Abstract
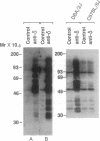
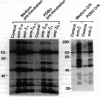
It has been found that the principal biochemical pathway activated in B cells stimulated by antigen- or anti-immunoglobulin-mediated crosslinking of surface immunoglobulin is that resulting in hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate with generation of diacylglycerol and inositol trisphosphate. Recent evidence suggests that surface immunoglobulin-mediated B-cell activation can proceed without detectable increases in the concentration of either diacylglycerol or intracellular Ca2+ concentration, implicating involvement of other non-protein-kinase-C/Ca2(+)-dependent signal-transduction pathways. Therefore, we sought evidence for activation of a signaling pathway that is associated with growth regulation in other cell types--i.e., the protein-tyrosine kinases. We now show that crosslinking of membrane immunoglobulin by mitogenic antibodies leads to rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of several cellular substrates, consistent with the induction of a tyrosine kinase activity. This increase in tyrosine phosphorylation is weakly (if at all) stimulated by other B-cell mitogens, including phorbol esters and ionophores, and does not require the presence of detectable protein kinase C. Furthermore, inhibition of anti-immunoglobulin-stimulated phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate hydrolysis does not inhibit activation of this tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. These findings suggest that occupancy of the membrane immunoglobulin receptor may induce multiple pathways of activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunswick M., Bonvini E., Francis M., Felder C. C., Hoffman T., Mond J. Absence of demonstrable phospholipid turnover in B cells stimulated by low mitogenic concentrations of dextran-anti-immunoglobulin conjugates. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):855–861. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunswick M., Finkelman F. D., Highet P. F., Inman J. K., Dintzis H. M., Mond J. J. Picogram quantities of anti-Ig antibodies coupled to dextran induce B cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3364–3372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunswick M., June C. H., Finkelman F. D., Dintzis H. M., Inman J. K., Mond J. J. Surface immunoglobulin-mediated B-cell activation in the absence of detectable elevations in intracellular ionized calcium: a model for T-cell-independent B-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6724–6728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunswick M., June C. H., Finkelman F. D., Mond J. J. Different patterns of inositol polyphosphate production are seen in B lymphocytes after cross-linking of sIg by anti-Ig antibody or by a multivalent anti-Ig antibody dextran conjugate. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1414–1421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dymecki S. M., Niederhuber J. E., Desiderio S. V. Specific expression of a tyrosine kinase gene, blk, in B lymphoid cells. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):332–336. doi: 10.1126/science.2404338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. A., DeFranco A. L. Cross-linking membrane IgM induces production of inositol trisphosphate and inositol tetrakisphosphate in WEHI-231 B lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3935–3942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goroff D. K., Stall A., Mond J. J., Finkelman F. D. In vitro and in vivo B lymphocyte-activating properties of monoclonal anti-delta antibodies. I. Determinants of B lymphocyte-activating properties. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2382–2392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Gordon J., Michell R. H., Brown G. Synergism between diacylglycerols and calcium ionophore in the induction of human B cell proliferation mimics the inositol lipid polyphosphate breakdown signals induced by crosslinking surface immunoglobulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91828-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hivroz C., Grillot-Courvalin C., Labaume S., Miglierina R., Brouet J. C. Cross-linking of membrane IgM on B CLL cells: dissociation between intracellular free Ca2+ mobilization and cell proliferation. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1811–1817. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsi E. D., Siegel J. N., Minami Y., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell activation induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of a limited number of cellular substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10836–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Angel P., Boyle W. J., Chiu R., Freed E., Gould K. L., Isacke C. M., Karin M., Lindberg R. A., van der Geer P. Targets for signal-transducing protein kinases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):131–142. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Samelson L. E. Increases in tyrosine phosphorylation are detectable before phospholipase C activation after T cell receptor stimulation. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1591–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., O'Garra A., Bijsterbosch M. K., Holman M. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. VIII. Induction of DNA synthesis in B cells by a combination of calcium ionophores and phorbol myristate acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):92–97. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Gutman G. A., Lewis D. E., Griswold S. T., Warner N. L. Monoclonal antibodies against rat immunoglobulin kappa chains. Hybridoma. 1982;1(2):125–131. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurindo I., Finkelman F. D., Mizuguchi J., Mond J. J. B-cell activation stimulated by monoclonal anti-Lyb2.1 antibody is mediated through a receptor distinct from the BSF-1 receptor. Cell Immunol. 1987 Sep;108(2):473–482. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maino V. C., Hayman M. J., Crumpton M. J. Relationship between enhanced turnover of phosphatidylinositol and lymphocyte activation by mitogens. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):247–252. doi: 10.1042/bj1460247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi J., Ji Y. Y., Nakabayaschi H., Huang K. P., Beaven M. A., Chused T., Paul W. E. Protein kinase C activation blocks anti-IgM-mediated signaling BAL17 B lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1054–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Balapure A., Feuerstein N., June C. H., Brunswick M., Lindsberg M. L., Witherspoon K. Protein kinase C activation in B cells by indolactam inhibits anti-Ig-mediated phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate hydrolysis but not B cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):451–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Feuerstein N., Finkelman F. D., Huang F., Huang K. P., Dennis G. B-lymphocyte activation mediated by anti-immunoglobulin antibody in the absence of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8588–8592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Mongini P. K., Sieckmann D., Paul W. E. Role of T lymphocytes in the response to TNP-AECM-Ficoll. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1066–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C., Wadsworth D. C., Schneider G. B. Activation of murine B lymphocytes by anti-immunoglobulin is an inductive signal leading to immunoglobulin secretion. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):138–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puré E., Isakson P. C., Takatsu K., Hamaoka T., Swain S. L., Dutton R. W., Dennert G., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Induction of B cell differentiation by T cell factors. I. Stimulation of IgM secretion by products of a T cell hybridoma and a T cell line. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1953–1958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom J. T., Harris L. K., Cambier J. C. Anti-Ig induces release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, which mediates mobilization of intracellular Ca++ stores in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein T. L., Baeker T. R., Miller R. A., Kolber D. L. Stimulation of murine B cells by the combination of calcium ionophore plus phorbol ester. Cell Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;102(2):364–373. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stall A. M., Loken M. R. Allotypic specificities of murine IgD and IgM recognized by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):787–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbarao B., Morris J., Baluyut A. R. Properties of anti-Lyb-2-mediated B-cell activation and the relationship between Lyb-2 molecules and receptors for B-cell stimulatory factor-1 on murine B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;112(2):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90302-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Scher I., Schaefer M. E., Lindsten T., Finkelman F. D., Mond J. J. Size-dependent B lymphocyte subpopulations: relationship of cell volume to surface phenotype, cell cycle, proliferative response, and requirements for antibody production to TNP-Ficoll and TNP-BA. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2333–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y. Antibodies for phosphotyrosine: analytical and preparative tool for tyrosyl-phosphorylated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]