Abstract
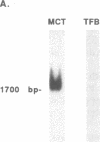
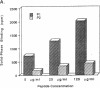
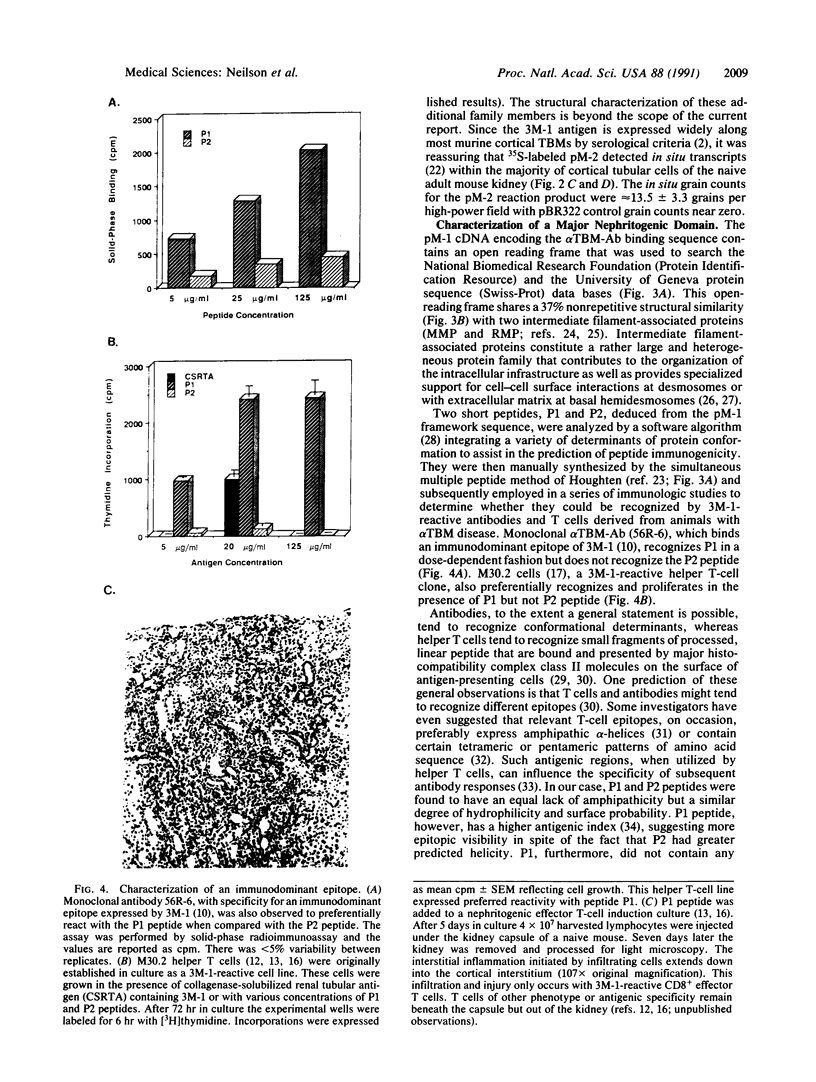
Anti-tubular basement membrane (alpha TBM) disease is a form of primary interstitial nephritis mediated by autoimmune T cells and alpha TBM antibodies. In mice and humans the nephritogenic immune response is directed to a glycoprotein (3M-1) found along the proximal tubule of the kidney. We have isolated cDNAs from an expression library that encodes for the common framework domain of the 3M-1 antigen. This common domain was once related evolutionarily to a family of intermediate filament-associated proteins. Northern hybridization revealed that all isoforms of 3M-1 range between 1700 and 1900 base pairs and in situ hybridization studies indicate that transcripts are found in tubular epithelium. Candidate peptide fragments were deduced and synthesized from the sequence encoding this common framework domain, and one of the peptide residues was able to bind a monoclonal 3M-1-reactive alpha TBM antibody, stimulate the growth of 3M-1-reactive helper T cells, and induce nephritogenic effector T cells capable of producing interstitial nephritis. Our results indicate that a unique, immunodominant region of the 3M-1 antigen is an informative participant in the emergence of autoimmune injury to certain basement membranes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin D. C., Berzofsky J. A., East I. J., Gurd F. R., Hannum C., Leach S. J., Margoliash E., Michael J. G., Miller A., Prager E. M. The antigenic structure of proteins: a reappraisal. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:67–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A. Structural basis of antigen recognition by T lymphocytes. Implications for vaccines. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1811–1817. doi: 10.1172/JCI113796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecka J. M., Stratton J. A., Miller A., Sercarz E. Structural aspects of immune recognition of lysozymes. III. T cell specificity restriction and its consequences for antibody specificity. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Sep;6(9):639–646. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayman M. D., Martinez-Hernandez A., Michaud L., Alper R., Mann R., Kefalides N. A., Neilson E. G. Isolation and characterization of the nephritogenic antigen producing anti-tubular basement membrane disease. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):290–305. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayman M. D., Michaud L., Brentjens J., Andres G. A., Kefalides N. A., Neilson E. G. Isolation of the target antigen of human anti-tubular basement membrane antibody-associated interstitial nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1143–1147. doi: 10.1172/JCI112414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayman M. D., Michaud L., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. VI. Characterization of the B cell response in anti-tubular basement membrane disease. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2242–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayman M. D., Sun M. J., Michaud L., Brill-Dashoff J., Riblet R., Neilson E. G. Clonotypic heterogeneity in experimental interstitial nephritis. Restricted specificity of the anti-tubular basement membrane B cell repertoire is associated with a disease-modifying crossreactive idiotype. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1296–1312. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton J. P., Gammon G. M., Ando D. G., Kono D. H., Hood L., Sercarz E. E. Peptide-specific prevention of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neonatal tolerance induced to the dominant T cell determinant of myelin basic protein. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1681–1691. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Baxter J. D. Structural analysis of the prolactin gene suggests a separate origin for its 5' end. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):603–606. doi: 10.1038/297603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E. Rat vitamin D binding protein. Determination of the full-length primary structure from cloned cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3441–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guery J. C., Hedrich H. J., Mercier P., Reetz I. C., Mandet C., Mahieu P., Neilson E. G., Druet P. Mapping of a gene for the Mr 48,000 tubular basement membrane antigen in the rat. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(5):350–354. doi: 10.1007/BF00352846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverty T. P., Watanabe M., Neilson E. G., Kelly C. J. Protective modulation of class II MHC gene expression in tubular epithelium by target antigen-specific antibodies. Cell-surface directed down-regulation of transcription can influence susceptibility to murine tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1133–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines W. H., Haverty T. P., Elias J. A., Neilson E. G., Kelly C. J. T cell recognition of epithelial self. Autoimmunity. 1989;5(1-2):37–47. doi: 10.3109/08916938909029141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines W. H., Mann R. A., Kelly C. J., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. IX. Induction of the nephritogenic effector T cell repertoire with an antigen-specific T cell cytokine. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson B. A., Wolf H. The antigenic index: a novel algorithm for predicting antigenic determinants. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):181–186. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. J., Silvers W. K., Neilson E. G. Tolerance to parenchymal self. Regulatory role of major histocompatibility complex-restricted, OX8+ suppressor T cells specific for autologous renal tubular antigen in experimental interstitial nephritis. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1892–1903. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman D. H., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Interstitial nephritis in rats immunized with heterologous tubular basement membrane. Kidney Int. 1974 Mar;5(3):187–195. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Kelly C. J., Hines W. H., Clayman M. D., Blanchard N., Sun M. J., Neilson E. G. Effector T cell differentiation in experimental interstitial nephritis. I. The development and modulation of effector lymphocyte maturation by I-J+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4200–4208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Zakheim B., Clayman M., McCafferty E., Michaud L., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. IV. Long-term cultured L3T4+ T cell lines transfer delayed expression of disease as I-A-restricted inducers of the effector T cell repertoire. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., McCafferty E., Neilson E. G., Gasser D. L. Mapping of the genes for tubular basement membrane antigen and a submaxillary gland protease in the rat. Immunogenetics. 1984;20(2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00364483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napolitano E. W., Chin S. S., Colman D. R., Liem R. K. Complete amino acid sequence and in vitro expression of rat NF-M, the middle molecular weight neurofilament protein. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2590–2599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G. Pathogenesis and therapy of interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 1989 May;35(5):1257–1270. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Phillips S. M. Murine interstitial nephritis. I. Analysis of disease susceptibility and its relationship of pleiomorphic gene products defining both immune-response genes and a restrictive requirement for cytotoxic T cells at H-2K. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietromonaco S., Kerjaschki D., Binder S., Ullrich R., Farquhar M. G. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a major pathogenic domain of the Heymann nephritis antigen gp330. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1811–1815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. M., Golub E. E. A computer graphics program system for protein structure representation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1801–1812. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Taylor W. R. A sequence pattern common to T cell epitopes. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela M. Antigenicity: some molecular aspects. Science. 1969 Dec 12;166(3911):1365–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3911.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Bond M., Somlyo A. P., Scarpa A. Inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release and contraction in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5231–5235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Liem R. K. Intermediate filament dynamics. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90651-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Wilson C. B. Characterization of anti-tubular basement membrane antibodies in rats. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2173–2179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]