Abstract
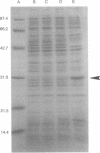
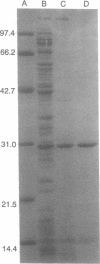
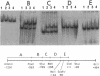
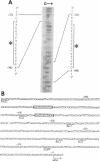
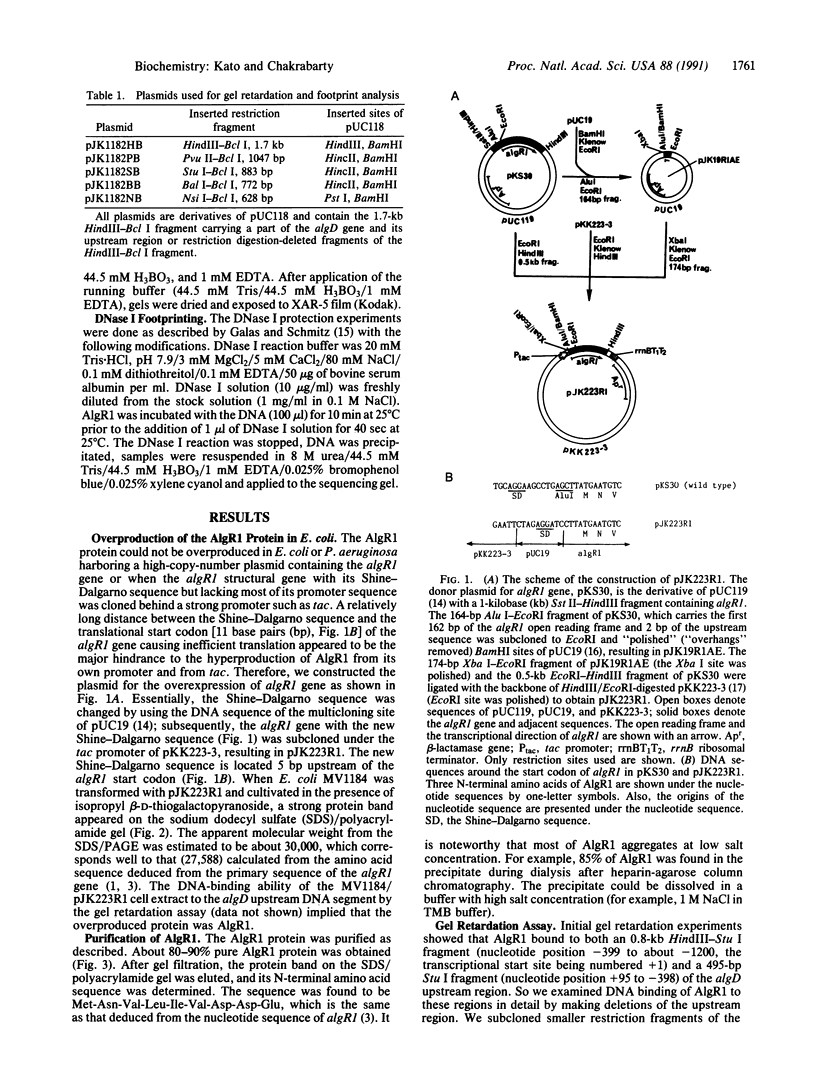
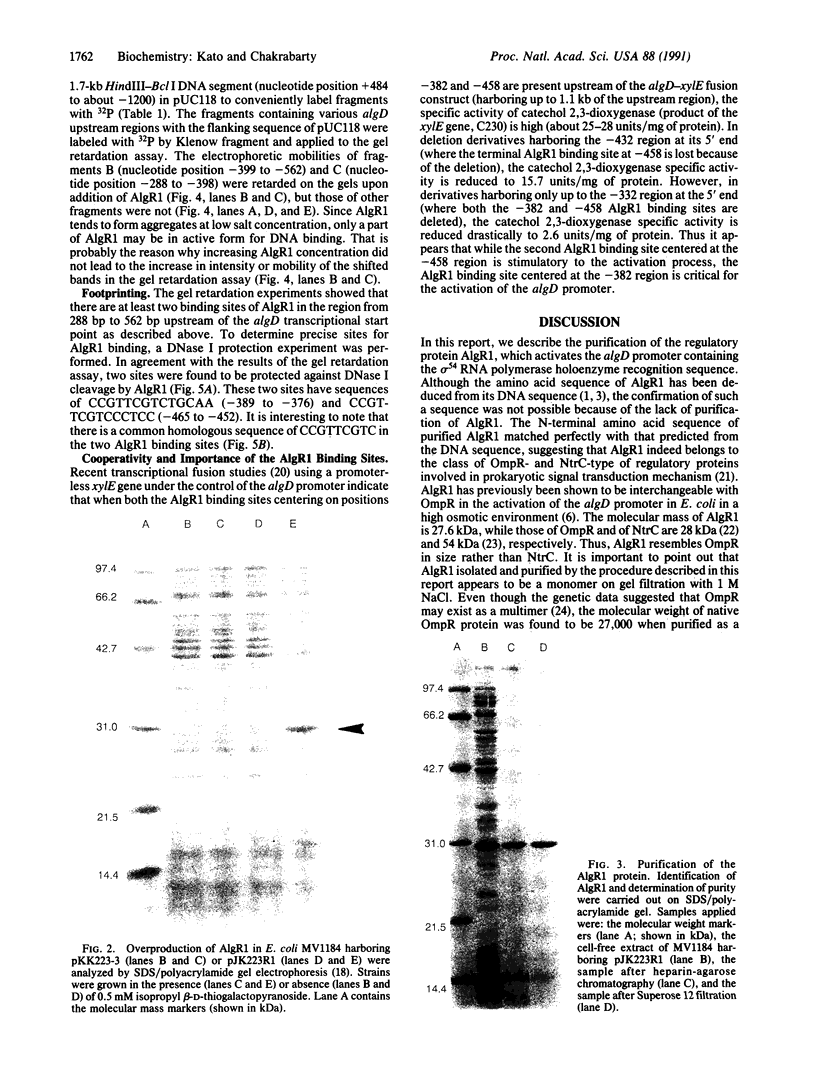
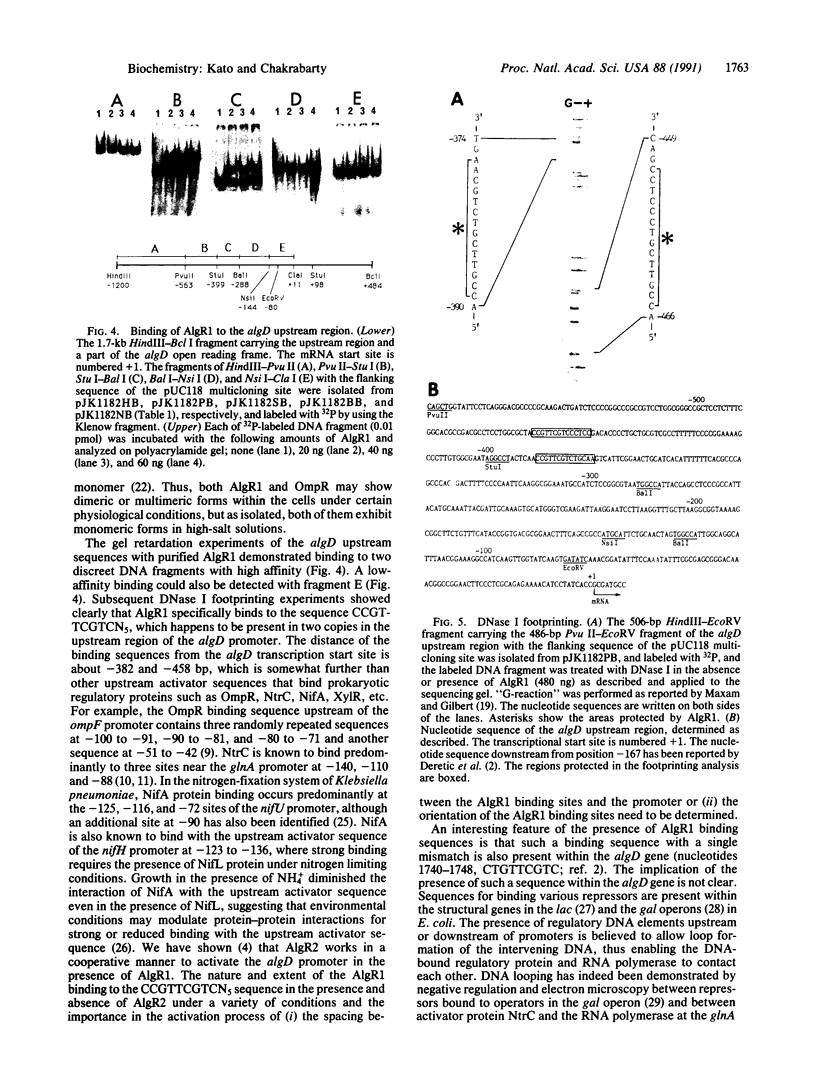
A regulatory protein AlgR1, previously suggested to be a member of a two-component sensory transduction system because of its homology to OmpR and NtrC and its ability to allow activation of the algD promoter under conditions of high osmolarity, has been hyperproduced in Escherichia coli after deletion of the upstream region including part of the Shine-Dalgarno sequence of the algR1 gene and its subsequent cloning under the tac promoter. The AlgR1 protein is purified as a monomer, and the sequence of the nine N-terminal amino acids of the monomer matches with that predicted from the DNA sequence of the algR1 gene. The purified AlgR1 protein binds to two separate DNA fragments of the algD upstream region. DNase protection experiments identify these two DNA segments as 14-mer sequences centered at -382 and -458 regions, which contain a common CCGT-TCGTC sequence in them. While the presence of at least one AlgR1 binding site is important for the activation of the algD promoter, the presence of both of the binding sites in the upstream region leads to a higher level of activation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry A., DeVault J. D., Chakrabarty A. M. High osmolarity is a signal for enhanced algD transcription in mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2312–2317. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2312-2317.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Holy A. Regulation of ribosomal RNA promoters with a synthetic lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6929–6933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W. V., Kreutzer R., Kent H. M., Morett E., Buck M. Activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifU promoter: identification of multiple and overlapping upstream NifA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1693–1701. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVault J. D., Kimbara K., Chakrabarty A. M. Pulmonary dehydration and infection in cystic fibrosis: evidence that ethanol activates alginate gene expression and induction of mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):737–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Dikshit R., Konyecsni W. M., Chakrabarty A. M., Misra T. K. The algR gene, which regulates mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, belongs to a class of environmentally responsive genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1278-1283.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic V., Gill J. F., Chakrabarty A. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional regulation of the algD gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4567–4581. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flashner Y., Gralla J. D. Dual mechanism of repression at a distance in the lac operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8968–8972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. Genetic analysis of the ompB locus in Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Orosz L., Adhya S. A control element within a structural gene: the gal operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jo Y. L., Nara F., Ichihara S., Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Purification and characterization of the OmpR protein, a positive regulator involved in osmoregulatory expression of the ompF and ompC genes in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15252–15256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Chu L., Kitano K., DeVault J. D., Kimbara K., Chakrabarty A. M., Misra T. K. Nucleotide sequence of a regulatory region controlling alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: characterization of the algR2 gene. Gene. 1989 Dec 7;84(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Misra T. K., Chakrabarty A. M. AlgR3, a protein resembling eukaryotic histone H1, regulates alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2887–2891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keener J., Kustu S. Protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatase activities of nitrogen regulatory proteins NTRB and NTRC of enteric bacteria: roles of the conserved amino-terminal domain of NTRC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4976–4980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbara K., Chakrabarty A. M. Control of alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: regulation of the algR1 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91502-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal N., Su W., Haber R., Adhya S., Echols H. DNA looping in cellular repression of transcription of the galactose operon. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):410–418. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr C. D., Martin D. W., Konyecsni W. M., Govan J. R., Lory S., Deretic V. Role of the far-upstream sites of the algD promoter and the algR and rpoN genes in environmental modulation of mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6576–6580. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6576-6580.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Kreutzer R., Cannon W., Buck M. The influence of the Klebsiella pneumoniae regulatory gene nifL upon the transcriptional activator protein NifA. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1253–1258. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsung K., Brissette R. E., Inouye M. Identification of the DNA-binding domain of the OmpR protein required for transcriptional activation of the ompF and ompC genes of Escherichia coli by in vivo DNA footprinting. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10104–10109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedel A., Weiss D. S., Popham D., Dröge P., Kustu S. A bacterial enhancer functions to tether a transcriptional activator near a promoter. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):486–490. doi: 10.1126/science.1970441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]