Abstract
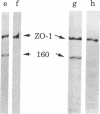
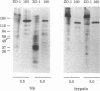
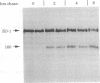
ZO-1 is a 210- to 220-kDa peripheral membrane protein associated with the cytoplasmic surface of the epithelial tight junction. Because ZO-1 may interact with other unidentified tight junction proteins, we have looked for other polypeptides that bind to ZO-1. A 160-kDa polypeptide was identified that coimmunoprecipitates with ZO-1 from detergent extracts of metabolically labeled Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells. This polypeptide appears to be distinct from ZO-1, rather than a degradation product, by several criteria. It lacks ZO-1 epitopes recognized by both monoclonal antibodies and a polyclonal serum to ZO-1, since it is not detectable in immunoblots of either whole cell extracts or ZO-1 immunoprecipitates. Also, it exhibits a peptide map different from that of ZO-1 on one-dimensional "Cleveland gels." Moreover, because the kinetics of appearance of newly synthesized 160-kDa polypeptide in anti-ZO-1 immunoprecipitates is much slower than that of ZO-1, its presence in immunoprecipitates cannot be simply explained by degradation of ZO-1 during cell lysis. Like ZO-1, the 160-kDa polypeptide seems to be a cytoplasmic peripheral membrane protein. It cannot be labeled by two different cell surface labeling reagents. It can be extracted from the membrane by high salt concentration in the absence of detergents. As expected for a protein complex, the 160-kDa polypeptide and ZO-1 turn over with similar kinetics. We propose that the 160-kDa polypeptide is a component of the tight junction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Stevenson B. R., Jesaitis L. A., Goodenough D. A., Mooseker M. S. Characterization of ZO-1, a protein component of the tight junction from mouse liver and Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1141–1149. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. M., Van Itallie C. M., Peterson M. D., Stevenson B. R., Carew E. A., Mooseker M. S. ZO-1 mRNA and protein expression during tight junction assembly in Caco-2 cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1047–1056. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. S., Gumbiner B. Expression of cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin in Xenopus embryos begins at gastrulation and predominates in the ectoderm. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2449–2458. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citi S., Sabanay H., Jakes R., Geiger B., Kendrick-Jones J. Cingulin, a new peripheral component of tight junctions. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):272–276. doi: 10.1038/333272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Goodenough D. A. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from "tight" and "leaky" epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):390–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings R. D., Kornfeld S. Fractionation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides by serial lectin-Agarose affinity chromatography. A rapid, sensitive, and specific technique. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11235–11240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Twenty-first Bowditch lecture. The epithelial junction: bridge, gate, and fence. Physiologist. 1977 Feb;20(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:375–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Mariscal L., Chávez de Ramirez B., Lázaro A., Cereijido M. Establishment of tight junctions between cells from different animal species and different sealing capacities. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jan;107(1):43–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01871082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B., Simons K. A functional assay for proteins involved in establishing an epithelial occluding barrier: identification of a uvomorulin-like polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):457–468. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. Structure, biochemistry, and assembly of epithelial tight junctions. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C749–C758. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachar B., Reese T. S. Evidence for the lipidic nature of tight junction strands. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):464–466. doi: 10.1038/296464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L. Tight junction dynamics: is paracellular transport regulated? Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):497–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90562-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Sorting of an apical plasma membrane glycoprotein occurs before it reaches the cell surface in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2131–2139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargiacomo M., Lisanti M., Graeve L., Le Bivic A., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Integral and peripheral protein composition of the apical and basolateral membrane domains in MDCK cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Mar;107(3):277–286. doi: 10.1007/BF01871942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Anderson J. M., Bullivant S. The epithelial tight junction: structure, function and preliminary biochemical characterization. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Oct;83(2):129–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00226141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Anderson J. M., Goodenough D. A., Mooseker M. S. Tight junction structure and ZO-1 content are identical in two strains of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells which differ in transepithelial resistance. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2401–2408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Heintzelman M. B., Anderson J. M., Citi S., Mooseker M. S. ZO-1 and cingulin: tight junction proteins with distinct identities and localizations. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):C621–C628. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.4.C621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Paul D. L. The molecular constituents of intercellular junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;1(5):884–891. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Siliciano J. D., Mooseker M. S., Goodenough D. A. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):755–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Hieda Y., Tsukita S. A new 82-kD barbed end-capping protein (radixin) localized in the cell-to-cell adherens junction: purification and characterization. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2369–2382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Itoh M., Tsukita S. A new 400-kD protein from isolated adherens junctions: its localization at the undercoat of adherens junctions and at microfilament bundles such as stress fibers and circumferential bundles. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2905–2915. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Gumbiner B., Simons K. The tight junction does not allow lipid molecules to diffuse from one epithelial cell to the next. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):639–641. doi: 10.1038/322639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Simons K. The function of tight junctions in maintaining differences in lipid composition between the apical and the basolateral cell surface domains of MDCK cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1455–1464. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04382.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]