Abstract
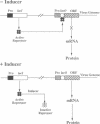
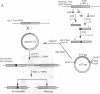
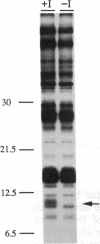
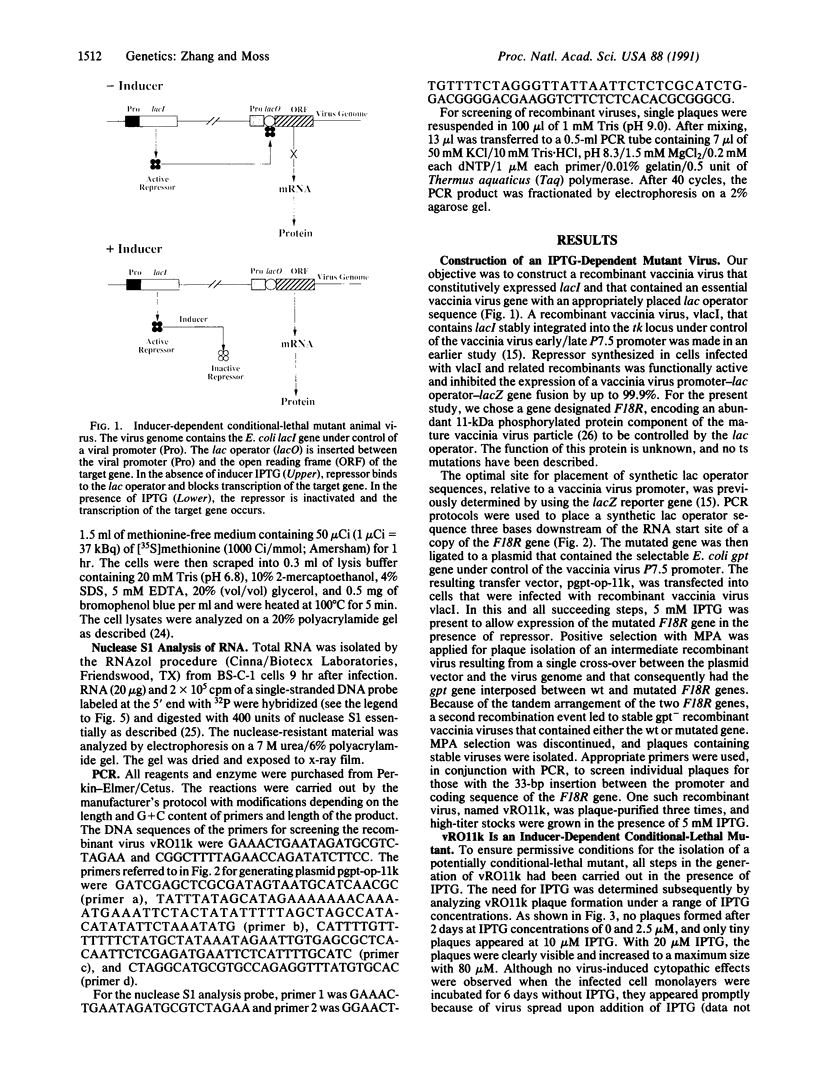
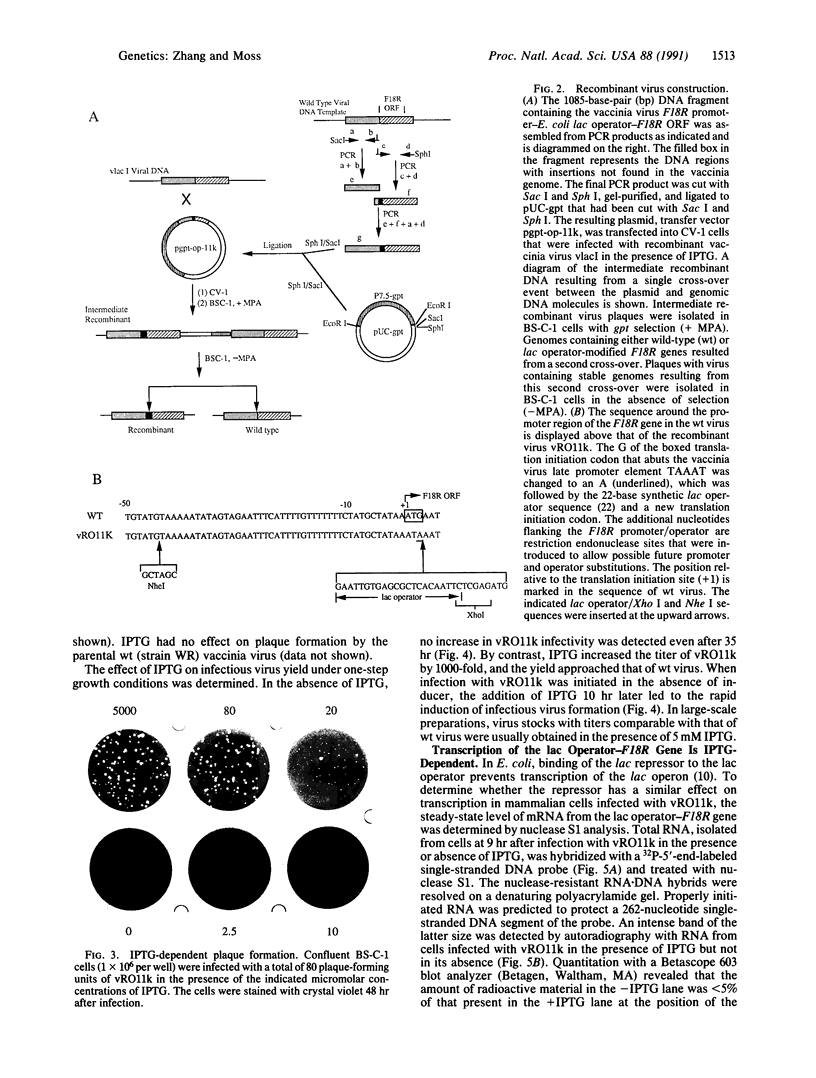
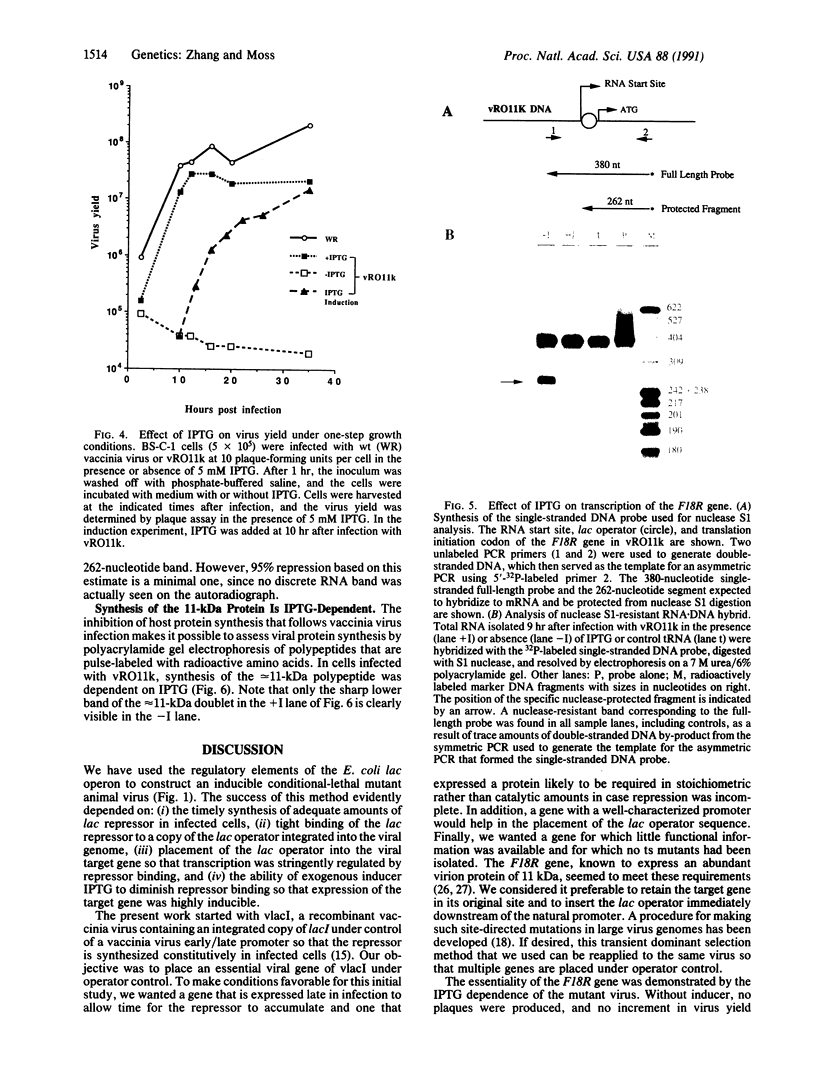
Regulatory elements of the Escherichia coli lac operon were used to construct an inducer-dependent conditional-lethal mutant animal virus. The gene encoding the repressor protein of the lac operon was integrated into the vaccinia virus genome so that it was expressed constitutively, and the lac operator was inserted next to the promoter of a gene that encodes an 11-kDa virion-associated protein of unknown function. The addition of inducer to the cell culture medium provided permissive conditions for isolation of a conditional-lethal mutant virus. Under nonpermissive conditions, the isolated virus did not form plaques, and the yield was decreased by at least 1000-fold under one-step growth conditions. Transcription of the operator-controlled gene was inducer-dependent and necessary for synthesis of the 11-kDa protein. Application of this mutagenesis strategy to other viruses is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENZER S., CHAMPE S. P. A change from nonsense to sense in the genetic code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1114–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):394–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Figge J., Hansen U., Wright C., Jeang K. T., Khoury G., Livingston D. M., Roberts T. M. lac repressor can regulate expression from a hybrid SV40 early promoter containing a lac operator in animal cells. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):603–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Pepperkok R., Wang F. B., Giordano T. J., McAllister W. T., Ansorge W., Bujard H. Regulated expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells under the control of coliphage T3 RNA polymerase and lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5400–5404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Moss B. Escherichia coli gpt gene provides dominant selection for vaccinia virus open reading frame expression vectors. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1849-1854.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Moss B. Transient dominant selection of recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3108–3111. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3108-3111.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge J., Wright C., Collins C. J., Roberts T. M., Livingston D. M. Stringent regulation of stably integrated chloramphenicol acetyl transferase genes by E. coli lac repressor in monkey cells. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):713–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Fernandez M. P., Moss B. Transfer of the inducible lac repressor/operator system from Escherichia coli to a vaccinia virus expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2549–2553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller G., Weber K. A phosphorylated basic vaccinia virion polypeptide of molecular weight 11,000 is exposed on the surface of mature particles and interacts with actin-containing cytoskeletal elements. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):647–657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.647-657.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. The inducible lac operator-repressor system is functional in mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak R. M., Laski F. A., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A., Capecchi M. R. Establishment of mammalian cell lines containing multiple nonsense mutations and functional suppressor tRNA genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Baim S. B., Shenk T., Levine A. J. Conversion of the lac repressor into an allosterically regulated transcriptional activator for mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3343–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L., Moss B. General method for production and selection of infectious vaccinia virus recombinants expressing foreign genes. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):857–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.857-864.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Smith G. L. IPTG-dependent vaccinia virus: identification of a virus protein enabling virion envelopment by Golgi membrane and egress. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5347–5351. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Smith G. L. Inducible gene expression from vaccinia virus vectors. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. R., Sasmor H., Betz J. L. A perfectly symmetric lac operator binds the lac repressor very tightly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedivy J. M., Capone J. P., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A. An inducible mammalian amber suppressor: propagation of a poliovirus mutant. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90492-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. T., McGeoch D. J. Isolation and characterization of conditional lethal amber nonsense mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3033–3044. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Hänggi M., Hiller G. Mapping of a gene coding for a major late structural polypeptide on the vaccinia virus genome. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):371–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.371-378.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]