Abstract
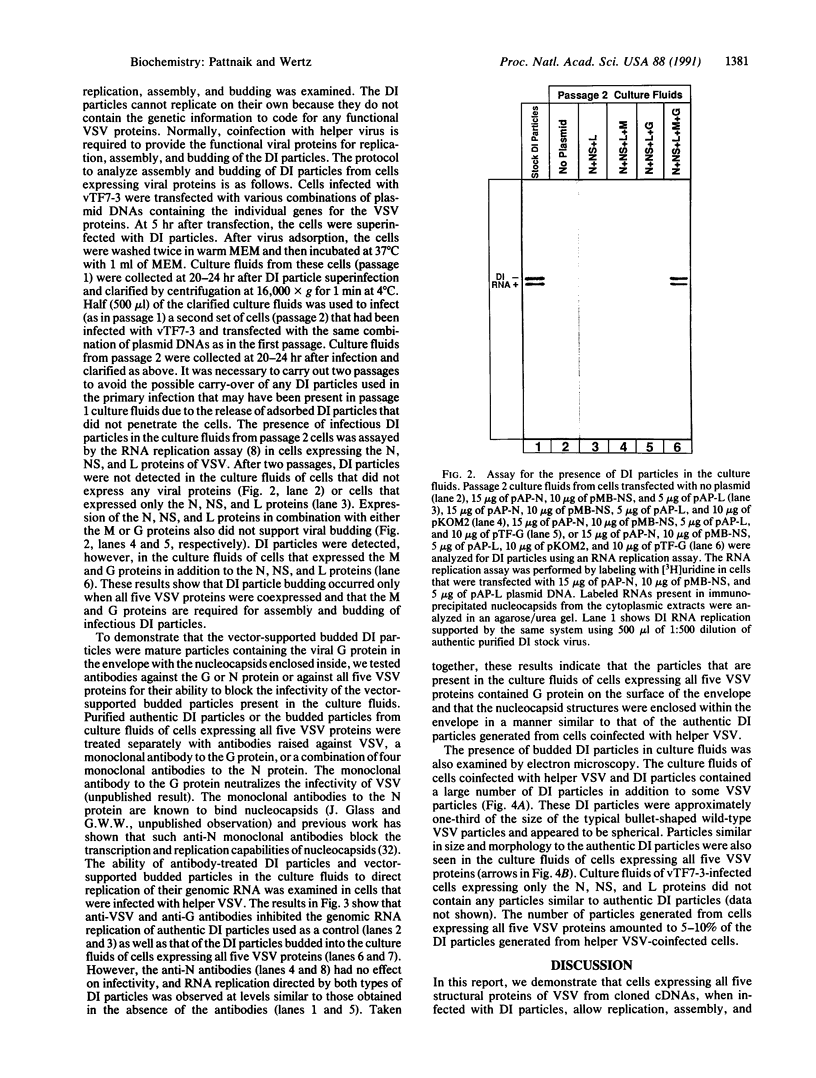
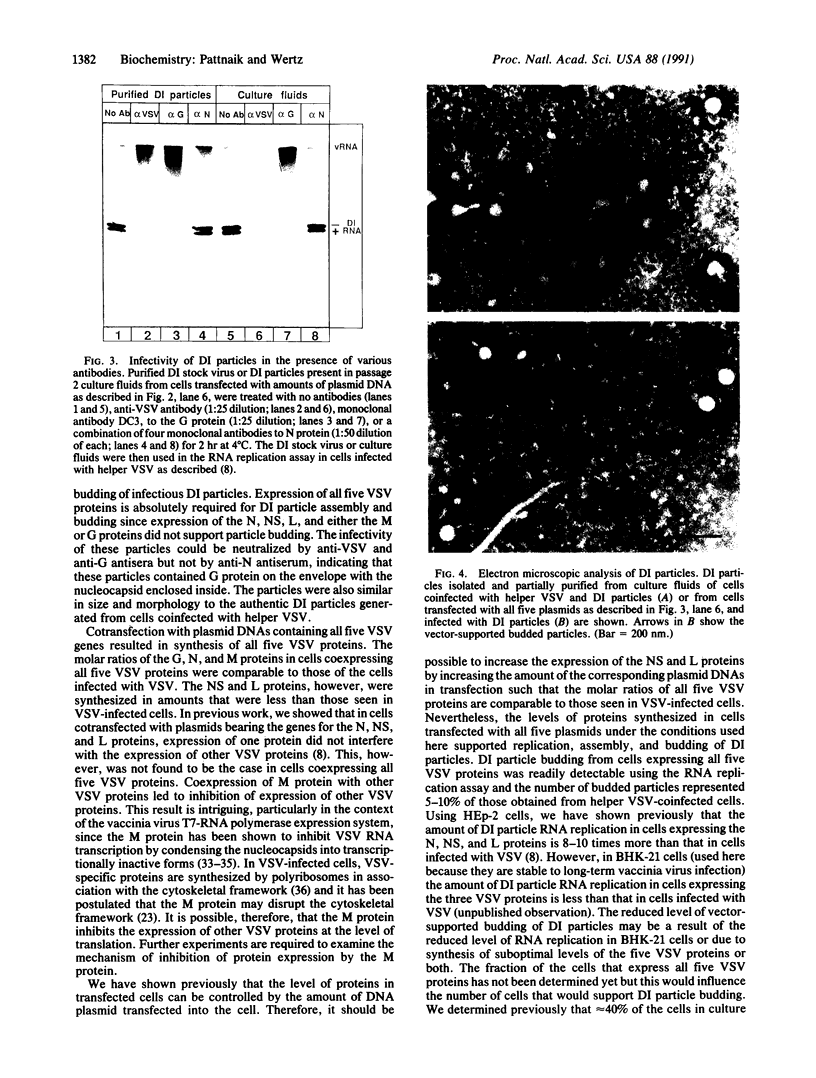
An alternative approach to structure-function analysis of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) gene products and their interactions with one another during each phase of the viral life cycle is described. We showed previously by using the vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase expression system that when cells expressing the nucleocapsid protein (N), the phosphoprotein (NS), and the large polymerase protein (L) of VSV were superinfected with defective interfering (DI) particles, rapid and efficient replication and amplification of (DI) particle RNA occurred. Here, we demonstrate that all five VSV proteins can be expressed simultaneously when cells are contransfected with plasmids containing the matrix protein (M) gene and the glycoprotein (G) gene of VSV in addition to plasmids containing the genes for the N, NS, and L proteins. When cells coexpressing all five VSV proteins were superinfected with DI particles, which because of their defectiveness are unable to express any viral proteins or to replicate, DI particle replication, assembly, and budding were observed and infectious DI particles were released into the culture fluids. Omission of either the M or G protein expression resulted in no DI particle budding. The vector-supported DI particles were similar in size and morphology to the authentic DI particles generated from cells coinfected with DI particles and helper VSV and their infectivity could be blocked by anti-VSV or anti-G antiserum. The successful replication, assembly, and budding of DI particles from cells expressing all five VSV proteins from cloned cDNAs provide a powerful approach for detailed structure-function analysis of the VSV gene products in each step of the replicative cycle of the virus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheiter H., Davis N. L., Wertz G., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A. Role of the nucleocapsid protein in regulating vesicular stomatitis virus RNA synthesis. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballart I., Eschle D., Cattaneo R., Schmid A., Metzler M., Chan J., Pifko-Hirst S., Udem S. A., Billeter M. A. Infectious measles virus from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):379–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Banerjee A. K. The transcription complex of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):363–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K. Transcription and replication of rhabdoviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):66–87. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.66-87.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel D., Harmison G. G., Schubert M. Role of matrix protein in cytopathogenesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1716–1725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1716-1725.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Role of the membrane (M) protein in endogenous inhibition of in vitro transcription by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.134-142.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervera M., Dreyfuss G., Penman S. Messenger RNA is translated when associated with the cytoskeletal framework in normal and VSV-infected HeLa cells. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Little S. P., Hagen F. S., Huang A. S. The matrix (M) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus regulates transcription. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubovi E. J., Wagner R. R. Spatial relationships of the proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: induction of reversible oligomers by cleavable protein cross-linkers and oxidation. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):500–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.500-509.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enami M., Luytjes W., Krystal M., Palese P. Introduction of site-specific mutations into the genome of influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3802–3805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Earl P. L., Moss B. Use of a hybrid vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase system for expression of target genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2538–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A. The use of intensifying screens or organic scintillators for visualizing radioactive molecules resolved by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):363–371. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz E. J., Pattnaik A. K., Ball L. A. Complementation of a vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein G mutant with wild-type protein expressed from either a bovine papilloma virus or a vaccinia virus vector system. Virology. 1990 Oct;178(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90334-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Luo L. Z., Snyder R. M., Wagner R. R. Expression of the M gene of vesicular stomatitis virus cloned in various vaccinia virus vectors. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):776–782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.776-782.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Luo L. Z., Snyder R. M., Wagner R. R. Site-specific mutations in vectors that express antigenic and temperature-sensitive phenotypes of the M gene of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3729–3737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3729-3737.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Krystal M., Enami M., Parvin J. D., Palese P. Amplification, expression, and packaging of foreign gene by influenza virus. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1107–1113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90766-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancarella D. A., Lenard J. Interactions of wild-type and mutant M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus with viral nucleocapsid and envelope in intact virions. Evidence from [125I]iodonaphthyl azide labeling and specific cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6872–6877. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsikkö K., Simons K. The budding mechanism of spikeless vesicular stomatitis virus particles. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1913–1920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Swanson R. E. In situ cross-linking of vesicular stomatitis virus proteins with reversible agents. Virology. 1978 Jul 15;88(2):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Tobin G. J., McGowan J. J., Brown J. C. In vitro reassembly of vesicular stomatitis virus skeletons. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1055-1062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Arnheiter H., Dubois-Dalcq M., Lazzarini R. A. Stereo images of vesicular stomatitis virus assembly. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):922–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.922-932.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattnaik A. K., Wertz G. W. Replication and amplification of defective interfering particle RNAs of vesicular stomatitis virus in cells expressing viral proteins from vectors containing cloned cDNAs. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2948–2957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2948-2957.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Harmison G. G., Meier E. Primary structure of the vesicular stomatitis virus polymerase (L) gene: evidence for a high frequency of mutations. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):505–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.505-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Harmison G. G., Richardson C. D., Meier E. Expression of a cDNA encoding a functional 241-kilodalton vesicular stomatitis virus RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7984–7988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger G., Lazzarini R. A. Analysis of the RNA of defective VSV particles. Cell. 1974 Sep;3(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Davis N. Characterization and mapping of RNase III cleavage sites in VSV genome RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6487–6503. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitt M. A., Chong L., Rose J. K. Glycoprotein cytoplasmic domain sequences required for rescue of a vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein mutant. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3569–3578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3569-3578.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Lenard J. Interaction of wild-type and mutant M protein vesicular stomatitis virus with nucleocapsids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]