Abstract
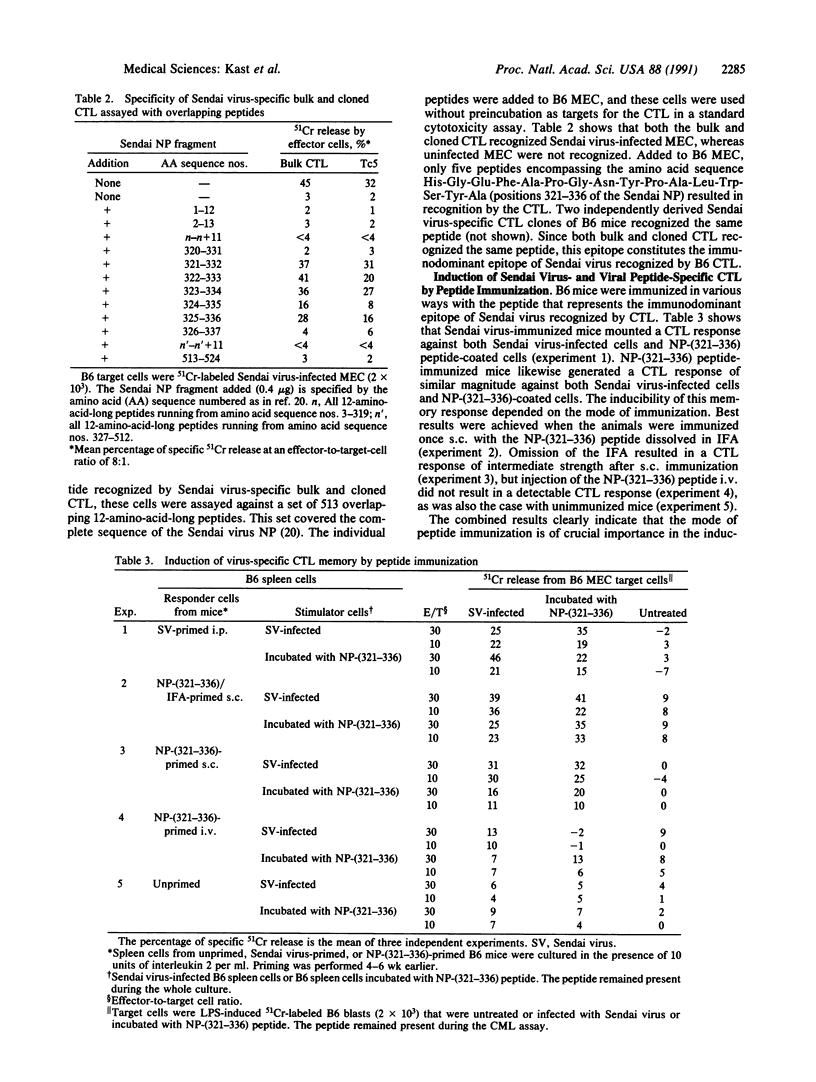
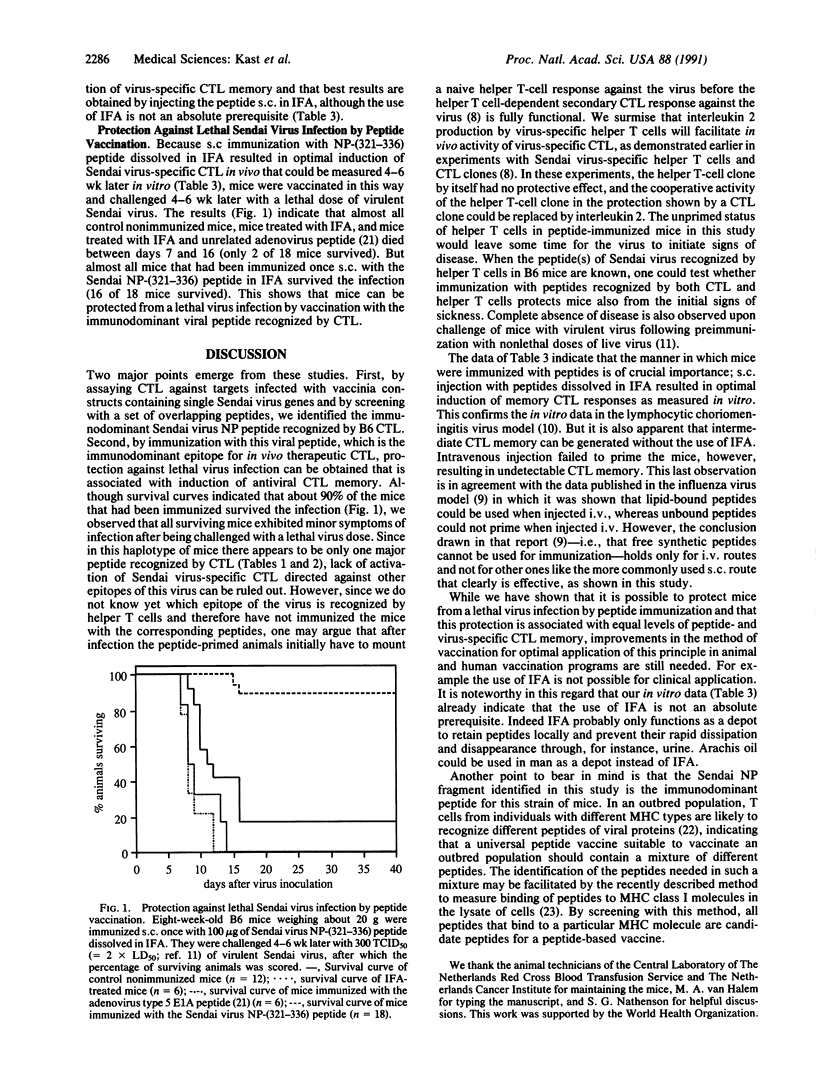
The only peptide of Sendai virus that is recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) in B6 mice was found with (i) the use of recombinant vaccinia virus constructs containing separate genes of Sendai virus and (ii) a set of overlapping peptides completely spanning the identified nucleoprotein (NP) gene product. This immunodominant NP peptide is recognized by Sendai virus-specific CTL that are known to have therapeutic effects in vivo. By subcutaneous immunization, this peptide induced Sendai virus and NP peptide-specific CTL memory responses in vivo. Most importantly, mice that had been immunized with this peptide were protected against a lethal virus dose, indicating that viral peptides can be used as antiviral T-cell vaccines. The induction of T-cell memory by free peptide immunization potentially has wide applicability in biology and medicine, including protection against infectious disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aichele P., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M., Schulz M. Antiviral cytotoxic T cell response induced by in vivo priming with a free synthetic peptide. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1815–1820. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Rose K., Simona M. G., Roux L., Giorgi C., Kolakofsky D. Analysis of the Sendai virus M gene and protein. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.656-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne J. A., Oldstone M. B. Biology of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: clearance of virus in vivo. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.682-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Scanning independent ribosomal initiation of the Sendai virus Y proteins in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):521–526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deres K., Schild H., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. In vivo priming of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes with synthetic lipopeptide vaccine. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):561–564. doi: 10.1038/342561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Barteling S. J., Meloen R. H. Small peptides induce antibodies with a sequence and structural requirement for binding antigen comparable to antibodies raised against the native protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):178–182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges R. S., Merrifield R. B. Monitoring of solid phase peptide synthesis by an automated spectrophotometric picrate method. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):241–272. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Bluestone J. A., Heemskerk M. H., Spaargaren J., Voordouw A. C., Ellenhorn J. D., Melief C. J. Treatment with monoclonal anti-CD3 antibody protects against lethal Sendai virus infection by induction of natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2254–2259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Bronkhorst A. M., de Waal L. P., Melief C. J. Cooperation between cytotoxic and helper T lymphocytes in protection against lethal Sendai virus infection. Protection by T cells is MHC-restricted and MHC-regulated; a model for MHC-disease associations. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):723–738. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Offringa R., Peters P. J., Voordouw A. C., Meloen R. H., van der Eb A. J., Melief C. J. Eradication of adenovirus E1-induced tumors by E1A-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Moskophidis D., Löhler J. Recovery from acute virus infection. Role of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the elimination of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from spleens of mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;532:238–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb36343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Biological properties of an influenza A virus-specific killer T cell clone. Inhibition of virus replication in vivo and induction of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):225–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacher A. E., Braciale V. L., Braciale T. J. In vivo effector function of influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones is highly specific. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):814–826. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher T. N., Heemels M. T., Neefjes J. J., Kast W. M., Melief C. J., Ploegh H. L. Direct binding of peptide to empty MHC class I molecules on intact cells and in vitro. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):563–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90020-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Omata Y., Schneweis K. E. Protection of mice from fatal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection by adoptive transfer of cloned virus-specific and H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):443–447. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Hidaka Y., Kanda T., Shibuta H., Nomoto A., Iwasaki K. Sequence of 3,687 nucleotides from the 3' end of Sendai virus genome RNA and the predicted amino acid sequences of viral NP, P and C proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7317–7330. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. M., Askonas B. A. Diversity in the biological properties of anti-influenza cytotoxic T cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Sep;13(9):707–711. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. M., Davey J., Howland K., Rothbard J. B., Askonas B. A. Class I MHC molecules rather than other mouse genes dictate influenza epitope recognition by cytotoxic T cells. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(4-5):267–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00346521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Zee R., Van Eden W., Meloen R. H., Noordzij A., Van Embden J. D. Efficient mapping and characterization of a T cell epitope by the simultaneous synthesis of multiple peptides. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal S., Mottet G., Kolakofsky D., Roux L. Addition of high-mannose sugars must precede disulfide bond formation for proper folding of Sendai virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):892–900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.892-900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal L. P., Kast W. M., Melvold R. W., Melief C. J. Regulation of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte response against Sendai virus analyzed with H-2 mutants. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1090–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


