Abstract
von Willebrand factor (vWF) supports platelet adhesion on thrombogenic surfaces by binding to platelet membrane glycoprotein (GP) Ib in the GP Ib-IX receptor complex. This interaction is physiologically regulated so that it does not occur between circulating vWF and platelets but, rather, only at a site of vascular injury. The abnormal vWF found in type IIB von Willebrand disease, however, has a characteristically increased affinity for GP Ib and binds to circulating platelets. We have analyzed the molecular basis of this abnormality by sequence analysis of a type IIB vWF cDNA and have identified a single amino acid change, Trp550 to Cys550, located in the GP Ib-binding domain of the molecule comprising residues 449-728. Bacterial expression of recombinant fragments corresponding to this vWF domain yielded molecules that, whether containing a normal Trp550 or a mutant Cys550 residue, bound directly to GP Ib in the absence of modulators and with similar affinity. In contrast, mammalian cell expression of the same segment of sequence yielded molecules that, when containing the normal Trp550, did not bind to GP Ib directly but, like native vWF, bound in the presence of ristocetin. However, molecules containing the point mutation (Cys550) behaved like type IIB vWF--namely, bound to GP Ib even without ristocetin modulation and, in the presence of ristocetin, had 10-fold higher affinity than molecules with normal sequence. These results identify a region of vWF that, although not thought to be directly involved in binding to GP Ib, may modulate the interaction through conformational changes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. K., Gorman J. J., Booth W. J., Corino G. L., Castaldi P. A., Berndt M. C. Cross-linking of a monomeric 39/34-kDa dispase fragment of von Willebrand factor (Leu-480/Val-481-Gly-718) to the N-terminal region of the alpha-chain of membrane glycoprotein Ib on intact platelets with bis(sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8326–8336. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger D. A., Nichols T. C., Read M. S., Reddick R. L., Lamb M. A., Brinkhous K. M., Evatt B. L., Griggs T. R. Prevention of occlusive coronary artery thrombosis by a murine monoclonal antibody to porcine von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8100–8104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Girolami A., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Interaction of purified type IIB von Willebrand factor with the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib induces fibrinogen binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex and initiates aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7424–7428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Mazzucato M., De Roia D., Casonato A., Federici A. B., Girolami A., Ruggeri Z. M. Distinct abnormalities in the interaction of purified types IIA and IIB von Willebrand factor with the two platelet binding sites, glycoprotein complexes Ib-IX and IIb-IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):785–792. doi: 10.1172/JCI114775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Mazzuccato M., Grazia Del Ben M., Budde U., Federici A. B., Girolami A., Ruggeri Z. M. Type IIB von Willebrand factor with normal sialic acid content induces platelet aggregation in the absence of ristocetin. Role of platelet activation, fibrinogen, and two distinct membrane receptors. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):475–482. doi: 10.1172/JCI113095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federici A. B., Bader R., Pagani S., Colibretti M. L., De Marco L., Mannucci P. M. Binding of von Willebrand factor to glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa complex: affinity is related to multimeric size. Br J Haematol. 1989 Sep;73(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Kostel P., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. A heparin-binding domain of human von Willebrand factor. Characterization and localization to a tryptic fragment extending from amino acid residue Val-449 to Lys-728. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1734–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Russell S. R., Roberts J. R., Elder J. H., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor. A reduced and alkylated 52/48-kDa fragment beginning at amino acid residue 449 contains the domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa M., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Ruggeri Z. M. The von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Characterization by monoclonal antibodies and partial amino acid sequence analysis of proteolytic fragments. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12579–12585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Nilsson I. M., Borge L., Gunnarsson M., Sjörin E. Platelet aggregation induced by 1-desamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin (DDAVP) in Type IIB von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 6;309(14):816–821. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310063091402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Firkin B. G. Ristocetin--a new tool in the investigation of platelet aggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Oct 31;26(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrle P. A., Niessner H., Dent J., Panzer S., Brenner B., Zimmerman T. S., Lechner K. IIB von Willebrand's disease: pathogenetic and therapeutic studies. Br J Haematol. 1988 May;69(1):55–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb07602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Worrall N. K., Shelton-Inloes B. B., Sorace J. M., Alevy Y. G., Sadler J. E. Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19514–19527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Fujimura Y., Shima M., Yoshioka A., Houghten R. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Structure of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17901–17904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
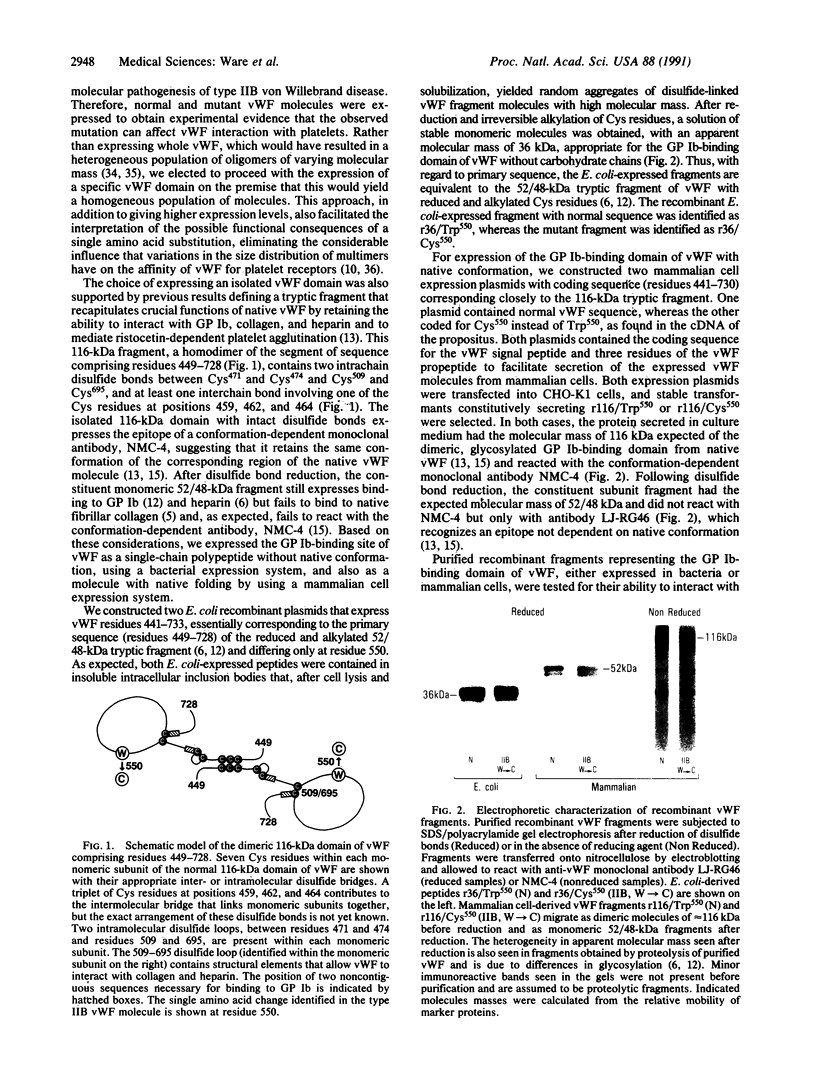
- Mohri H., Yoshioka A., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib, heparin, and collagen and characterization of its three distinct functional sites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17361–17367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. J., Gorski J., White G. C., 2nd, Gidwitz S., Cretney C. J., Aster R. H. Enzymatic amplification of platelet-specific messenger RNA using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):739–743. doi: 10.1172/JCI113656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pareti F. I., Niiya K., McPherson J. M., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and characterization of two domains of human von Willebrand factor that interact with fibrillar collagen types I and III. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13835–13841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Titani K., Hoyer L. W., Hickey M. J. Localization of binding sites within human von Willebrand factor for monomeric type III collagen. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8357–8361. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Mannucci P. M., Ciavarella N., Zimmerman T. S. Heightened interaction between platelets and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in a new subtype of von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1047–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Variant von Willebrand's disease: characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1318–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI109795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
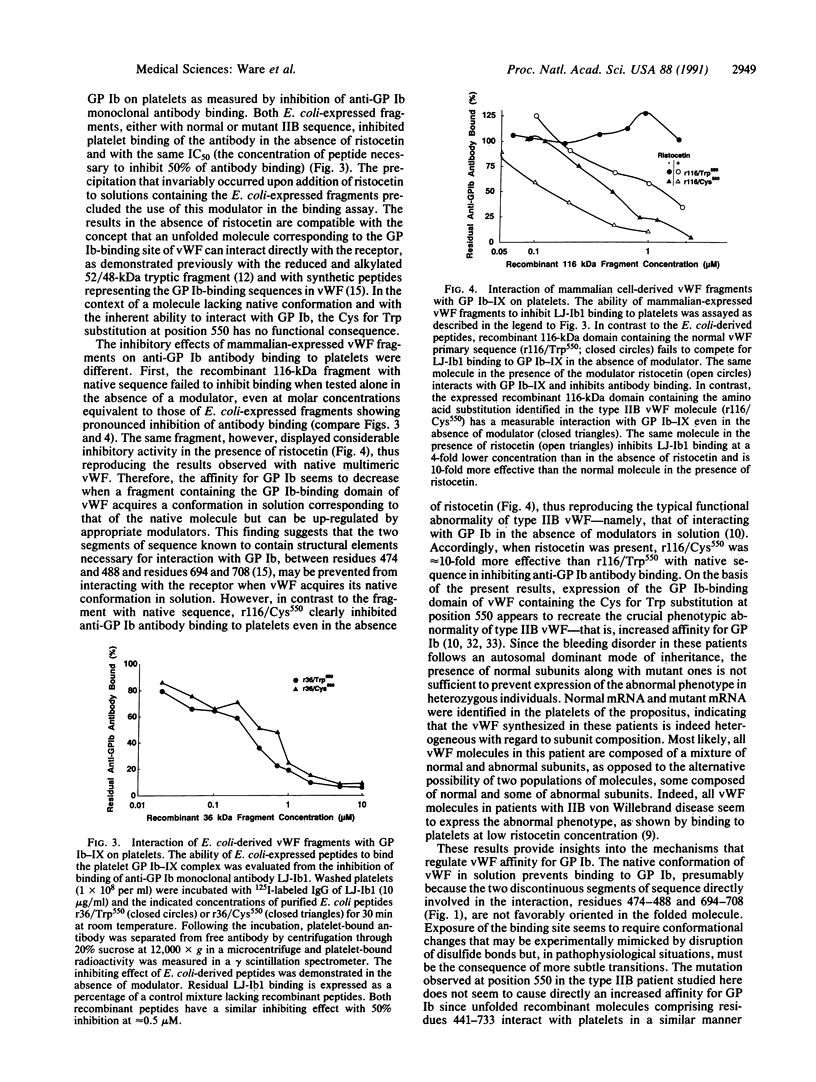
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):895–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij C. L., Hart M., Pannekoek H. Expression of variant von Willebrand factor (vWF) cDNA in heterologous cells: requirement of the pro-polypeptide in vWF multimer formation. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2885–2890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente V., Kostel P. J., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and functional characterization of the von Willebrand factor-binding domain located between residues His1-Arg293 of the alpha-chain of glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18473–18479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Tschopp T. B., Baumgartner H. R., Sussman I. I., Johnson M. M., Egan J. J. Decreased adhesion of giant (Bernard-Soulier) platelets to subendothelium. Further implications on the role of the von Willebrand factor in hemostasis. Am J Med. 1974 Dec;57(6):920–925. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Pittman D. D., Handin R. I., Kaufman R. J., Orkin S. H. The propeptide of von Willebrand factor independently mediates the assembly of von Willebrand multimers. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]