Abstract
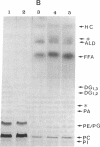
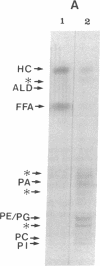
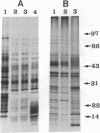
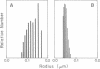
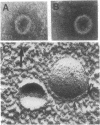
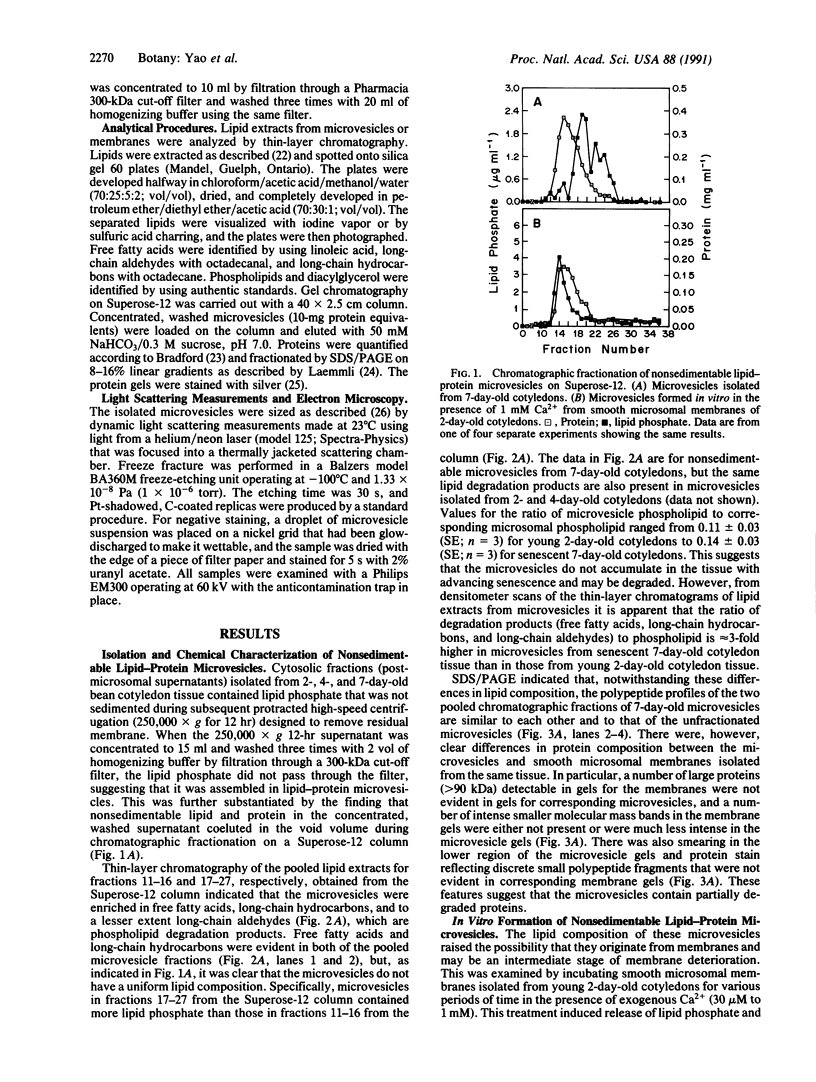
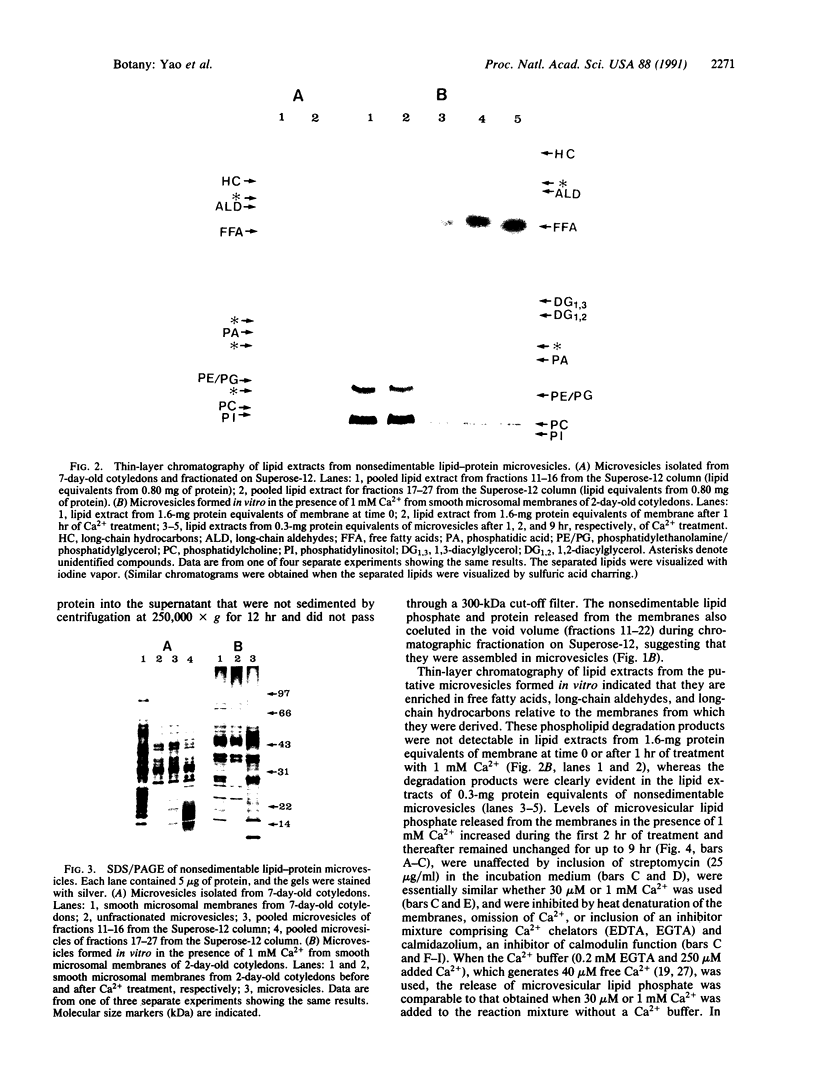
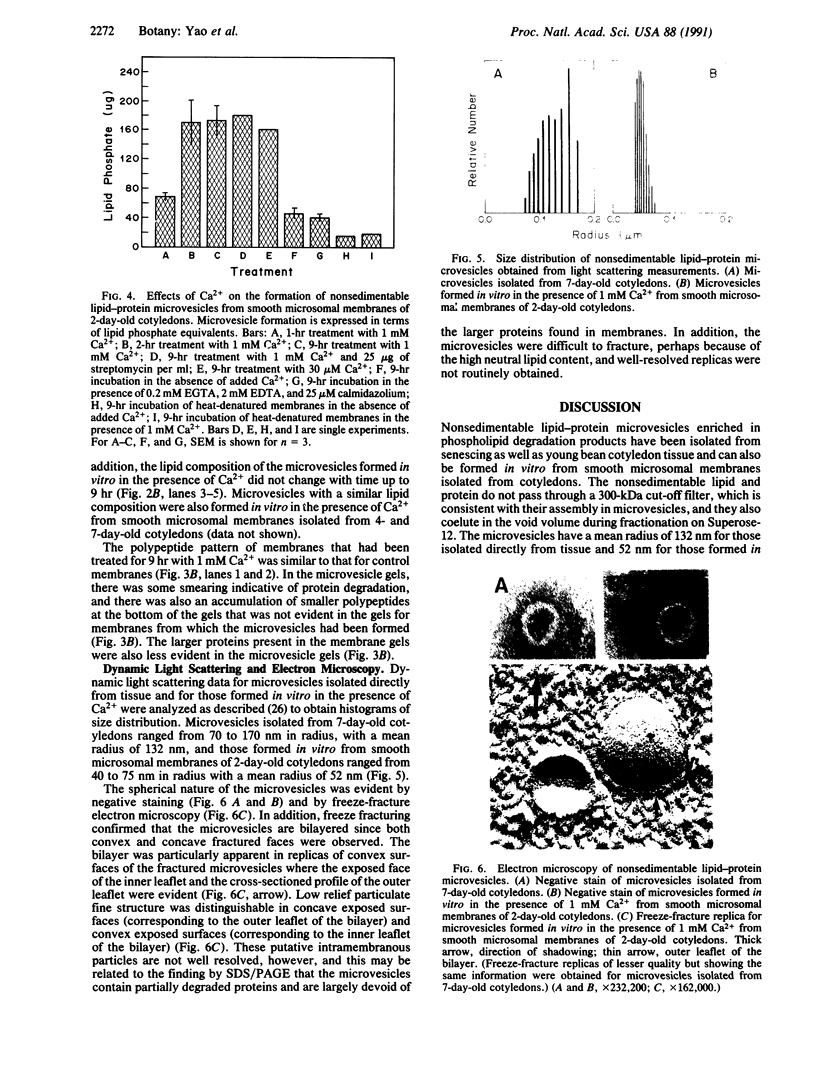
Previously uncharacterized lipid-protein microvesicles have been isolated from young and senescing bean cotyledon tissue. The microvesicles are nonsedimentable and enriched in phospholipid degradation products (free fatty acids, long-chain aldehydes, and long-chain hydrocarbons). They range from 70 to 170 nm (radius) with a mean radius of 132 nm, and it is clear from freeze-fracture electron micrographs that they are bilayered in nature. Nonsedimentable lipid-protein microvesicles containing the same products of phospholipid degradation but smaller were also formed in vitro when smooth microsomal membranes from young cotyledon tissue were treated with Ca2+ to stimulate enzymatic degradation of phospholipids. The data suggest that these microvesicles comprise an intermediate stage of membrane lipid deterioration. They appear to serve as a vehicle for moving phospholipid degradation products out of membranes into the cytosol during senescence and perhaps also during normal membrane lipid turnover.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan D., Billah M. M., Finean J. B., Michell R. H. Release of diacylglycerol-enriched vesicles from erythrocytes with increased intracellular (Ca2+). Nature. 1976 May 6;261(5555):58–60. doi: 10.1038/261058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Low M. G., Finean J. B., Michell R. H. Changes in lipid metabolism and cell morphology following attack by phospholipase C (Clostridium perfringens) on red cells or lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 1;413(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bognar A. L., Paliyath G., Rogers L., Kolattukudy P. E. Biosynthesis of alkanes by particulate and solubilized enzyme preparations from pea leaves (Pisum sativum). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 15;235(1):8–17. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90249-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diesperger H., Müller C. R., Sandermann H., Jr Rapid isolation of a plant microsomal fraction by Mg2+--precipitation. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 15;43(2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80990-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fobel M., Lynch D. V., Thompson J. E. Membrane deterioration in senescing carnation flowers : coordinated effects of phospholipid degradation and the action of membranous lipoxygenase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):204–211. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon-Kamm W. J., Steponkus P. L. Lamellar-to-hexagonalII phase transitions in the plasma membrane of isolated protoplasts after freeze-induced dehydration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6373–6377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman E. M., Chrispeels M. J. Characteristics and subcellular localization of phospholipase d and phosphatidic Acid phosphatase in mung bean cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):1001–1007. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara K., Norikura S., Fujii S. Microsomal phosphatidate phosphatase in maturing safflower seeds. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jun;90(2):413–419. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. S., Lord J. M., Kagawa T., Beevers H. Enzymes of phospholipid metabolism in the endoplasmic reticulum of castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jul;52(1):50–53. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliyath G., Thompson J. E. Calcium- and calmodulin-regulated breakdown of phospholipid by microsomal membranes from bean cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jan;83(1):63–68. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauls K. P., Thompson J. E. Evidence for the accumulation of peroxidized lipids in membranes of senescing cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1152–1157. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughan P. G., Slack C. R. Is phospholipase D really an enzyme? A comparison of in situ and in vitro activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 22;431(1):86–95. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S. Freezing Injury and Phospholipid Degradation in Vivo in Woody Plant Cells: II. Regulatory Effects of Divalent Cations on Activity of Membrane-bound Phospholipase D. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):247–251. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S. Freezing injury and phospholipid degradation in vivo in woody plant cells: I. Subcellular localization of phospholipase d in living bark tissues of the black locust tree (robinia pseudoacacia L.). Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):241–246. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]