Abstract
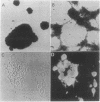
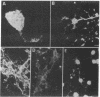
We synthesized the 60-amino acid polypeptide corresponding to the sequence of the Drosophila antennapedia gene homeobox. This peptide (pAntp) recognized the consensus motif for binding to the promoter region of Hox-1.3. pAntp mechanically introduced into mammalian nerve cells provoked a dramatic morphological differentiation of the neuronal cultures. Moreover, pAntp directly added to already differentiated neuronal cultures penetrated the cells and further augmented their morphological differentiation. Examination of live and fixed neurons in classical and confocal fluorescence microscopy demonstrated that pAntp was captured at all regions of the nerve cells and accumulated in the nuclei. In addition, the effect of pAntp on neurite extension was blocked in the presence of the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide. Thus, our results demonstrate that neurons possess an efficient uptake system for the antennapedia homeobox peptide and suggest that binding of pAntp to consensus motifs present in nerve cell nuclei influences neuronal morphogenetic programs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acampora D., D'Esposito M., Faiella A., Pannese M., Migliaccio E., Morelli F., Stornaiuolo A., Nigro V., Simeone A., Boncinelli E. The human HOX gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10385–10402. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayala J., Touchot N., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Prochiantz A. The product of rab2, a small GTP binding protein, increases neuronal adhesion, and neurite growth in vitro. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):797–805. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90206-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldin V., Roman A. M., Bosc-Bierne I., Amalric F., Bouche G. Translocation of bFGF to the nucleus is G1 phase cell cycle specific in bovine aortic endothelial cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1511–1517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors and the control of Drosophila development. Trends Genet. 1989 Nov;5(11):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borasio G. D., John J., Wittinghofer A., Barde Y. A., Sendtner M., Heumann R. ras p21 protein promotes survival and fiber outgrowth of cultured embryonic neurons. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1087–1096. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco A. E., Malacinski G. M. Localization of Xenopus homoeo-box gene transcripts during embryogenesis and in the adult nervous system. Dev Biol. 1987 May;121(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamak B., Prochiantz A. Influence of extracellular matrix proteins on the expression of neuronal polarity. Development. 1989 Jul;106(3):483–491. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe C. Q., Scott M. P. Segmentation and homeotic gene function in the developing nervous system of Drosophila. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Mar;11(3):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber R. L., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Genomic and cDNA clones of the homeotic locus Antennapedia in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2027–2036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01696.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Johnson A. D. Homeo domain of the yeast repressor alpha 2 is a sequence-specific DNA-binding domain but is not sufficient for repression. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1007–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2887035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. R., Gaugler L., Deagostini-Bazin H., Bally-Cuif L., Goridis C. Identification of positive and negative regulatory elements governing cell-type-specific expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1959–1968. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W. Homeobox genes and the vertebrate head. Development. 1988;103 (Suppl):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. The molecular genetics of embryonic pattern formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):25–34. doi: 10.1038/335025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., O'Farrell P. H. Activation and repression of transcription by homoeodomain-containing proteins that bind a common site. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):744–749. doi: 10.1038/336744a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Saffman E. E., Kornfeld K., Hogness D. S. Transcriptional activation and repression by Ultrabithorax proteins in cultured Drosophila cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1031–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Garbern J., Arnheiter H., Tournier-Lasserve E., Lazzarini R. A. The Hox-1.3 homeo box protein is a sequence-specific DNA-binding phosphoprotein. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):158–172. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Taylor C. F., Palmer-Hill F. J., Friedrich V., Jr, Tani M., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a homeo domain protein in noncontact-inhibited cultured cells and postmitotic neurons. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):482–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubartelli A., Cozzolino F., Talio M., Sitia R. A novel secretory pathway for interleukin-1 beta, a protein lacking a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1503–1510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08268.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson M. L., Jackson-Grusby L., Brent R. Gene activation and DNA binding by Drosophila Ubx and abd-A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1045–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90342-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani M., Odenwald W. F., Lazzarini R. A., Friedrich V. L., Jr Progressive restriction in the distribution of the Hox-1.3 homeodomain protein during embryogenesis. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Dec;24(4):457–469. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triller A., Seitanidou T., Franksson O., Korn H. Size and shape of glycine receptor clusters in a central neuron exhibit a somato-dendritic gradient. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):637–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Cook M., Boncinelli E., Krumlauf R. Segmental expression of Hox-2 homoeobox-containing genes in the developing mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):405–409. doi: 10.1038/341405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]