Abstract
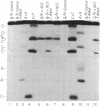
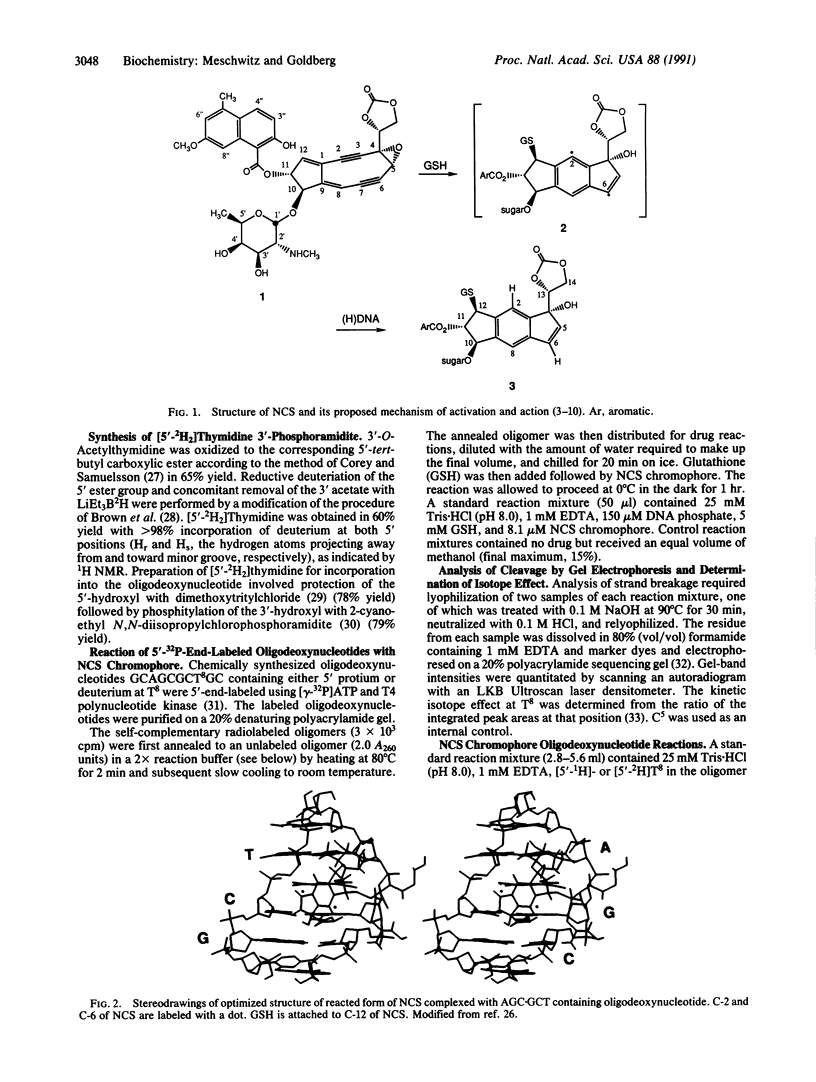
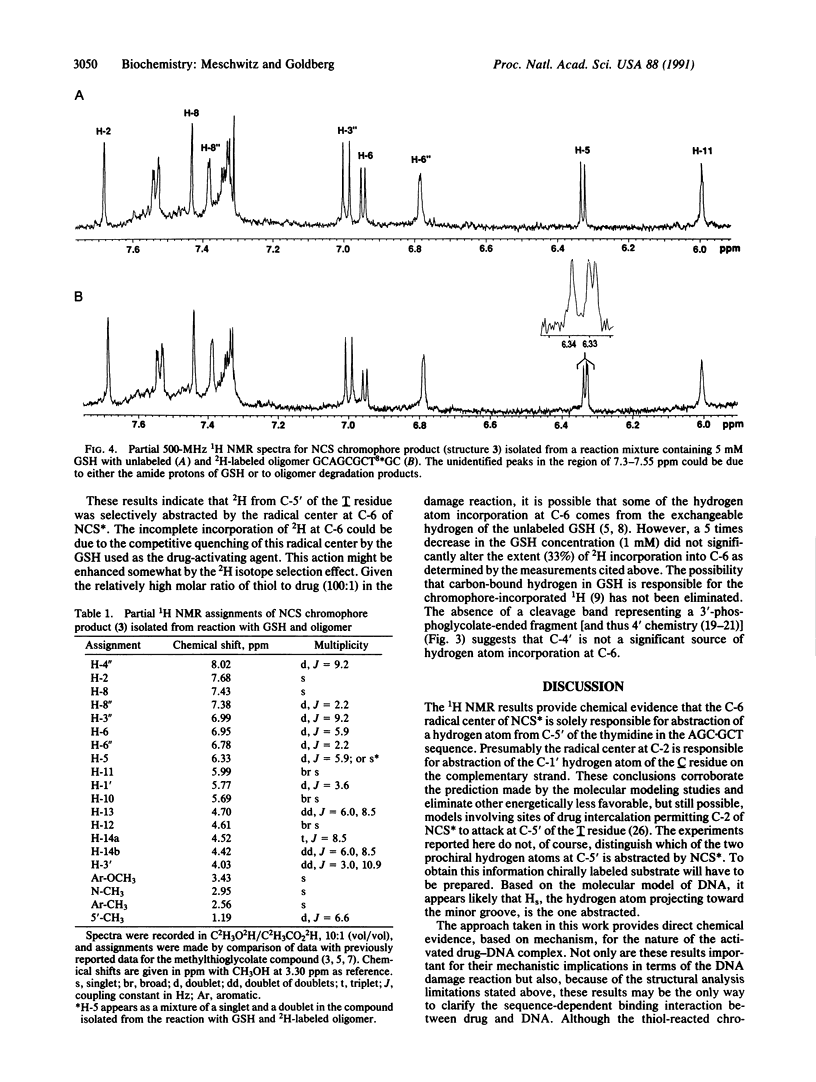
Use has been made of the mechanism of DNA deoxyribose damage by the ene-diyne-containing chromophore of the antitumor antibiotic neocarzinostatin to provide chemical evidence for the structure of the activated drug-DNA complex. Radical centers at C-2 and C-6 of the diradical form of the glutathione-activated chromophore abstract hydrogen atoms from C-1' of the C residue and C-5' of the T residue in AGC.GCT to generate a bistranded lesion consisting of an abasic site at C and a strand break at T. This laboratory has proposed a molecular model for the drug-DNA interaction in which the naphthoate moiety of the chromophore intercalates between A.T and G.C, placing the diradical core in the minor groove, so that the radical centers at C-6 and C-2 are close to C-5' of T and C-1' of C, respectively. To determine which radical center abstracts one of the hydrogen atoms from C-5', the self-complementary oligodeoxynucleotide GCAGCGCTGC was synthesized with 2H at both 5' positions of the T residue and treated with glutathione-activated chromophore. Sequencing-gel electrophoresis showed that drug attack was limited to the T and C residues and that abstraction of 2H from C-5' exhibited a small isotope selection effect of 1.25. 1H NMR spectroscopic examination of the reacted chromophore, isolated by HPLC, indicated that 2H was selectively abstracted by C-6, providing experimental corroboration of the model and further elucidating the chemical mechanism. Since direct strand breakage at the T residue exceeds (44% more) abasic site formation at the C residue, other models of drug-DNA interaction leading to only single-strand breaks are also considered.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin D. H., Zeng C. H., Costello C. E., Goldberg I. H. Sites in the diyne-ene bicyclic core of neocarzinostatin chromophore responsible for hydrogen abstraction from DNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8106–8114. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta D., Goldberg I. H. Mode of reversible binding of neocarzinostatin chromophore to DNA: evidence for binding via the minor groove. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6913–6920. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedon P. C., Goldberg I. H. Sequence-specific double-strand breakage of DNA by neocarzinostatin involves different chemical mechanisms within a staggered cleavage site. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14713–14716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galat A., Goldberg I. H. Molecular models of neocarzinostatin damage of DNA: analysis of sequence dependence in 5'GAGCG:5'CGCTC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2093–2099. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. H. Free radical mechanisms in neocarzinostatin-induced DNA damage. Free Radic Biol Med. 1987;3(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(87)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensens O. D., Dewey R. S., Liesch J. M., Napier M. A., Reamer R. A., Smith J. L., Albers-Schönberg G., Goldberg I. H. Neocarzinostatin chromophore: presence of a highly strained ether ring and its reaction with mercaptan and sodium borohydride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 15;113(2):538–547. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensens O. D., Goldberg I. H. Mechanism of activation of the antitumor antibiotic neocarzinostatin by mercaptan and sodium borohydride. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 May;42(5):761–768. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen L. S., Chen C. Q., Goldberg I. H. Atypical abasic sites generated by neocarzinostatin at sequence-specific cytidylate residues in oligodeoxynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4331–4340. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen L. S., Goldberg I. H. Activation of neocarzinostatin chromophore and formation of nascent DNA damage do not require molecular oxygen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1637–1648. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen L. S., Goldberg I. H. Deoxyribonucleic acid damage by neocarzinostatin chromophore: strand breaks generated by selective oxidation of C-5' of deoxyribose. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):4872–4878. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen L. S., Goldberg I. H., Frank B. L., Worth L., Jr, Christner D. F., Kozarich J. W., Stubbe J. Neocarzinostatin-induced hydrogen atom abstraction from C-4' and C-5' of the T residue at a d(GT) step in oligonucleotides: shuttling between deoxyribose attack sites based on isotope selection effects. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2034–2042. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen L. S., Goldberg I. H. Identification of 2-deoxyribonolactone at the site of neocarzinostatin-induced cytosine release in the sequence d(AGC). Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1027–1032. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napier M. A., Goldberg I. H. Neocarzinostatin chromophore. Assignment of spectral properties and structural requirements for binding to DNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;23(2):500–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napier M. A., Holmquist B., Strydom D. J., Goldberg I. H. Neocarzinostatin: spectral characterization and separation of a non-protein chromophore. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 27;89(2):635–642. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90677-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Dattagupta N., Warf B. C., Goldberg I. H. Neocarzinostatin chromophore binds to deoxyribonucleic acid by intercalation. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4007–4014. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Goldberg I. H. Base substitution mutations induced in the cI gene of lambda phage by neocarzinostatin chromophore: correlation with depyrimidination hotspots at the sequence AGC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1417–1426. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Goldberg I. H. Binding of the nonprotein chromophore of neocarzinostatin to deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4773–4780. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Goldberg I. H. Endonuclease-resistant apyrimidinic sites formed by neocarzinostatin at cytosine residues in DNA: evidence for a possible role in mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3182–3186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Houlgrave C. W., Han Y. H. Neocarzinostatin-induced DNA base release accompanied by staggered oxidative cleavage of the complementary strand. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19263–19266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Kappen L. S., Grollman A. P., Eisenberg M., Goldberg I. H. Strand scission of deoxyribonucleic acid by neocarzinostatin, auromomycin, and bleomycin: studies on base release and nucleotide sequence specificity. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7599–7606. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wemmer D. E., Chou S. H., Hare D. R., Reid B. R. Duplex-hairpin transitions in DNA: NMR studies on CGCGTATACGCG. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3755–3772. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]