Abstract
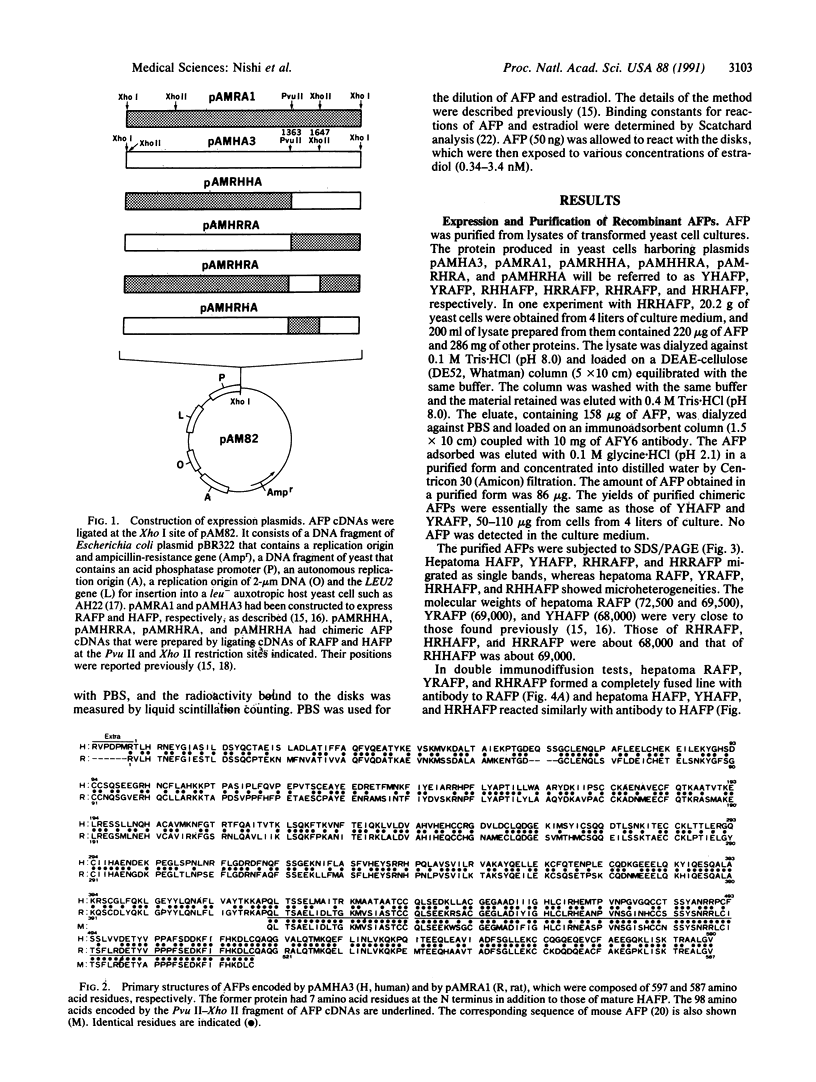
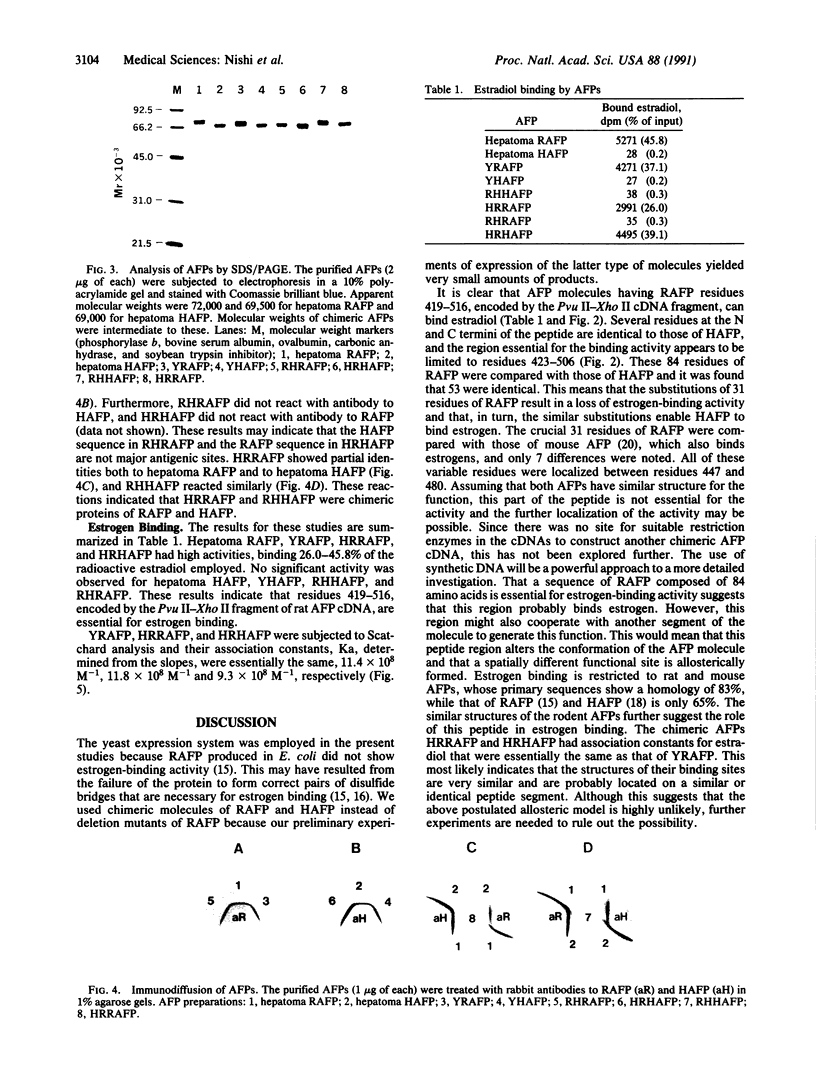
Rat alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) has been demonstrated to bind estrogen, whereas human AFP lacks the activity. We constructed four chimeric molecules from cDNAs encoding these AFPs with the use of two restriction sites common to them and expressed them as well as rat and human AFP cDNA in yeast. The recombinant molecules were purified, characterized, and found to have the predicted structures. Analyses of estrogen binding indicated that a rat AFP sequence composed of residues 423-506 that contains 31 rat-specific amino acids is essential for the activity.
Full text
PDF
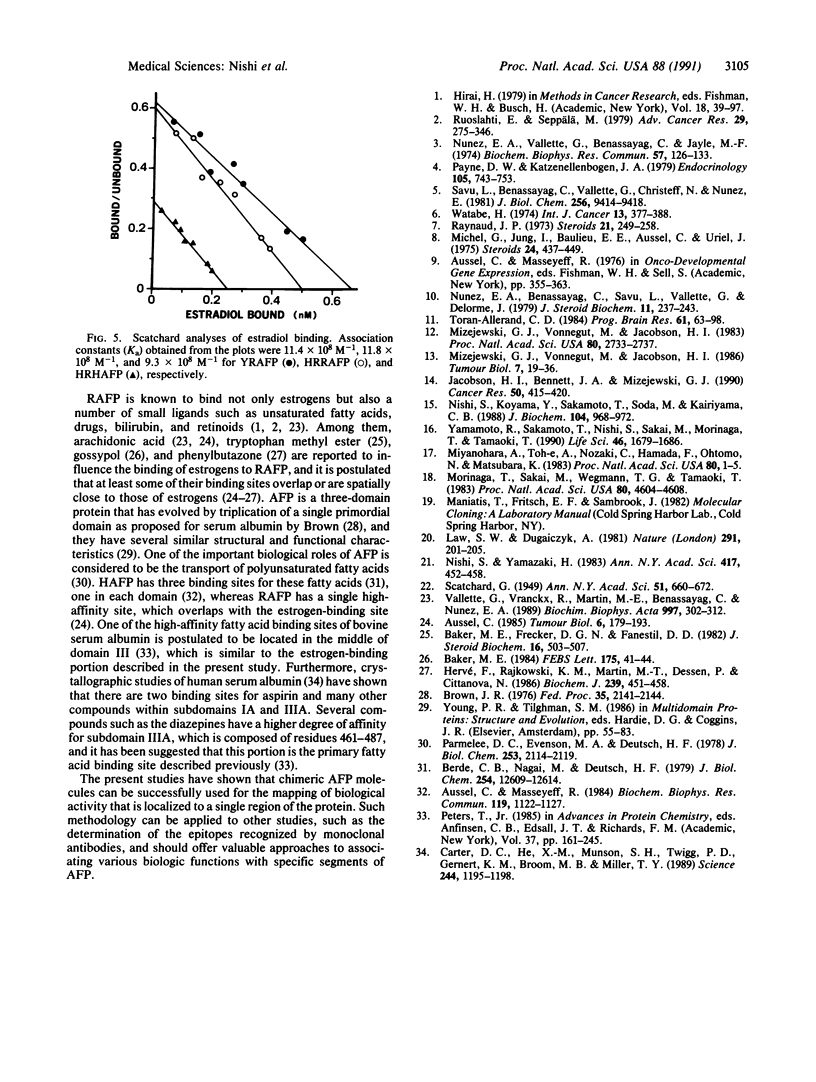
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aussel C., Masseyeff R. Interaction of retinoids and bilirubin with the binding of arachidonic acid to human alpha-fetoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 30;119(3):1122–1127. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90891-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aussel C. Presence of three different binding sites for retinoids, bilirubin and estrogen or arachidonic acid on rat alpha-fetoprotein. Tumour Biol. 1985;6(2):179–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. E., Frecker D. G., Fanestil D. D. Inhibition of estrogen binding to rat alpha-fetoprotein by tryptophan p-nitrophenyl esters. J Steroid Biochem. 1982 Apr;16(4):503–507. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(82)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. E. Gossypol inhibits estrogen binding to rat alpha-fetoprotein. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80565-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berde C. B., Nagai M., Deutsch H. F. Human alpha-fetoprotein. Fluorescence studies on binding and proximity relationships for fatty acids and bilirubin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12609–12614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R. Structural origins of mammalian albumin. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2141–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. C., He X. M., Munson S. H., Twigg P. D., Gernert K. M., Broom M. B., Miller T. Y. Three-dimensional structure of human serum albumin. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1195–1198. doi: 10.1126/science.2727704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervé F., Rajkowski K. M., Martin M. T., Dessen P., Cittanova N. Drug-binding properties of rat alpha-foetoprotein. Specificities of the phenylbutazone-binding and warfarin-binding sites. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):451–458. doi: 10.1042/bj2390451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. I., Bennett J. A., Mizejewski G. J. Inhibition of estrogen-dependent breast cancer growth by a reaction product of alpha-fetoprotein and estradiol. Cancer Res. 1990 Jan 15;50(2):415–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Dugaiczyk A. Homology between the primary structure of alpha-fetoprotein, deduced from a complete cDNA sequence, and serum albumin. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):201–205. doi: 10.1038/291201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel G., Jung I., Baulieu E. E., Aussel C., Uriel J. Two high affinity estrogen binding proteins of different specificity in the immature rat uterus cytosol. Steroids. 1974 Oct;24(4):437–449. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(74)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizejewski G. J., Vonnegut M., Jacobson H. I. Estradiol-activated alpha-fetoprotein suppresses the uterotropic response to estrogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2733–2737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizejewski G. J., Vonnegut M., Jacobson H. I. Studies of the intrinsic antiuterotropic activity of murine alpha-fetoprotein. Tumour Biol. 1986;7(1):19–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinaga T., Sakai M., Wegmann T. G., Tamaoki T. Primary structures of human alpha-fetoprotein and its mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4604–4608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., Koyama Y., Sakamoto T., Soda M., Kairiyama C. B. Expression of rat alpha-fetoprotein cDNA in Escherichia coli and in yeast. J Biochem. 1988 Dec;104(6):968–972. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., Yamazaki H. Monoclonal antibodies against AFP: application in immunoassay and affinity chromatography. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;417:452–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb32887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez E. A., Benassayag C., Savu L., Vallette G., Delorme J. Oestrogen binding function of alpha 1-fetoprotein. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Jul;11(1A):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez E., Vallette G., Benassayag C., Jayle M. F. Comparative study on the binding of estrogens by human and rat serum proteins in development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):126–133. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80366-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmelee D. C., Evenson M. A., Deutsch H. F. The presence of fatty acids in human alpha-fetoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2114–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. W., Katzenellenbogen J. A. Binding specificity of rat alpha-fetoprotein for a series of estrogen derivatives: studies using equilibrium and nonequilibrium binding techniques. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):745–753. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynaud J. P. Influence of rat estradiol binding plasma protein (EBP) on uterotrophic activity. Steroids. 1973 Feb;21(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(73)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Seppälä M. alpha-Fetoprotein in cancer and fetal development. Adv Cancer Res. 1979;29:275–346. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60849-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Benassayag C., Vallette G., Christeff N., Nunez E. Mouse alpha 1-fetoprotein and albumin. A comparison of their binding properties with estrogen and fatty acid ligands. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9414–9418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toran-Allerand C. D. On the genesis of sexual differentiation of the general nervous system: morphogenetic consequences of steroidal exposure and possible role of alpha-fetoprotein. Prog Brain Res. 1984;61:63–98. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64429-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallette G., Vranckx R., Martin M. E., Benassayag C., Nunez E. A. Conformational changes in rodent and human alpha-fetoprotein: influence of fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 31;997(3):302–312. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe H. Purification and chemical characterization of alpha-fetoprotein from rat and mouse. Int J Cancer. 1974 Mar 15;13(3):377–388. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto R., Sakamoto T., Nishi S., Sakai M., Morinaga T., Tamaoki T. Expression of human alpha-fetoprotein in yeast. Life Sci. 1990;46(23):1679–1686. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90383-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]