Abstract
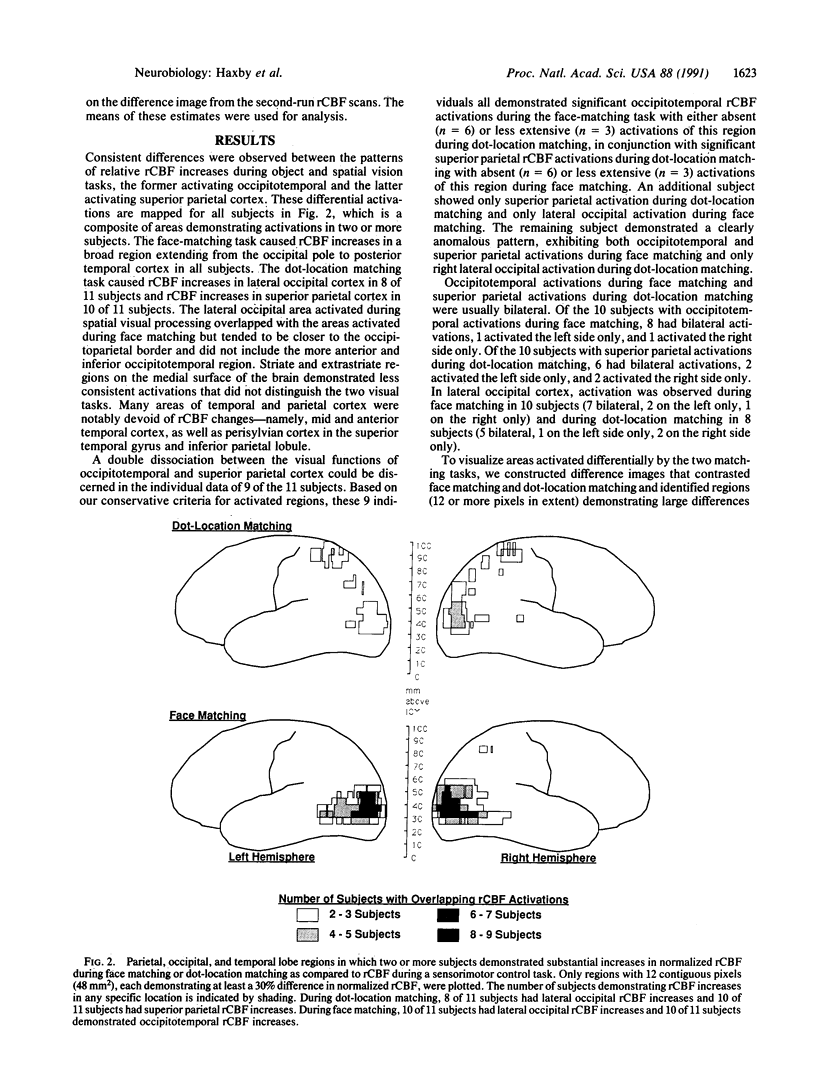
The existence and neuroanatomical locations of separate extrastriate visual pathways for object recognition and spatial localization were investigated in healthy young men. Regional cerebral blood flow was measured by positron emission tomography and bolus injections of H2(15)O, while subjects performed face matching, dot-location matching, or sensorimotor control tasks. Both visual matching tasks activated lateral occipital cortex. Face discrimination alone activated a region of occipitotemporal cortex that was anterior and inferior to the occipital area activated by both tasks. The spatial location task alone activated a region of lateral superior parietal cortex. Perisylvian and anterior temporal cortices were not activated by either task. These results demonstrate the existence of three functionally dissociable regions of human visual extrastriate cortex. The ventral and dorsal locations of the regions specialized for object recognition and spatial localization, respectively, suggest some homology between human and nonhuman primate extrastriate cortex, with displacement in human brain, possibly related to the evolution of phylogenetically newer cortical areas.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert N. M., Eriksson L., Chang J. Y., Bergstrom M., Litton J. E., Correia J. A., Bohm C., Ackerman R. H., Taveras J. M. Strategy for the measurement of regional cerebral blood flow using short-lived tracers and emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Mar;4(1):28–34. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbetta M., Miezin F. M., Dobmeyer S., Shulman G. L., Petersen S. E. Attentional modulation of neural processing of shape, color, and velocity in humans. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1556–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.2360050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowey A., Gross C. G. Effects of foveal prestriate and inferotemporal lesions on visual discrimination by rhesus monkeys. Exp Brain Res. 1970;11(2):128–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00234318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damasio A. R., Benton A. L. Impairment of hand movements under visual guidance. Neurology. 1979 Feb;29(2):170–174. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damasio A. R., Damasio H., Van Hoesen G. W. Prosopagnosia: anatomic basis and behavioral mechanisms. Neurology. 1982 Apr;32(4):331–341. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.4.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farah M. J., Hammond K. M., Levine D. N., Calvanio R. Visual and spatial mental imagery: dissociable systems of representation. Cogn Psychol. 1988 Oct;20(4):439–462. doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(88)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Miezin F. M., Allman J. M., Van Essen D. C., Raichle M. E. Retinotopic organization of human visual cortex mapped with positron-emission tomography. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):913–922. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00913.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Mintun M. A., Raichle M. E., Miezin F. M., Allman J. M., Van Essen D. C. Mapping human visual cortex with positron emission tomography. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):806–809. doi: 10.1038/323806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Mintun M. A., Reiman E. M., Raichle M. E. Enhanced detection of focal brain responses using intersubject averaging and change-distribution analysis of subtracted PET images. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Oct;8(5):642–653. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Perlmutter J. S., Raichle M. E. A stereotactic method of anatomical localization for positron emission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985 Jan-Feb;9(1):141–153. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198501000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friston K. J., Passingham R. E., Nutt J. G., Heather J. D., Sawle G. V., Frackowiak R. S. Localisation in PET images: direct fitting of the intercommissural (AC-PC) line. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Oct;9(5):690–695. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattass R., Sousa A. P., Gross C. G. Visuotopic organization and extent of V3 and V4 of the macaque. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):1831–1845. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-01831.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueck C. J., Zeki S., Friston K. J., Deiber M. P., Cope P., Cunningham V. J., Lammertsma A. A., Kennard C., Frackowiak R. S. The colour centre in the cerebral cortex of man. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):386–389. doi: 10.1038/340386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe F., Ratcliff G., Damasio H. Dissociable visual and spatial impairments following right posterior cerebral lesions: clinical, neuropsychological and anatomical evidence. Neuropsychologia. 1987;25(1B):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(87)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen S. E., Fox P. T., Posner M. I., Mintun M., Raichle M. E. Positron emission tomographic studies of the cortical anatomy of single-word processing. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):585–589. doi: 10.1038/331585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner M. I., Walker J. A., Friedrich F. J., Rafal R. D. Effects of parietal injury on covert orienting of attention. J Neurosci. 1984 Jul;4(7):1863–1874. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-07-01863.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliff G., Davies-Jones G. A. Defective visual localization in focal brain wounds. Brain. 1972;95(1):49–60. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliff G., Newcombe F. Spatial orientation in man: effects of left, right, and bilateral posterior cerebral lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Jun;36(3):448–454. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Friberg L. Localization of cortical areas activated by thinking. J Neurophysiol. 1985 May;53(5):1219–1243. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.5.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumsey J. M., Duara R., Grady C., Rapoport J. L., Margolin R. A., Rapoport S. I., Cutler N. R. Brain metabolism in autism. Resting cerebral glucose utilization rates as measured with positron emission tomography. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985 May;42(5):448–455. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790280026003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





