPA-13C12 239.2 → 224.1; BPAG: 403.1 → 113.1; BPAG: 403.1 → 227.0. |
(i) LOD: lowest concentration that gives signal to noise ratio ≥ 3. LOQ: lowest concentration that gives signal to noise ratio ≥ 10. (ii) BPA: 0.03 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.10 ng/mL (iii) BPA: 0.08 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.33 ng/mL |
[85] |
| 7 | (i) Humans (ii) Urine (iii) 1.0 mL for aglycone BPA, and 1.5 mL for BPAG, BPAS, and BPADS analysis |
(i) No enzymatic hydrolysis for the analysis of aglycone BPA, BPAG, BPAS, and BPADS. (ii) 13C12-BPA, BPAS- d6; BPADS-d6; BPAG-d6 |
(i) 10 µL (ii) Acquity UPLC HSS T3 column (50 mm × 2.1 mm × 1.8 µm). Column temperature @ 30°C (iii) Aglycone BPA:: Mobile phase: Solvent A: 0.1% aqueous formic acid solution; and Solvent B: acetonitrile. BPAG, BPAS, and BPADS:: Mobile phase: Solvent A: Solvent A: 2% NH4OH in H2O pH=11.0; and Solvent B: 0.1% NH4OH in methanol. (iv) Aglycone BPA ESI, positive ion mode BPAG, BPAS, and BPADS ESI, negative ion mode (v) BPA: 695.5 → 171.2, 156.2; BPA-13C12: 707.5 → 171.2, 156.2; BPAS: 307.3 → 212.3, 227.2; BPAS-d6 313.3 → 215.3, 233.3; BPADS: 387.2 → 227.3, 212.3, 307.3; BPADS- d6 393.2 → 233.4; BPAG: 403.4 → 212.3, 227.3; BPAG-d6 409.5 → 215.3, 233.3. |
(i) LOD: estimated concentration that gives a signal to noise ratio ≥3. A sample with 7 to 10 fold concentration of the estimated LOD is analyzed in ten replicates on the same day and by the same analyst. Final LOD is three times the standard deviation of these runs. LOQ: Ten times the standard deviation of the ten replicates. (ii) BPA (0.012 ng/mL); BPAS (0.011 ng/mL); BPADS (0.38 ng/mL); BPAG (0.097 ng/mL). (iii) BPA (0.039 ng/mL); BPAS (0.037 ng/mL); BPADS (1.3 ng/mL); BPAG (0.32 ng/mL). |
[86] |
| 8 | (i) Humans (ii) Serum (iii) Lab 1: 0.2 mL; Lab 2: 0.5 mL; Lab 3: 0.25 mL; Lab 4: 0.55–1 mL. |
(i) No enzymatic hydrolysis for the analysis of aglycone BPA and BPAG. (ii) Lab 1: BPA-d6 and BPAG-13C12; Lab 2: BPA-13C12; Lab 3: BPA-d6 and BPAG-13C12; Lab 4: BPA-13C12 and BPAG- 13C12. |
(i) Lab 1: 5 µL; Lab 2: 10 µL; Lab 2: 25 µL; and Lab 2: 10 µL. (ii) Lab 1: Shimadzu Shimpack XR-ODS III (2.0 mm × 50 mm, 1.6 µm). Column temperature @ 50°C Lab 2: C18, Betasil(Thermo Electron Corporation), (100 × 2.1 mm, 5 µm). Column temperature @ room temperature. Lab 3: Agilent Extend C-18 (4.6 × 100 mm, 1.8 μm). Column temperature @ 50°C. Lab 4: C18 BDS, Hyperclone (Phenomenex, CA, USA), (100 × 4.6 mm, 3 µm). Column temperature @ not heated. (iii) Mobile phase:: Lab 1: Acetonitrile (10 to 100%). Aqueous ammonium actetae (1 mM) as a co-solvent. Lab 2: Solvent A: methanol; Solvent B: ammonium acetate (10 mM) @ pH ~5.0. Lab 3: Solvent A: a mixture of water and ammonium acetate (0.05%) @ pH 7.80; and Solvent B: a mixture of methanol and ammonium acetate (0.05%) @ pH 7.80. Lab 4: Solvent A: a mixture of acetonitrile and water with 0.01% ammonia (pH 9) (10:90 v/v); Solvent B: acetonitrile. (iv) Lab 1, 2, 3, and 4: ESI, negative ion mode (v) Lab 1: BPA: 227.0 → 212.0, 133.0; BPA-d6 233.0 → 215.0; BPAG: 403.0 → 227.0, 133.0; BPAG-13C12 415.0 → 239.0. Lab 2: BPA: 227.0 → 212.0; BPA-13C12 239.0 → 224.0; BPAG: 403.0 → 113.0. Lab 3: BPA: 227.0 → 133.1, 212.1; BPA-d6 233.0 → 85.0, 122.8; BPAG: 402.9 → 112.9, 226.9; BPAG-13C12 415.0 → 112.8, 239.1. Lab 4: BPA: 227.0 → 212.0; BPA-13C12 239.0 → 224.0; BPA-d6 233.0 → 138.0; BPAG: 403.0 → 113.0; BPAG-13C12 414.0 → 239.0. |
(i) Lab 1:: Standard FDA guidelines Lab 2:: LOD: 3xSD, and LOQ: 10xSD (standard deviation) of five replicate analyses of a 0.01 ng/mL standard solution. Lab 3:: LOD: signal to noise ration > 10, and LOQ: lowest concentration on the calibration curve that yield ≥ 0.95 linear regression coefficient. Lab 4:: LOD: 3xSD, and LOQ: 10xSD (standard deviation) of three replicate analyses of the lowest calibration standard solution. (ii) Lab 1:: BPA: 0.02 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.002 ng/mL Lab 2:: BPA: 0.003 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.02 ng/mL Lab 3:: BPA: 0.05 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.05 ng/mL Lab 4:: BPA: 0.04 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.02 ng/mL (iii) LLOQ Lab 1:: BPA: 0.10 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.01 ng/mL Lab 2:: BPA: 0.01 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.05 ng/mL Lab 3:: BPA: 0.10 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.10 ng/mL Lab 4:: BPA: 0.13 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.06 ng/mL |
[90] |
| 9 | (i) Humans (ii) Urine (iii)a 0.2 mL |
(i)a Noenzymatic hydrolysis for simultaneous analysis of aglycone BPA and BPAG. (ii) BPA- d6; BPAG-d6 |
(i)a 6 µL (ii)a Thermo-Scientific BetaBasic C8 column (50 mm × 1.0 mm × 5 µm). Note: Changed to a C18 column with 2.0mm internal diameter in [83]. (iii)a Mobile phase: Solvent A: 0.1% formic acid in water; and Solvent B: 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile. (iv)a ESI, positive ion mode (v)a BPA(dansyl)2 695 → 170. |
(i) LOD: NA LOQ: five times LOD (ii) BPA: 0.02 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.02 ng/mL (iii) BPA: 0.1 ng/mL; BPAG: 0.1 ng/mL |
[83]; [84] a[56] |
| 10 | (i) Humans (ii) Urine (iii) 1.0 mL |
(i) No enzymatic hydrolysis for simultaneous analysis of aglycone BPA and BPAG. (ii) BPAG-13C12 |
(i) 2 µL (ii) Acquity UPLC BEH amide column (100 mm × 2.1 mm × 1.7 µm; Waters, MA, USA) (iii) Mobile phase: acetonitrile with 1 mM ammonium acetate in water. (iv) ESI, negative ion mode (v) BPAG: 403 → 113, 175; BPAG-13C12 415 → 113, 175. |
(i) NA (ii) BPAG: 1 ng/mL (iii) BPAG: 5 ng/mL |
[87] |
Nachman et al. (2013 and 2015) analyzed dansyl chloride-derivatized BPAG in addition to free BPA as per their primary method reported by Fox et al. (2011).
Electrospray ionization (ESI) mode was the only ionization mode used. The presence of a phenolic hydroxyl functional group in aglycone BPA and its conjugates promotes efficient ionization in the negative electrospray ionization mode and hence was preferred in 86% of the studies listed in this review (Figure SI–3H). In studies where a derivatization step was used, the polarity was switched so that positive mode was more effective for ionization [84, 86, 91]. In the ESI negative mode, most studies used the following multiple reaction monitoring mass transitions for the accurate detection and quantification of BPA: m/z 227→212; BPAG: m/z 403→113; BPAS: m/z 307→227; and BPADS: m/z 387→307. Use of isotope-labeled internal standards in the very beginning of sample preparation ensures quantification is not affected significantly by matrix effects. Both deuterated and carbon isotope labeled BPA conjugate standards were used such as BPAG-d16 [28, 88], BPAG-d6 [56, 86], BPAG-13C12 [87, 90], and BPAS- d6 and BPADS-d6 [86].
Limits of detection (LOD) and quantitation (LOQ) are used to define the analytical sensitivity of a method. These are usually different between the laboratories because of the differences in definitions and procedures to estimating them. Though different, the intention of the definitions remains the same. LOD is the smallest concentration of an analyte that can be detected beyond a doubt, and LOQ is the lowest concentration that can be quantified without a bias. Sample volume or injection volume was not an indicator of the reported LOD and LOQ in the study matrices (Table 1, Table SI–2). The sensitivity of analytical methods was dependent on the matrix, sample extraction, chromatography and detector features and parameters (Table SI–2). The lowest reported LOD values are (i) 0.003 ng/mL for aglycone BPA in human urine (using 0.5 mL sample for SPE with Oasis HLB, 10 µL injection volume onto a Betasil C18 LC column with methanol mobile phase, and an API 5500 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer) [82], (ii) 0.002 ng/mL for BPAG in human serum (using 0.2 mL sample for LLE with protein precipitation, 5 µL injection volume onto a Shimpack XR-ODS III LC column with acetonitrile mobile phase, and a Shimadzu LCMS-8080 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer) (Lab 1 in [90]), (iii) 0.011 ng/mL for BPADS in human urine (using 1.5 mL sample for SPE with Strata X-AW, 10 µL injection volume onto a Acquity UPLC HSS T3 LC column with ammonium hydroxide in methanol mobile phase, and a Xevo TQ-S tandem mass spectrometer) [86], and (iv) 0.02 ng/mL for BPADS in human urine (using 0.5 mL sample for SPE with Strata NH2, 10 µL injection volume onto a Betasil C18 LC column with methanol mobile phase, and an API 5500 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer) [82]. It is very important to distinguish the LOD and LOQ estimation procedures and capabilities between the studies while studying BPA conjugates at such trace concentrations. Nevertheless, it is essential to determine the “fit for purpose” of a method for its use in quantifying BPA conjugates in human exposure assessment studies.
Individual study details in regards to LOD and LOQ definitions and values that are dependent on the respective sample preparation protocols, and chromatography and mass spectrometry method features are presented in Table SI–2.
5. Perspectives: Inclusion of BPAG and BPAS conjugates as additional biomarkers of BPA exposure
Total BPA measurements in urine are a reliable measure only when external contamination is controlled. Because the introduction of BPA from external sources not only elevates the aglycone but also total BPA levels, measuring either one is not necessarily a reliable biomarker of exposure to BPA. However, BPAG and BPAS quantification are gaining consideration and value because the levels are unaffected by the general sample handling procedures either during collection or analysis. BPA and its conjugates in human matrices were quantified primarily as a component of method development [28, 56, 82, 85–91], while very few studies have applied this approach for biomonitoring of human exposures to BPA [84, 92–94]. Specificity of BPAG is similar to aglycone BPA in exposure assessment studies; however, frequency of detection of BPAG in urine is almost always greater than aglycone BPA. In the studied populations, BPAG was measured in almost all human matrices and at a higher detection frequency and concentration compared to the aglycone BPA (Table 2). The first report on BPAG levels in humans was published in 2005 [28]. Since then 12 peer-reviewed studies have been published reporting BPA conjugates in various human matrices such as, urine, plasma, serum, and umbilical cord blood. A summary of these studies with key details of the study populations, sample type, analytical method features and performance parameters, BPA and conjugates detection rates and concentrations in human matrices is presented in Table 2.
Table 2.
Use of BPA conjugates in humans’ exposure assessment and biomonitoring studies.
| Study # |
Study (i) Size (ii) Location (iii) Year |
Analysis (i) Matrix (ii) Extraction (iii) Instrumentation (iv) References of sample analysis relevance cited in the study |
BPA-aglycone (i) LOD (ii) LOQ (iii) Detection frequency (iv) Concentration |
BPAG (i) LOD (ii) LOQ (iii) Detection frequency (iv) Concentration |
BPAS (i) LOD (ii) LOQ (iii) Detection frequency (iv) Concentration |
Study Reference (chronological) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (i) n = 19 (7 males and 12 females) (ii) Germany (iii) NA |
(i) Urine and plasma (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. LLE. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) NA |
(i) 1.14 ng/mL (ii) 3.42 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD (no intentional exposure to BPA):: Urine: 0%; Plasma: 0%. (iv) Range (no intentional exposure to BPA):: Urine: <LOD; Plasma: <LOD. |
(i) 10.1 ng/mL (ii) 26.26 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD (no intentional exposure to BPA):: Urine: Most samples; Plasma: 0%. (iv) Range (no intentional exposure to BPA):: Urine: <LOQ; Plasma: <LOD. |
NA | [28] |
| 2 | (i) n = 31 (urine) and 14 (serum) (ii) Albany, United States of America (iii) August-September 2011 |
(i) Urine and Serum (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. SPE. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [62, 89, 127] |
(i) 0.003 ng/mL (ii) 0.01 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD:: Urine: 96.8%; Serum: 57.1%. (iv) Range:: Urine : <LOQ-18.7 ng/mL; Serum : <LOQ-0.588 ng/mL. |
(i) 0.02 ng/mL (ii) 0.05 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD:: Urine: 87.1%; Serum: 50.0%. (iv) Range:: Urine : <LOQ-65.2 ng/mL; Serum : <LOQ-11.9 ng/mL. |
(i) 0.02 ng/mL (ii) 0.05 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD:: Urine: 35.5%; Serum: 50.0%. (iv) Range:: Urine : <LOQ-6.16 ng/mL; Serum : <LOQ-1.77 ng/mL. Note : BPADS conjugate was monitored. |
[82] |
| 3 | (i) n = 85 (ii) Northern and Central California, United States of America (iii) 2010–21012 |
(i) Umbilical cord serum (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. SPE. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [88, 128, 129] |
(i) 0.05 ng/mL (ii) 0.10 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD: 47% (iv) Range: <LOD-52.26 ng/mL |
(i) 0.05 ng/mL (ii) 0.10 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD: 76% (iv) Range: <LOD-5.41 ng/mL |
(i) 0.025 ng/mL (ii) 0.10 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD: 96% (iv) Range: <LOD-12.65 ng/mL Note : BPAS conjugate was monitored. |
[91] |
| 4 | (i) n = 12 (ii) Baltimore, United States of America (iii) January-February 2012 |
(i) Urine (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. No solvent extraction. Dansyl chloride derivatization. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [56] |
(i) 0.02 ng/mL (ii) 0.1 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOQ:: 7–44 days age: 0% (iv) Median: <LOQ |
(i) 0.02 ng/mL (ii) 0.1 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOQ:: 7–44 days age: 100% (iv) Median: 0.66 ng/mL |
NA | [84] |
| 5 | (i) n = 15 (ii) Mersin, Turkey (iii) NA |
(i) Urine (ii) Protein precipitation. Dilution and LLE. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [85] |
(i) 0.03 ng/mL (ii) 0.08 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD: 93.33% (iv) Range: 0.06–1.39 µg/g |
(i) 0.10 ng/mL (ii) 0.33 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD: 100% (iv) Range: 2.22–105.97 µg/g |
NA | [85] |
| 6 | (i) n = 200 (adult male = 74, adult female = 69, and children = 57) (ii) Mersin, Turkey (iii) March-September 2012 |
(i) Urine (ii) Protein precipitation. Dilution and LLE. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [85] |
(i) 0.03 ng/mL (ii) 0.08 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD:: Adult male: 9%; Adult female: 12%; Children: 4%. (iv) Mean:: Adult male: 0.54 µg/g; Adult female: 0.31 µg/g; Children: 0.60 µg/g. |
(i) 0.10 ng/mL (ii) 0.33 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD:: Adult male: 41%; Adult female: 39%; Children: 39%. (iv) Mean:: Adult male: 31.37 µg/g; Adult female: 57.57 µg/g; Children: 56.68 µg/g. |
NA | [92] |
| 7 | (i) n = 46 (males = 26, females = 20) (ii) Quebec, Canada (iii) March 2013 |
(i) Urine (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. Dansyl chloride derivatization and LLE for aglycone BPA. SPE for BPAG, BPAS and BPADS. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) NA |
(i) 0.012 ng/mL (ii) 0.039 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD: 41.3% (iv) Range: <LOD (0.012 µg BPA eq/L)-0.215 µg BPA eq/L |
(i) 0.097 ng/mL (ii) 0.32 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD: 95.7% (iv) Range: <LOD(0.11 µg BPA eq/L)-20.6 µg BPA eq/L |
(i) BPAS: 0.011 ng/mL; BPADS: 0.38 ng/mL (ii) BPAS: 0.037 ng/mL; BPADS: 1.30 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOD: BPAS: 28.3%; BPADS: 0%. 95.7% (iv) Range: BPAS: <LOD(0.03 µg BPA eq/L)-0.192 µg BPA eq/L; BPADS: NA |
[86] |
| 8 | (i) n = 1150 (cases with post- menopausal breast cancer = 575, controls = 575) (ii) Warsaw and Lodz, Poland (iii) January 2000-January 2003 |
(i) Urine (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. No solvent extraction. Dansyl chloride derivatization. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [56, 84] |
(i) NA (ii) NA (iii) Percent above LOD: 3% (iv) Geometric Mean:: NA |
(i) NA (ii) NA (iii) Percent above LOD: 97.2% (iv) Geometric Mean:: Cases with post- menopausal breast cancer: 4.11 ng/mg; Controls: 3.92 ng/mg. |
NA | [93] |
| 9 | (i) n = 5 (unspiked samples from healthy donors) (ii) Four laboratories in the United States participated in a Round Robin experiment. The labs were located in San Francisco (CA), Chicago (IL), Albany (NY), and Columbia (CO). (iii) NA |
(i) Serum (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. Lab 1: protein precipitation and LLE; and Lab 2–4: SPE. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [82, 91, 130] |
(i) Lab 1: 0.02 ng/mL, Lab 2: 0.003 ng/mL, Lab 3: 0.05 ng/mL, and Lab 4: 0.04 ng/mL. (ii) LLOQ:: Lab 1: 0.10 ng/mL, Lab 2: 0.01 ng/mL, Lab 3: 0.10 ng/mL, and Lab 4: 0.13 ng/mL. (iii) Percent above LOD: 100% in all the four labs. (iv) Range: Mostly below 0.5 ng/mL and few between 0.5 and 1.0 ng/mL. |
(i) Lab 1: 0.002 ng/mL, Lab 2: 0.02 ng/mL, Lab 3: 0.05 ng/mL, and Lab 4: 0.02 ng/mL. (ii) LLOQ:: Lab 1: 0.01 ng/mL, Lab 2: 0.05 ng/mL, Lab 3: 0.10 ng/mL, and Lab 4: 0.06 ng/mL. (iii) Percent above LOD: 100% in all the four labs. (iv) Range: Mostly below 0.5 ng/mL and few between 0.5 and 1.0 ng/mL. Except for one sample with a mean 18.9 ng/mL for the data from four labs. |
NA | [90] |
| 10 | (i) n = 1890 (ii) 10 cities in Canada (iii) 2008–2011 |
(i) Urine (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. LLE for aglycone BPA and SPE for BPAS, BPASD, and BPAG. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [86] |
(i) 0.012 µg equivalents/L (ii) NA (iii) Percent above LOD: 43.2% (iv) Range: <LOD-2.82 µg equivalents/L |
(i) 0.11 µg equivalents/L (ii) NA (iii) Percent above LOD: 94.8% (iv) Range: <LOD-136.15 µg equivalents/L |
(i) BPAS: 0.03 µg equivalents/L; BPADS: 0.47 µg equivalents/L (ii) BPAS: NA; BPADS: NA (iii) Percent above LOD: BPAS: 23.4%; BPADS: 0%. (iv) Range: BPAS: <LOD-1.79 µg equivalents/L; BPADS: <LOD-0.36 µg equivalents/L |
[94] |
| 11 | (i) n = 78 (ii) Baltimore, United States of America (iii) December 2012-August 2013 |
(i) Urine (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. No solvent extraction. Dansyl chloride derivatization. (iii) HPLC-MS/MS (iv) [56] |
(i) NA (ii) 0.1 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOQ:: 3–6 days: 0%; 7–27 days: 0%. (iv) Median:: 3–6 days: <LOQ; 7–27 days: <LOQ. |
(i) NA (ii) 0.1 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LOQ:: 3–6 days: 77%; 7–27 days: 64%. (iv) Median:: 3–6 days age: 0.49 ng/mL; 7–27 days age: 0.16. ng/mL. |
NA | [83] |
| 12 | (i) n = 110 (ii) Chicago, United States of America (iii) NA |
(i) Urine (ii) No enzymatic de- conjugation. SPE with mixed-mode reversed phase/ strong-anion exchange sorbent (iii) UHPLC-MS/MS (iv) NA |
NA | (i) 1.0 ng/mL (ii) 5.0 ng/mL (iii) Percent above LLOD: 61% (iv) Mean: 58 ng/mL; Range: 6–236 ng/mL |
NA | [87] |
BPAG was more frequently detected than BPAS or BPADS. The detection rates for BPAG in the reported study matrices ranged between (i) 61% [87] and 100% in urine [84, 85], and (ii) 0% [28] and 100% in blood [90] (Table 2). BPAG concentrations were comparatively higher than aglycone BPA in the reported matrices. For example, BPAG was in the range of <0.05–65.2 ng/mL in urine and <0.05–11.9 ng/mL in serum compared to aglycone BPA in the range of <0.01–18.7 ng/mL and <0.01–0.59 ng/mL in the respective matrices from the same study population [82]. BPAS was above detection limits in adult serum [82], umbilical cord serum [91], and urine [86, 94]. BPADS was less frequently included in the BPA conjugates analyses, and rarely above the limits of detection in studies where it was included (Table 2). Improvement in detection limits is required when the reported LODs are higher than the observed BPA levels in general population. For example, the detection limits of BPA and BPAG were 2 and 10 ng/mL in urine [88] and are not suitable for biomonitoring studies where the total BPA levels in urine from a general population are about 1 ng/mL. Even with a LOD of 1 ng/mL, BPAG went undetected in 39% of urine samples in one human study (n = 110) [87].
Urinary BPAG concentrations represented 90 – 95% of the total BPA while aglycone BPA constituted only 1 – 2% [86, 94]. In contrast, one study reported BPAG and aglycone BPA as 57% and 32% of the total BPA in urine [82]. The lower proportion of BPAG in this study was attributed to possible external contamination of samples with BPA and underestimation of BPAG from using an inappropriate internal standard (labeled BPA instead of BPAG). In the case of umbilical cord serum, BPAS was frequently detected and was the predominant fraction contributing to 45% of the total BPA followed by 36% aglycone BPA and 19% BPAG [91]. The authors concluded that the sulfonation pathway was preferred over glucuronidation for BPA detoxification during midgestation. A very interesting approach was taken to compare BPAG and BPAS levels with total BPA by multiplying BPAG level with 0.5614 (ratio of the molecular weight of BPA to that of BPAG) to obtain concentration of BPA in glucuronide form, and multiplying BPAS level with 0.7404 (ratio of the molecular weight of BPA to that of BPAS) to obtain concentration of BPA in sulfate form [91]. These conversion factors are important when BPAG and BPAS are measured directly before they can be compared with previous BPA exposure data.
Efficiency of BPA conjugation metabolism in neonates was assessed by measuring urinary aglycone BPA and BPAG [83, 84]. A difference in BPA conjugates composition and detection frequency in different bio-matrices collected at different life stages can further enhance our understanding on BPA metabolism and its effects in humans. Detectable aglycone BPA was higher in lipid-rich bio fluids such as breast milk [95, 96] versus urine [27, 28]. This observation could help to further explore and understand the partition preference of conjugated and aglycone BPA in systemic circulation [90]. Measuring conjugated BPA forms in infant and children matrices could help to investigate their potential health effects during the development of the detoxification mechanisms. Interestingly, urinary BPAG concentrations were tested for associations with postmenopausal breast cancer in a case-control study and found no statistical significant relationship [93]. Aglycone BPA was detected only in 37 out of 1150 samples and was not evaluated for statistical relationships with breast cancer prevalence in this study. The authors conclude that BPAG measurement in a spot urine sample may not represent the long-term exposure and/or critical window exposure in relation to breast cancer development.
A mismatch in BPA exposure assessment was observed between the two approaches, total BPA versus sum of the individual forms of BPA in urine [82].The sum of the geometric mean concentration of six forms of BPA (aglycone BPA, conjugates BPAG and BPADS, and chlorinated derivatives BPAMC, BPADC and BPATrC) in urine (GM: 3.119 ng/mL) was approximately 0.2 fold lower than the total BPA in urine (GM: 5.40 ng/mL) [82], which indicates the presence of unidentified forms that are unaccounted for in the total BPA pool. Rapid metabolism of BPA should not be considered as risk-free [67] because BPA may undergo different metabolic pathways resulting in a different subset of metabolites ranging in estrogenic activity [61, 64, 65, 97–113].Underexplored metabolic pathways of BPA yielding higher estrogenic activity metabolites needs attention towards understanding the role of such understudied metabolites in endocrine disruption outcomes [114]. Effects of unconventional metabolites of BPA in in vitro assays were recently discussed [115].
6. Challenges and opportunities
The major limitation in using BPAG and BPAS as additional biomarkers of exposure to BPA is that conjugated forms could degrade within a day or two if the urine samples are stored at room temperature [78, 87, 116]. This results in underestimating the BPA exposure when the conjugates alone were analyzed and measured directly. BPAG was stable at −80°C for the entire study duration of 28 days and stable for at least 3 freeze and thaw cycles [87].Though the urine samples are stored appropriately, it is likely that they are exposed to ambient temperatures for certain periods during collection, handling and shipping that could potentially compromise the utility of these alternative biomarkers. A field blank and reagent blank are used as a quality control measure to assess and/or control background contamination of BPA when using total BPA as a biomarker, but no such measure is available to estimate the degradation of urine sample between post-specimen collection and pre-analysis in the laboratory. This remains a major caveat for BPA conjugates application in human exposure assessment until and unless the appropriate storage conditions are practiced for urine specimen integrity. Other potential limitations of this approach are (i) that it is unclear at the moment what fraction of the total BPA is precisely covered by measuring BPAG and BPAS conjugates, (ii) lack of documentation whether a statistically significant, positive, and linear correlation exists between BPAG and total BPA, and (iii) unknown and unidentified conjugates of BPA other than BPAG and BPAS go unmonitored and unmeasured. Except for the study by Kannan’s group [82], no other study calculated the percent contribution of concentration of each metabolite of BPA towards total BPA.
Glucuronide and sulfate conjugates are the most common metabolites of xenobiotics and exogenous chemicals that undergo phase II metabolism in humans as a detoxification measure [117–126]. This creates a critical analytical challenge of lack of MRM transitions selectivity and possible interferences from other conjugates. For example, one of the dietary isoflavones namely resveratrol (m/z 227→185) and its conjugated urinary metabolites such as resveratrol-4’-O-glucuronide (m/z 403→227) and resveratrol-4’-sulfate (m/z 307→227) share similar molecular weights and fragmentation patterns as that of BPA, BPAG and BPAS, respectively [28]. Utilization of labeled standards for BPAG and BPAS that became recently available commercially can help to overcome this situation by including additional mass transitions as well as retention times for better exposure biomarker validation.
Further studies are deemed necessary to accurately determine the difference between the conjugated fraction assessed by taking the difference between total and aglycone BPA as per the conventional approach and the sum of aglycone BPA, BPAG and BPAS from the novel simultaneous detection approach. This effort will also shed light on the occurrence and approximate concentration of unknown metabolites of BPA in human matrices. Though BPAG is a major fraction of total BPA in urine specimens, there is not sufficient evidence that it is a good biomarker for BPA exposure because the ratios of individual BPA conjugates to total BPA vary depending on exposure sources. Associations with a disease or risk factor are not established at this time and hence additional studies are deemed necessary before considering BPAG as a good alternative biomarker. Future research directions include finding correlations between total BPA with individual conjugates to strengthen the usefulness of conjugates as biomarkers of exposure to BPA and predicting total BPA exposure based on the slopes of the exposure-response curves for the individual conjugates.
7. Conclusion
This review presents novel approaches and analytical methods for the simultaneous extraction and detection of BPA and conjugates in biological matrices. Recent advances in the commercial availability of standards and respective labelled internal standards, SPE phases, LC columns, and MS detectors have enabled highly specific and sensitive analysis of BPA conjugates. Detection limits at trace levels is possible and documented. Because BPA conjugates are formed only after the exposure to BPA, biomonitoring of BPAG and other minor conjugates can be considered as reliable biomarkers of exposure, and avoid misinterpretations while paving new directions in assessing human risks to BPA. The analytical approaches can also be useful for further understanding of BPA pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Though BPA conjugate measurement is possible because of the recent advances in analytical methods, there are certain limitations and challenges to overcome before considering their use in human biomonitoring studies. If successful, then the analysis of BPA conjugates as additional biomarkers might contribute to a better understanding of life-stage differences in metabolism and distribution, inter-individual variability, and the potential health effects of bio-active forms.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Bisphenol A conjugates require in vivo metabolism and not prone to external contamination.
Analytical trends in the measurement of BPA conjugates are reviewed in this work.
BPA conjugates can be potential additional biomarkers of human exposure to BPA.
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the comments and suggestions from Dr. Suramya Waidyanatha (Chemistry and ADME Resources Group Leader, Division of National Toxicology Program, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences), whose contribution was very helpful in guiding our thoughts.
Financial support
This work is supported by National Institutes of Environmental Health Sciences grant 1U2CES026561-01.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Geens T, et al. A review of dietary and non-dietary exposure to bisphenol-A. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2012;50(10):3725–3740. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.07.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Geens T, et al. Levels of bisphenol-A in thermal paper receipts from Belgium and estimation of human exposure. Science of the Total Environment. 2012;435–436:30–33. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Geens T, Goeyens L, Covaci. A. Are potential sources for human exposure to bisphenol-A overlooked? International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health. 2011;214(5):339–347. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2011.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kang JH, Kito K, Kondo F. Factors influencing the migration of bisphenol A from cans. Journal of Food Protection. 2003;66(8):1444–1447. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-66.8.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Takao Y, et al. Release of bisphenol A from food can lining upon heating. Journal of Health Science. 2002;48(4):331–334. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cao XL, et al. Levels of bisphenol A in canned liquid infant formula products in Canada and dietary intake estimates. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2008;56(17):7919–7924. doi: 10.1021/jf8008712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cao XL, Corriveau J. Migration of bisphenol A from polycarbonate baby and water bottles into water under severe conditions. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2008;56(15):6378–6381. doi: 10.1021/jf800870b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cao XL, Corriveau J. Survey of bisphenol A in bottled water products in Canada. Food Additives and Contaminants: Part B Surveillance. 2008;1(2):161–164. doi: 10.1080/02652030802563290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cao XL, et al. Bisphenol A in baby food products in glass jars with metal lids from canadian markets. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2009;57(12):5345–5351. doi: 10.1021/jf9006888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cao XL, Corriveau J, Popovic S. Migration of bisphenol A from can coatings to liquid infant formula during storage at room temperature. Journal of Food Protection. 2009;72(12):2571–2574. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-72.12.2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cao XL, et al. Background bisphenol A in experimental materials and its implication to low-dose in vitro study. Chemosphere. 2010;81(6):817–820. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.07.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cao XL, Corriveau J, Popovic S. Bisphenol a in canned food products from canadian markets. Journal of Food Protection. 2010;73(6):1085–1089. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-73.6.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Brede C, et al. Increased migration levels of bisphenol A from polycarbonate baby bottles after dishwashing, boiling and brushing. Food Additives and Contaminants. 2003;20(7):684–689. doi: 10.1080/0265203031000119061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Santhi VA, et al. Occurrence of bisphenol A in surface water, drinking water and plasma from Malaysia with exposure assessment from consumption of drinking water. Science of the Total Environment. 2012;427–428:332–338. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Amiridou D, Voutsa D. Alkylphenols and phthalates in bottled waters. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2011;185(1):281–286. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Carwile JL, et al. Polycarbonate bottle use and urinary bisphenol A concentrations. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2009;117(9):1368–1372. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0900604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Carwile JL, et al. Canned soup consumption and urinary bisphenol A: A randomized crossover trial. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association. 2011;306(20):2218–2220. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wilson NK, et al. Aggregate exposures of nine preschool children to persistent organic pollutants at day care and at home. Journal of Exposure Analysis and Environmental Epidemiology. 2003;13(3):187–202. doi: 10.1038/sj.jea.7500270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liao C, Kannan K. Widespread occurrence of bisphenol A in paper and paper products: implications for human exposure. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45(21):9372–9379. doi: 10.1021/es202507f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schwartz AW, Landrigan PJ. Bisphenol A in thermal paper receipts: An opportunity for evidence-based prevention. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2012;120(1):A14–A15. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1104004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dalhamn T, Edfors ML, Rylander R. Mouth Absorption of Various Compounds in Cigarette Smoke. Archives of Environmental Health. 1968;16(6):831–835. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1968.10665162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Loganathan SN, Kannan K. Occurrence of bisphenol a in indoor dust from two locations in the Eastern United States and implications for human exposures. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 2011;61(1):68–73. doi: 10.1007/s00244-010-9634-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rudel RA, et al. Phthalates, alkylphenols, pesticides, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, and other endocrine-disrupting compounds in indoor air and dust. Environmental Science and Technology. 2003;37(20):4543–4553. doi: 10.1021/es0264596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mielke H, Partosch F, Gundert-Remy U. The contribution of dermal exposure to the internal exposure of bisphenol A in man. Toxicology Letters. 2011;204(2–3):190–198. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.04.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vandenberg LN, et al. Biomonitoring studies should be used by regulatory agencies to assess human exposure levels and safety of bisphenol A. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2010;118(8):1051–1054. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0901717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vandenberg LN, et al. Human exposures to bisphenol A: Mismatches between data and assumptions. Reviews on Environmental Health. 2013;28(1):37–58. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2012-0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Volkel W, et al. Metabolism and kinetics of bisphenol a in humans at low doses following oral administration. Chem Res Toxicol. 2002;15(10):1281–1287. doi: 10.1021/tx025548t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Volkel W, Bittner N, Dekant W. Quantitation of bisphenol A and bisphenol A glucuronide in biological samples by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Metab Dispos. 2005;33(11):1748–1757. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.005454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Volkel W, Kiranoglu M, Fromme H. Determination of free and total bisphenol A in human urine to assess daily uptake as a basis for a valid risk assessment. Toxicol Lett. 2008;179(3):155–162. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Teeguarden JG, et al. Twenty-four hour human urine and serum profiles of bisphenol a during high-dietary exposure. Toxicol Sci. 2011;123(1):48–57. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.vom Saal FS, Welshons WV. Evidence that bisphenol A (BPA) can be accurately measured without contamination in human serum and urine, and that BPA causes numerous hazards from multiple routes of exposure. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;398(1–2):101–113. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.09.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Birnbaum LS, et al. Consortium-based science: the NIEHS’s multipronged, collaborative approach to assessing the health effects of bisphenol A. Environ Health Perspect. 2012;120(12):1640–1644. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1205330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Stahlhut RW, Welshons WV, Swan SH. Bisphenol A data in NHANES suggest longer than expected half-life, substantial nonfood exposure, or both. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2009;117(5):784–789. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0800376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mustieles V, et al. Bisphenol A: Human exposure and neurobehavior. NeuroToxicology. 2015;49:174–184. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ranciere F, et al. Bisphenol A and the risk of cardiometabolic disorders: a systematic review with meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence. Environ Health. 2015;14:46. doi: 10.1186/s12940-015-0036-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Oppeneer SJ, Robien K. Bisphenol A exposure and associations with obesity among adults: a critical review. Public Health Nutr. 2015;18(10):1847–1863. doi: 10.1017/S1368980014002213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vom Saal FS, et al. The estrogenic endocrine disrupting chemical bisphenol A (BPA) and obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;354(1–2):74–84. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bodin J, Stene LC, Nygaard UC. Can exposure to environmental chemicals increase the risk of diabetes type 1 development? 2015;2015:208947. doi: 10.1155/2015/208947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mileva G, et al. Bisphenol-A: epigenetic reprogramming and effects on reproduction and behavior. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11(7):7537–7561. doi: 10.3390/ijerph110707537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Peretz J, et al. Bisphenol A and reproductive health: Update of experimental and human evidence, 2007–2013. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2014;122(8):775–786. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1307728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rutkowska A, Rachon D. Bisphenol A (BPA) and its potential role in the pathogenesis of the polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Gynecol Endocrinol. 2014;30(4):260–265. doi: 10.3109/09513590.2013.871517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gonzalez-Parra E, et al. Bisphenol a in chronic kidney disease. Int J Nephrol. 2013;2013:437857. doi: 10.1155/2013/437857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vaidya SV, Kulkarni H. Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with allergic asthma: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005–2006. J Asthma. 2012;49(8):800–806. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2012.721041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Stein TP, et al. Bisphenol A Exposure in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism Research. 2015;8(3):272–283. doi: 10.1002/aur.1444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fenichel P, Chevalier N, Brucker-Davis F. Bisphenol A: An endocrine and metabolic disruptor. Annales d’Endocrinologie. 2013;74(3):211–220. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2013.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Asimakopoulos AG, Thomaidis NS, Koupparis MA. Recent trends in biomonitoring of bisphenol A, 4-t-octylphenol, and 4-nonylphenol. Toxicology Letters. 2012;210(2):141–154. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.07.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Calafat AM, et al. Optimal Exposure Biomarkers for Nonpersistent Chemicals in Environmental Epidemiology. Environ Health Perspect. 2015;123(7):A166–A168. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1510041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Calafat AM, et al. Response to “Comment on ‘Optimal Exposure Biomarkers for Nonpersistent Chemicals in Environmental Epidemiology’”. Environ Health Perspect. 2016;124(4):A66–A67. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1611282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stahlhut RW, et al. Comment on “Optimal Exposure Biomarkers for Nonpersistent Chemicals in Environmental Epidemiology”. Environ Health Perspect. 2016;124(4):A66. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1511057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Andra SS, et al. Biomonitoring of human exposures to chlorinated derivatives and structural analogs of bisphenol A. Environ Int. 2015;85:352–379. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.09.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ye X, et al. Quantification of urinary conjugates of bisphenol A, 2,5-dichlorophenol, and 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone in humans by online solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2005;383(4):638–644. doi: 10.1007/s00216-005-0019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kosarac I, et al. A novel method for the quantitative determination of free and conjugated bisphenol A in human maternal and umbilical cord blood serum using a two-step solid phase extraction and gas chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B: Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences. 2012;898:90–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.04.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lee YJ, et al. Maternal and fetal exposure to bisphenol A in Korea. Reprod Toxicol. 2008;25:413–419. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2008.05.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Padmanabhan V, et al. Maternal bisphenol-A levels at delivery: A looming problem? Journal of Perinatology. 2008;28(4):258–263. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ye X, et al. Potential external contamination with bisphenol A and other ubiquitous organic environmental chemicals during biomonitoring analysis: An elusive laboratory challenge. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2013;121(3):283–286. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1206093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fox SD, et al. Quantitation of free and total bisphenol A in human urine using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci. 2011;34(11):1268–1274. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201100087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Corbel T, et al. Bidirectional placental transfer of Bisphenol A and its main metabolite, Bisphenol A-Glucuronide, in the isolated perfused human placenta. Reprod Toxicol. 2014;47:51–58. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Matthews JB, Twomey K, Zacharewski TR. In vitro and in vivo interactions of bisphenol A and its metabolite, bisphenol A glucuronide, with estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Chem Res Toxicol. 2001;14(2):149–157. doi: 10.1021/tx0001833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Viñas R, Goldblum RM, Watson CS. Rapid estrogenic signaling activities of the modified (chlorinated, sulfonated, and glucuronidated) endocrine disruptor bisphenol A. Endocrine Disruptors. 2013;1(1):e25411. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Boucher JG, Boudreau A, Atlas E. Bisphenol A induces differentiation of human preadipocytes in the absence of glucocorticoid and is inhibited by an estrogen-receptor antagonist. Nutr Diabetes. 2014;4:e102. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2013.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pritchett JJ, Kuester RK, Sipes IG. Metabolism of bisphenol a in primary cultured hepatocytes from mice, rats, and humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002;30(11):1180–1185. doi: 10.1124/dmd.30.11.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lindholst C, et al. Metabolism of bisphenol A in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in relation to estrogenic response. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2003;135(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/s1532-0456(03)00088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Suzuki T, et al. Environmental fate of bisphenol A and its biological metabolites in river water and their xeno-estrogenic activity. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38(8):2389–2396. doi: 10.1021/es030576z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zalko D, et al. Biotransformations of bisphenol A in a mammalian model: answers and new questions raised by low-dose metabolic fate studies in pregnant CD1 mice. Environ Health Perspect. 2003;111(3):309–319. doi: 10.1289/ehp.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yoshihara S, et al. Potent estrogenic metabolites of bisphenol A and bisphenol B formed by rat liver S9 fraction: their structures and estrogenic potency. Toxicol Sci. 2004;78(1):50–59. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfh047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Nakagawa Y, Suzuki T. Metabolism of bisphenol A in isolated rat hepatocytes and oestrogenic activity of a hydroxylated metabolite in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Xenobiotica. 2001;31(3):113–123. doi: 10.1080/00498250110040501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ginsberg G, Rice. DC. Does rapid metabolism ensure negligible risk from bisphenol A? Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117(11):1639–1643. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0901010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Stowell CL, et al. A role for sulfation-desulfation in the uptake of bisphenol a into breast tumor cells. Chem Biol. 2006;13(8):891–897. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Nishikawa M, et al. Placental transfer of conjugated bisphenol A and subsequent reactivation in the rat fetus. Environ Health Perspect. 2010;118(9):1196–1203. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0901575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Collier AC, et al. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity, expression and cellular localization in human placenta at term. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2002;63(3):409–419. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(01)00890-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mattison DR, et al. Pharmaco- and toxicokinetics of selected exogenous and endogenous estrogens: a review of the data and identification of knowledge gaps. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014;44(8):696–724. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2014.930813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kang JH, Katayama Y, Kondo F. Biodegradation or metabolism of bisphenol A: from microorganisms to mammals. Toxicology. 2006;217(2–3):81–90. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Matsumoto J, Yokota H, Yuasa A. Developmental increases in rat hepatic microsomal UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activities toward xenoestrogens and decreases during pregnancy. Environ Health Perspect. 2002;110(2):193–196. doi: 10.1289/ehp.02110193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Strassburg CP, et al. Developmental aspects of human hepatic drug glucuronidation in young children and adults. Gut. 2002;50(2):259–265. doi: 10.1136/gut.50.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Coughtrie MW, et al. The inadequacy of perinatal glucuronidation: immunoblot analysis of the developmental expression of individual UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoenzymes in rat and human liver microsomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1988;34(6):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Pottenger LH, et al. The relative bioavailability and metabolism of bisphenol A in rats is dependent upon the route of administration. Toxicol Sci. 2000;54(1):3–18. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/54.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Elsby R, et al. Comparison of the modulatory effects of human and rat liver microsomal metabolism on the estrogenicity of bisphenol A: implications for extrapolation to humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;297(1):103–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Waechter J, et al. Factors affecting the accuracy of bisphenol a and bisphenol a-monoglucuronide estimates in Mammalian tissues and urine samples. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2007;17(1):13–24. doi: 10.1080/15376510600803581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Vandenberg LN, et al. Should oral gavage be abandoned in toxicity testing of endocrine disruptors? Environmental health : a global access science source. 2014;13(1) doi: 10.1186/1476-069X-13-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Nachman RM, et al. Early Life Metabolism of Bisphenol A: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2014;1(1):90–100. doi: 10.1007/s40572-013-0003-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Nahar MS, et al. Fetal liver bisphenol A concentrations and biotransformation gene expression reveal variable exposure and altered capacity for metabolism in humans. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2013;27(2):116–123. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Liao C, Kannan K. Determination of free and conjugated forms of bisphenol A in human urine and serum by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Environmental Science and Technology. 2012;46(9):5003–5009. doi: 10.1021/es300115a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Nachman RM, et al. Serial Free Bisphenol A and Bisphenol A Glucuronide Concentrations in Neonates. J Pediatr. 2015;167(1):64–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.03.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Nachman RM, et al. Urinary free bisphenol a and bisphenol A-glucuronide concentrations in newborns. Journal of Pediatrics. 2013;162(4):870–872. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.11.083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Battal D, et al. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantitative analysis of free and conjugated bisphenol A in human urine. Biomedical Chromatography. 2014;28(5):686–693. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Provencher G, et al. Determination of bisphenol A, triclosan and their metabolites in human urine using isotope-dilution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A. 2014;1348:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Hauck ZZ, et al. Determination of bisphenol A-glucuronide in human urine using ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2016;30(3):400–406. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Lacroix MZ, et al. Simultaneous quantification of bisphenol A and its glucuronide metabolite (BPA-G) in plasma and urine: applicability to toxicokinetic investigations. Talanta. 2011;85(4):2053–2059. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2011.07.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Coughlin JL, Winnik B, Buckley B. Measurement of bisphenol A, bisphenol A -d-glucuronide, genistein, and genistein 4′ - D-glucuronide via SPE and HPLC-MS/MS. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2011;401(3):995–1002. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5151-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Vandenberg LN, et al. A round robin approach to the analysis of bisphenol a (BPA) in human blood samples. Environmental Health. 2014:13. doi: 10.1186/1476-069X-13-25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Gerona RR, et al. Bisphenol-A (BPA), BPA glucuronide, and BPA sulfate in midgestation umbilical cord serum in a northern and central california population. Environmental Science and Technology. 2013;47(21):12477–12485. doi: 10.1021/es402764d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Battal D, et al. Determination of urinary levels of Bisphenol A in a Turkish population. Environ Monit Assess. 2014;186(12):8443–8452. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-4015-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Trabert B, et al. Urinary bisphenol A-glucuronide and postmenopausal breast cancer in Poland. Cancer Causes Control. 2014;25(12):1587–1593. doi: 10.1007/s10552-014-0461-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Arbuckle TE, et al. Exposure to free and conjugated forms of bisphenol A and triclosan among pregnant women in the MIREC cohort. Environ Health Perspect. 2015;123(4):277–284. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Mendonca K, et al. Bisphenol A concentrations in maternal breast milk and infant urine. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health. 2014;87(1):13–20. doi: 10.1007/s00420-012-0834-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Zimmers SM, et al. Determination of free Bisphenol A (BPA) concentrations in breast milk of U.S. women using a sensitive LC/MS/MS method. Chemosphere. 2014;104:237–243. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.12.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kovacic P. How safe is bisphenol A? Fundamentals of toxicity: metabolism, electron transfer and oxidative stress. Med Hypotheses. 2010;75(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2010.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kolsek K, Sollner Dolenc M, Mavri J. Computational study of the reactivity of bisphenol A-3,4-quinone with deoxyadenosine and glutathione. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013;26(1):106–111. doi: 10.1021/tx300411d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Jiang HM, et al. New insights for the risk of bisphenol A: inhibition of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) Chemosphere. 2013;93(6):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Jaeg JP, et al. Characterization of new bisphenol a metabolites produced by CD1 mice liver microsomes and S9 fractions. J Agric Food Chem. 2004;52(15):4935–4942. doi: 10.1021/jf049762u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Yoshihara S, et al. Metabolic activation of bisphenol A by rat liver S9 fraction. Toxicol Sci. 2001;62(2):221–227. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/62.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Ishibashi H, et al. Toxicity to early life stages and an estrogenic effect of a bisphenol A metabolite, 4-methyl-2,4-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)pent-1-ene on the medaka (Oryzias latipes) Life Sci. 2005;77(21):2643–2655. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Yamaguchi A, et al. Short-term effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on the expression of estrogen-responsive genes in male medaka (Oryzias latipes) Aquat Toxicol. 2005;72(3):239–249. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Okuda K, et al. Novel pathway of metabolic activation of bisphenol A-related compounds for estrogenic activity. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(9):1696–1703. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.040121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Okuda K, Takiguchi M, Yoshihara S. In vivo estrogenic potential of 4-methyl-2,4-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)pent-1-ene, an active metabolite of bisphenol A, in uterus of ovariectomized rat. Toxicol Lett. 2010;197(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Nakamura S, et al. Ipso substitution of bisphenol A catalyzed by microsomal cytochrome P450 and enhancement of estrogenic activity. Toxicol Lett. 2011;203(1):92–95. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ye X, et al. In-vitro oxidation of bisphenol A: Is bisphenol A catechol a suitable biomarker for human exposure to bisphenol A? Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;399(3):1071–1079. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-4344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Qiu SX, Yang RZ, Gross ML. Synthesis and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometric characterization of the adducts of bisphenol A o-quinone with glutathione and nucleotide monophosphates. Chem Res Toxicol. 2004;17(8):1038–1046. doi: 10.1021/tx049953r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Edmonds JS, et al. The reaction of bisphenol A 3,4-quinone with DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;319(2):556–561. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Schmidt J, et al. Bioactivation of bisphenol A and its analogs (BPF, BPAF, BPZ and DMBPA) in human liver microsomes. Toxicol In Vitro. 2013;27(4):1267–1276. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2013.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Li M, et al. Biotransformation of bisphenol AF to its major glucuronide metabolite reduces estrogenic activity. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e83170. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Cabaton N, et al. Biotransformation of bisphenol F by human and rat liver subcellular fractions. Toxicol In Vitro. 2008;22(7):1697–1704. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2008.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Bursztyka J, et al. Biotransformation of genistein and bisphenol A in cell lines used for screening endocrine disruptors. Toxicol In Vitro. 2008;22(6):1595–1604. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2008.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Michalowicz J. Bisphenol A--sources, toxicity and biotransformation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2014;37(2):738–758. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Chen D, et al. Bisphenol Analogues Other Than BPA: Environmental Occurrence, Human Exposure, and Toxicity-A Review. Environ Sci Technol. 2016;50(11):5438–5453. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b05387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Ye X, et al. Temporal stability of the conjugated species of bisphenol A, parabens, and other environmental phenols in human urine. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2007;17(6):567–572. doi: 10.1038/sj.jes.7500566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Holčapek M, Kolářová L, Nobilis M. High-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in the identification and determination of phase I and phase II drug metabolites. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2008;391(1):59–78. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-1962-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Levsen K, et al. Structure elucidation of phase II metabolites by tandem mass spectrometry: an overview. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1067(1–2):55–72. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2004.08.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Mullangi R, Bhamidipati RK, Srinivas NR. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2005;1:251–264. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Kamel A, Prakash C. High performance liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure ionization/tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC/API/MS/MS) in drug metabolism and toxicology. Current Drug Metabolism. 2006;7(8):837–852. doi: 10.2174/138920006779010593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Ketola RA, Hakala KS. Direct analysis of glucuronide s with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric techniques and methods. Curr Drug Metab. 2010;11(7):561–582. doi: 10.2174/138920010792927343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Staack RF, Hopfgartner G. New analytical strategies in studying drug metabolism. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2007;388(7):1365–1380. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1367-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Brown AK, Wong CS. Current trends in environmental analysis of human metabolite conjugates of pharmaceuticals. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry. 2015;5:8–17. [Google Scholar]
- 124.Kalogera E, et al. Androgen glucuronides analysis by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry: could it raise new perspectives in the diagnostic field of hormone-dependent malignancies? J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013;940:24–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.09.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Scheidweiler KB, Desrosiers NA, Huestis MA. Simultaneous quantification of free and glucuronidated cannabinoids in human urine by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;413(23–24):1839–1847. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.06.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Kaushik R, Levine B, LaCourse WR. A brief review: HPLC methods to directly detect drug glucuronides in biological matrices (Part I) Analytica Chimica Acta. 2006;556(2):255–266. [Google Scholar]
- 127.Zhang Z, et al. Urinary bisphenol a concentrations and their implications for human exposure in several Asian countries. Environmental Science and Technology. 2011;45(16):7044–7050. doi: 10.1021/es200976k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Taylor JA, et al. Similarity of bisphenol A pharmacokinetics in rhesus monkeys and mice: relevance for human exposure. Environ Health Perspect. 2011;119(4):422–430. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1002514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Inoue K, et al. Determination of bisphenol A in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography with multi-electrode electrochemical detection. Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications. 2000;749(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)00351-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Calafat AM, et al. Exposure to bisphenol A and other phenols in neonatal intensive care unit premature infants. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2009;117(4):639–644. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0800265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.