Abstract
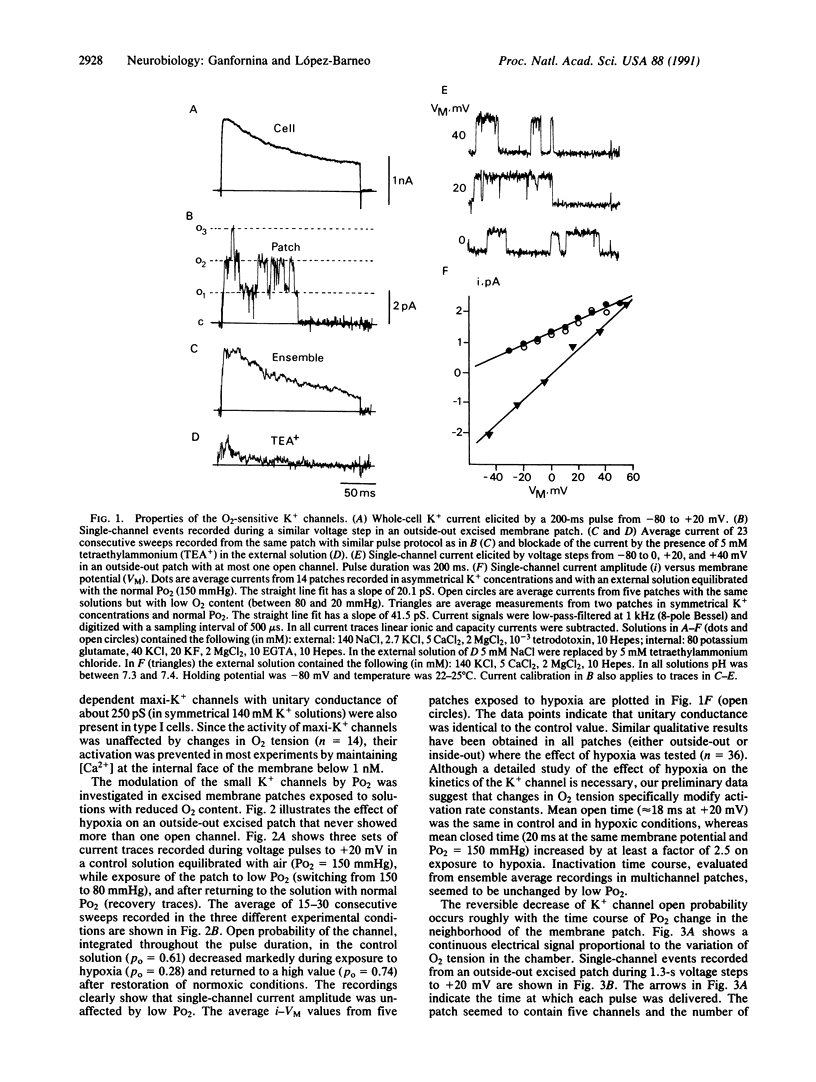
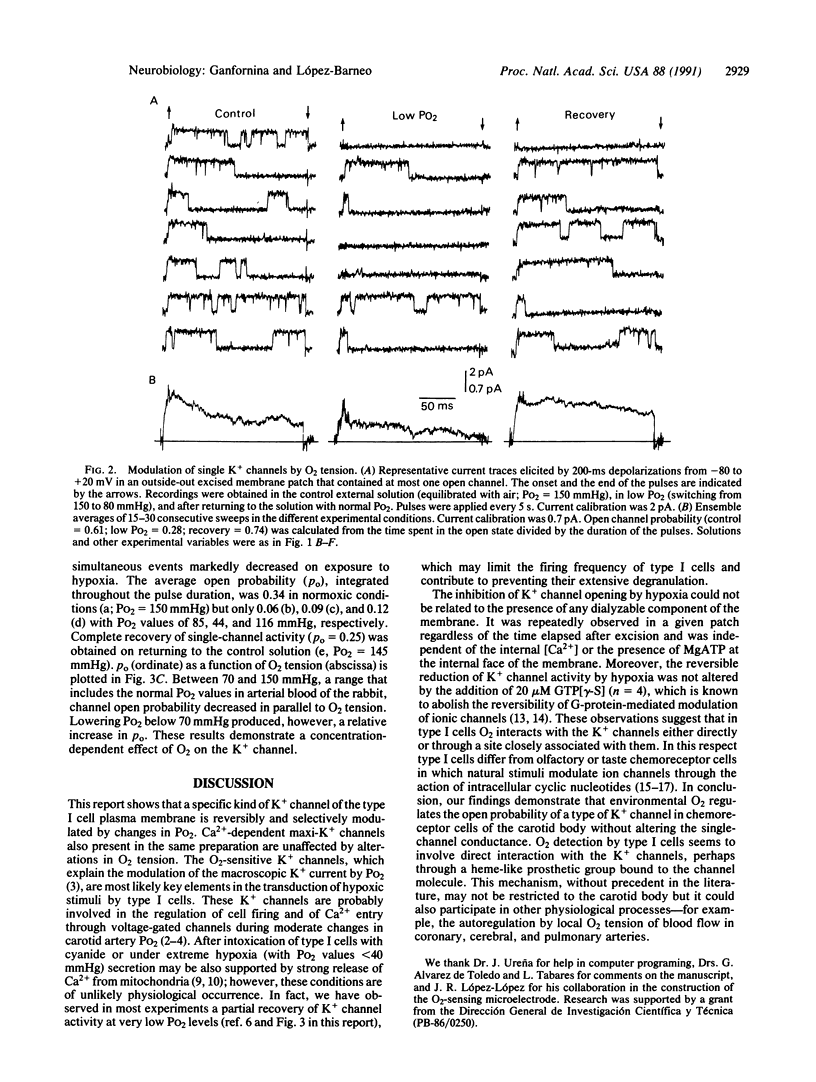
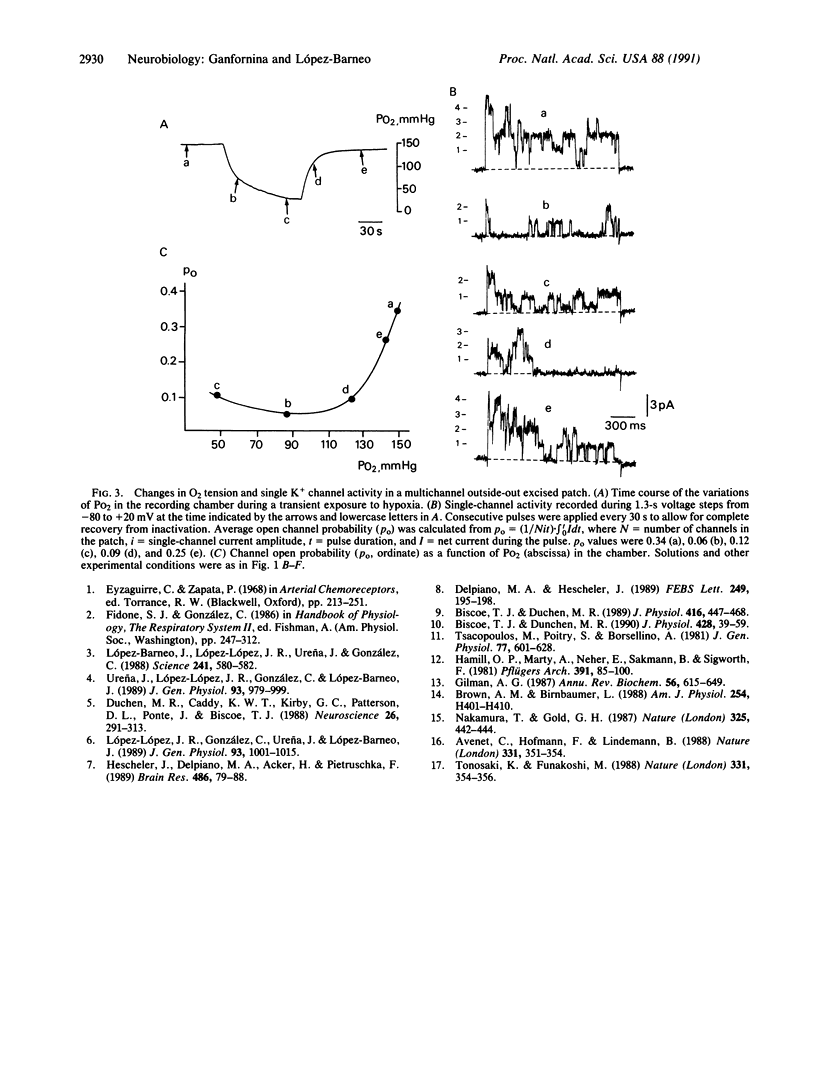
Type I cells of the carotid body are known to participate in the detection of O2 tension in arterial blood but the primary chemotransduction mechanisms are not well understood. Here we report the existence in excised membrane patches of type I cells of a single K+ channel type modulated by changes in PO2. Open probability of the O2-sensitive K+ channel reversibly decreased by at least 50% on exposure to hypoxia but single-channel conductance (approximately 20 pS) was unaltered. In the range between 70 and 150 mmHg (1 mmHg = 133 Pa) the decrease of single-channel open probability was proportional to the PO2 measured in the vicinity of the membrane patch. The inhibition of K+ channel activity by low PO2 was independent of the presence of non-hydrolyzable guanine triphosphate analogues at the internal face of the membrane. The results indicate that the O2 sensor of type I cells is in the plasma membrane and suggest that environmental O2 interacts directly with the K+ channels.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avenet P., Hofmann F., Lindemann B. Transduction in taste receptor cells requires cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):351–354. doi: 10.1038/331351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Duchen M. R. Electrophysiological responses of dissociated type I cells of the rabbit carotid body to cyanide. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:447–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Duchen M. R. Responses of type I cells dissociated from the rabbit carotid body to hypoxia. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:39–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct G protein gating of ion channels. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):H401–H410. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.3.H401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpiano M. A., Hescheler J. Evidence for a PO2-sensitive K+ channel in the type-I cell of the rabbit carotid body. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen M. R., Caddy K. W., Kirby G. C., Patterson D. L., Ponte J., Biscoe T. J. Biophysical studies of the cellular elements of the rabbit carotid body. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):291–311. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Delpiano M. A., Acker H., Pietruschka F. Ionic currents on type-I cells of the rabbit carotid body measured by voltage-clamp experiments and the effect of hypoxia. Brain Res. 1989 May 1;486(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Barneo J., López-López J. R., Ureña J., González C. Chemotransduction in the carotid body: K+ current modulated by PO2 in type I chemoreceptor cells. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):580–582. doi: 10.1126/science.2456613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-López J., González C., Ureña J., López-Barneo J. Low pO2 selectively inhibits K channel activity in chemoreceptor cells of the mammalian carotid body. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):1001–1015. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Gold G. H. A cyclic nucleotide-gated conductance in olfactory receptor cilia. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):442–444. doi: 10.1038/325442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonosaki K., Funakoshi M. Cyclic nucleotides may mediate taste transduction. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):354–356. doi: 10.1038/331354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsacopoulos M., Poitry S., Borsellino A. Diffusion and consumption of oxygen in the superfused retina of the drone (Apis mellifera) in darkness. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jun;77(6):601–628. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.6.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ureña J., López-López J., González C., López-Barneo J. Ionic currents in dispersed chemoreceptor cells of the mammalian carotid body. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):979–999. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


