Abstract
Diseases that favor colonization of the respiratory tract with Pseudomonas aeruginosa are characterized by an altered airway microbiome. Virulence of P. aeruginosa respiratory tract infection is likely influenced by interactions with other lung microbiota or their products. The bacterial fermentation product 2,3-butanediol enhances virulence and biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa in vitro. This study assessed the effects of 2,3-butanediol on P. aeruginosa persistence, inflammatory response, and the lung microbiome in vivo. Here, P. aeruginosa grown in the presence of 2,3-butanediol and encapsulated in agar beads persisted longer in the murine respiratory tract, induced enhanced TNF-α and IL-6 responses and resulted in increased colonization in the lung tissue by environmental microbes. These results led to the following hypothesis that now needs to be tested with a larger study: fermentation products from the lung microbiota not only have a role in P. aeruginosa virulence and abundance, but also on the increased colonization of the respiratory tract with environmental microbes, resulting in dynamic shifts in microbiota diversity and disease susceptibility.
Airway microbiome dynamics and microbe-to-microbe interactions are increasingly recognized as critical factors in lung diseases (Cui et al., 2014). Particularly for chronic lung diseases with frequent bacterial infections, such as cystic fibrosis (CF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, airway microbiome dynamics have been associated with disease progression (Hunter et al., 2012, Pragman et al., 2012; Huang et al., 2014). CF predisposes the respiratory tract to polymicrobial infections, and the frequent emergence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with a reduction in bacterial richness (Lynch and Bruce, 2013; Chmiel et al., 2014). Phenotype and virulence of P. aeruginosa are affected by interactions with the host and cohabiting microbes (Sibley et al., 2008a; Hunter et al., 2012; Venkataraman et al., 2014; Whiteson et al., 2014). An improved characterization of the human lung microbiome will be instrumental to delineate these interactions (Dickson and Huffnagle, 2015; Venkataraman et al., 2015).
It has been previously demonstrated in vitro that the fermentation product 2,3-butanediol, which can be produced by fermenting bacteria, mediates cross-feeding to P. aeruginosa and increases biofilm formation and other critical factors of P. aeruginosa virulence (Venkataraman et al., 2014). The relevance of this finding was further emphasized by the identification of 2,3-butanedione, which is a volatile compound produced in the same acetoin fermentation pathway as 2,3-butanediol, in the breaths of individuals with CF (Whiteson et al., 2014). 2,3-Butanedione is primarily produced by Streptococcus spp. and other fermenters that can potentially cross-feed and enhance P. aeruginosa pathogenicity. Here, we evaluate whether 2,3-butanediol increases P. aeruginosa virulence within the respiratory tract in vivo and assess its effect on the airway microbiota in an agar bead P. aeruginosa murine model (Kukavica-Ibrulj and Levesque, 2008). Although the agar bead model of P. aeruginosa infection is often used to mimic more chronic infections, as a preliminary study, we investigated the initial acute stage of infection.
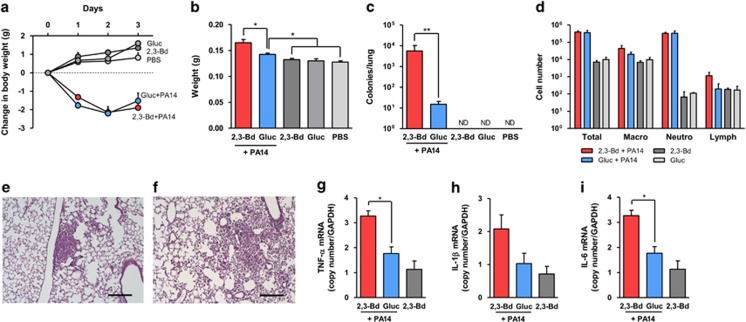
P. aeruginosa strain PA14 was cultured and encapsulated in agar beads in AB minimal media containing 30 mm of 2,3-butanediol or glucose and then administered to C57Bl/6 mice via the intratracheal route. Controls included empty media agar beads prepared under both conditions. Mice infected with PA14 lost body weight, irrespective of P. aeruginosa was grown with 2,3-butanediol or glucose (Figure 1a). Lung weight was increased in both groups that received PA14, indicating considerable inflammation, and was higher with 2,3-butanediol-grown P. aeruginosa compared with glucose-grown P. aeruginosa (Figure 1b). Clearance of P. aeruginosa was delayed in mice infected with PA14 grown in 2,3-butanediol compared with PA14 grown in glucose, as indicated by P. aeruginosa quantification after 3 days (Figure 1c). The cellular composition of bronchioalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) showed an increase in neutrophils in mice infected with PA14 grown in 2,3-butanediol and PA14 grown in glucose compared with mice that received beads with only 2,3-butanediol or glucose (Figure 1d). Lung histology showed similar levels of local inflammation in mice infected with PA14 grown in 2,3-butanediol (Figure 1e) and PA14 grown in glucose (Figure 1f). There was, however, an increase in inflammatory cytokines expression in mice infected with PA14 grown in 2,3-butanediol at 3 days of infection (Figures 1g–i). These cytokines are involved in the P. aeruginosa lung pathogenesis (Meduri et al., 1999) and lung levels usually peak within the first 24 h following infection with planktonic P. aeruginosa (van Heeckeren et al., 2006), while a sustained response that lasts for a few days is present using the agar beads model (van Heeckeren and Schluchter, 2002). Glucose, which was used in our controls, has been shown to inhibit the type III secretion system in P. aeruginosa, particularly the secretion of exoS (Rietsch and Mekalanos, 2006). However, strain PA14 does not encode for exoS (Miyata et al., 2003) and it is, therefore, unlikely that this mechanism is present here. Furthermore, inhibition of type III secretion system does not affect the replication and survival of P. aeruginosa in the lungs of mice (Vance et al., 2005). This strongly suggests that increased virulence of P. aeruginosa cultured with 2,3-butanediol, which was previously seen in vitro (Venkataraman et al., 2014), translates to increased virulence in the respiratory tract in vivo. Compared with conditions in the CF lung, where it is expected that 2,3-butanediol is continuously supplied by co-localized fermenting bacteria, our bead model is limited by the likely decreasing concentrations of 2,3-butanediol by diffusion out of the beads and consumption by P. aeruginosa. This could be reflected by the small but significant differences in the acute inflammatory cytokine levels after three days (Figures 1g–i) despite larger differences in the bacterial loads (Figure 1c) between the 2,3-butanediol-exposed lungs and their controls.
Figure 1.
2,3-butanediol enhances virulence and persistence of P. aeruginosa in the respiratory tract. C57BL/6 mice were infected with agar-encapsulated PA14 grown in the presence of 2,3-butanediol or glucose and with beads with just these substrates. (a) Body weight following infection. (b) Lung weight. (c) P. aeruginosa counts from lung homogenates plated on MacConkey agar plates. (d) Bronchioalveolar lavage cellular composition. (e–f) HE-stained lung section two days following PA14 grown in 2,3-butanediol (e) and glucose (f); bar=200 μm. (g–i) Inflammatory cytokine expression in lung. Expression of mRNA of TNF-α (g), IL-1β (h), and IL-6 (i) was quantified by TaqMan Real-Time RT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH RNA. Data are shown as means±s.e.m. of five mice per group. ND=none detected. *P<0.05; **P<0.001.
After comparing the basal microbiome from lungs (Supplementary Figure S1A) and BAL (Supplementary Figure S1B), Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Cyanobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria were detected as the most prominent phyla, with similar contributions in lung tissue and BAL for most phyla. Proteobacteria was more abundant in lung tissue samples (37–79% P=0.022), while Firmicutes was more abundant in BAL samples (30–39% P=0.001). In general, the relative distribution of phyla within each sample was found to be similar to the human respiratory microbiomes from oropharyngeal or BAL samples (Hilty et al., 2010; Erb-Downward et al., 2011; Sze et al, 2012). For the rest of the study, we selected lung tissue to include all community members within the respiratory tract.
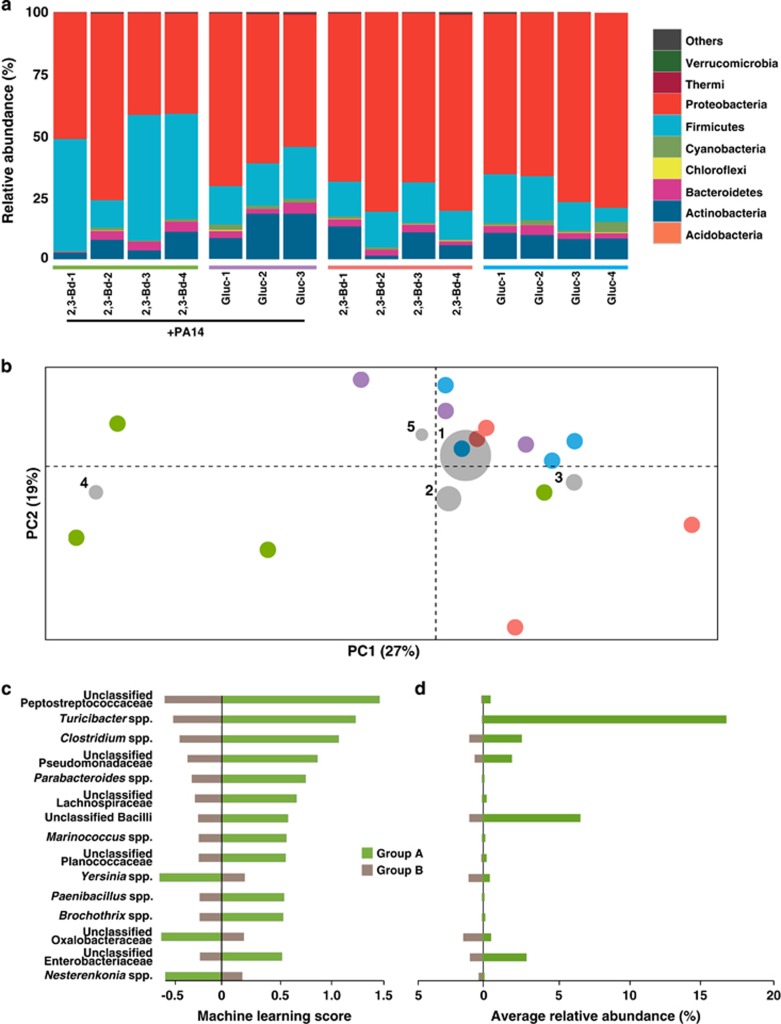
To characterize the murine lung bacterial community, we amplified and sequenced the V4 region of the 16S rRNA genes from murine lungs, and observed a total of 3174 unique operational taxonomic units from 9 24 182 quality sequences (see detailed descriptions of the methods in the Supplementary Materials). Taxonomic distributions at the phyla level were summarized for each murine lung tissue sample (Figure 2a). The phylum Firmicutes was more abundant (P=0.001) in mice that received PA14 in 2,3-butanediol, whereas the relative abundance of Proteobacteria was lower (P=0.015). Correlation analysis of sequence and operational taxonomic unit counts per lung tissue showed adequate representation of microbiota diversity in lung samples irrespective of sample sequence depth (Supplementary Figure S1C). Principal Coordinates Analysis was used to visualize dissimilarities between lung microbiomes. Calculation of weighted UniFrac distances based on taxonomic abundances in each sample showed clustering of lung microbiomes except those treated with PA14 in 2,3-butanediol (Figure 2b), suggesting that lung microbiomes become dissimilar when treated with PA14 in 2,3-butanediol. Analysis with unweighted UniFrac distances showed a similar clustering with less distinction (Supplementary Figure S2). Qualitative visualization of the five most abundant taxa that are driving the dissimilarity between samples indicated that Turicibacter spp. contributed to the dissimilarity found in two of four mice lungs treated with PA14 in 2,3-butanediol (Figure 2b, Supplementary figure S2). Supervised machine-learning analysis was performed to quantitatively identify taxa that explain the dissimilarities found in lungs treated with PA14 in 2,3-butanediol (Figure 2c). Caution is needed for such a machine-learning analysis because it is used to generate hypotheses on small data sets that are then validated on larger data sets. Here, we built hypothesis based on a small data set. Lung bacterial communities were classified as Group A (2,3-butanediol with PA14) or Group B (glucose medium with PA14, 2,3-butanediol medium, and glucose medium) and tested with the nearest shrunken centroid method (Tibshirani et al., 2002). This method had already been utilized for supervised learning with microbiota (Knights et al., 2011; Werner et al., 2012) and calculates a machine-learning (prediction) score for each taxon, with a more negative or more positive score indicating better predictability for the taxon. All 593 taxa were ranked for predicting treatment type. The overall machine-learning error rate was 0.19, which indicates that this trained algorithm has an 81% accuracy to classify a murine lung microbiome to its correct treatment type. Although murine lungs that received PA14 in 2,3-butanediol were not significantly more or less diverse than other lungs in our small data set (Supplementary Figures S1D and E), several taxa were found to be closely associated in these lungs, including unclassified genera from the families Peptostreptococcaceae and Pseudomonadaceae, and the gastrointestinal tract- and feces-associated Turicibacter spp., Clostridium spp. and Parabacteroides spp. (Figures 2c and d). We observed significant increases in the relative taxonomic abundances for the three most predictive taxa from the machine-learning analysis for Group A when compared to Group B (Peptostreptococcaceae P=0.001; Turicibacter spp. P=0.011; Clostridium spp. P=0.019; Supplementary Figure S3A). A possible source of Turicibacter spp. is via coprophagy within the cage, and the same is true for Peptostreptococcaceae and Clostridium spp., which are also found in the lower gastrointestinal tract. From these results, we hypothesize that fermentation product 2,3-butanediol from the lung microbiota not only have a role in P. aeruginosa virulence and abundance, but also on the increased colonization of the respiratory tract with environmental microbes. In addition, inflammation in the lung may also result in an advantageous environment for Turicibacter spp. (Rausch et al., 2015).
Figure 2.
Microbiome of the murine lung. (a) Taxonomic summary of lung microbiota. 16S rRNA gene sequences of lung bacterial community of 15 mice 3 days after infection with varying agar beads treatments, indicated by colored bars above the sample ID: PA14 with 2,3-butanediol (2,3-Bd+PA14, green); PA14 with glucose (Gluc+PA14, purple); 2,3-butanediol medium only (2,3-Bd, red); and glucose medium only (Gluc, blue). Each column represents a sample from one mouse. Bacteria are presented at the phyla level. (b) Principal Coordinates Analysis biplot of murine lung microbiomes. Beta diversity Principal Coordinates Analysis of a weighted UniFrac distance matrix from taxonomic composition within these samples. Only the first two axes are shown. Each circle represents one mouse, which is colored by agar beads treatment: PA14 with 2,3-butanediol (green; n=4); PA14 with glucose (purple; n=3); 2,3-butanediol medium only (red; n=4); and glucose medium only (blue; n=4). Gray circles represent taxa coordinates that are calculated based on mean relative abundance (size of circle) for each taxon in all 15 lung samples (1-Pseudomonas spp.; 2-Acinetobacter spp.; 3-Escherichia spp.; 4-Turicibacter spp.; 5-Staphylococcus spp.). The percentage of distribution described by each axis is as indicated. (c) Machine-learning analysis of murine lung microbiomes. Machine-learning analysis of lung samples binned into two groups based on agar treatment: Group A (2,3-butanediol with PA14; green; n=4) and Group B (glucose medium with PA14, 2,3-butanediol medium, and glucose medium; brown; n=11). Shown are the 15 highest correlated taxa (of the 593 taxa used to train the algorithm); the overall machine-learning error rate was 0.19 via nearest shrunken centroid method. (d). The average relative abundances of the 15 most predictive taxa from machine-learning analysis, and colored as in c.
To further explore the role of Pseudomonas spp. in infection, we compared their relative abundance in the lungs with sample origin and with change in body weight (Supplementary Figure S3D). The colonization of the lungs by environmental microbes (for example, Turicibacter spp.), resulted in a decreased relative abundance of Pseudomonas spp. In other words, a relative increase in environmental operational taxonomic units for sample 2,3-Bd-3 (Supplementary Figure S3A) caused a relative decrease in Pseudomonas spp., but this does not inform the absolute numbers of P. aeruginosa (Supplementary Figure S3B). In fact, the corresponding absolute abundance of P. aeruginosa was still higher in murine lungs treated with PA14 in 2,3-butanediol even with the increased colonization of environmental microbes (Supplementary Figure S3C). Our results are also consistent with the recent studies that have shown the impact of gut microbiome on acquisition of the lung microbiome in CF (Madan, 2016).
Understanding the microbe-to-microbe interactions that stimulate P. aeruginosa virulence and aid in creating a niche for P. aeruginosa to persist in the respiratory tract could help to develop novel anti-P. aeruginosa strategies by impairing the capacity of the lung microbiota to produce fermentation products that we have shown to induce virulence in P. aeruginosa. This has been suggested previously by clinical observations that elimination of Streptococcus milleri, which is a member of the CF lung microbiota associated with severe exacerbations, led to decreased P. aeruginosa virulence (Sibley et al., 2008b). Despite the relatively low microbial densities present in healthy lungs (Dickson and Huffnagle, 2015), alteration of the pulmonary microenvironment to favor a microbial community that is easier to clear may be a promising approach against pulmonary pathogens, which warrant further investigations. A future study with a larger data set to test the hypothesis that was proposed here could help to better understand the role of microbe-to-microbe interactions in disease pathogenesis. Further studies should also include CFTR mutants, ENaC overexpressing mice, later time points, and addition of antibiotics.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Cornell University Seed Grant for Collaborations between Cornell University-Ithaca and Weill Cornell Medical College Faculty to LTA and SW and a grant from the Sloan Foundation with grant no. 2012-6-04 to LTA. We thank Dr. Kirk Harris (University of Colorado Denver—Anschutz Medical Campus) for fruitful discussions, Catherine Spirito (Cornell University) for microbiome advice, Nancy and Dan Paduano for their enthusiastic support, and anonymous reviewers for suggestions that improved the language of the manuscript.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website (http://www.nature.com/ismej)
Supplementary Material
References
- Chmiel JF, Aksamit TR, Chotirmall SH, Dasenbrook EC, Elborn JS, LiPuma JJ et al. (2014). Antibiotic management of lung infections in cystic fibrosis. I. the microbiome, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative bacteria, and multiple infections. Ann Am Thorac Soc 11: 1120–1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui L, Morris A, Huang L, Beck JM, Twigg HL 3rd, von Mutius E et al. (2014). The microbiome and the lung. Ann Am Thorac Soc 11: S227–S232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson RP, Huffnagle GB. (2015). The lung microbiome: new principles for respiratory bacteriology in health and disease. PLoS Pathog 11: e1004923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb-Downward JR, Thompson DL, Han MK, Freeman CM, McCloskey L, Schmidt LA et al. (2011). Analysis of the lung microbiome in the "healthy" smoker and in COPD. PLoS One 6: e16384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilty M, Burke C, Pedro H, Cardenas P, Bush A, Bossley C et al. (2010). Disordered microbial communities in asthmatic airways. PLoS One 5: e8578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang YJ, Sethi S, Murphy T, Nariya S, Boushey HA, Lynch SV. (2014). Airway microbiome dynamics in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Clin Microbiol 52: 2813–2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter RC, Klepac-Ceraj V, Lorenzi MM, Grotzinger H, Martin TR, Newman DK. (2012). Phenazine content in the cystic fibrosis respiratory tract negatively correlates with lung function and microbial complexity. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 47: 738–745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knights D, Costello EK, Knight R. (2011). Supervised classification of human microbiota. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35: 343–359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukavica-Ibrulj I, Levesque RC. (2008). Animal models of chronic lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: useful tools for cystic fibrosis studies. Lab Anim 42: 389–412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch SV, Bruce KD. (2013). The cystic fibrosis airway microbiome. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3: a009738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan JC. (2016). Neonatal Gastrointestinal and Respiratory Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis: Potential Interactions and Implications for Systemic Health. Clin Ther 38: 740–746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meduri GU, Kanangat S, Stefan J, Tolley E, Schaberg D. (1999). Cytokines IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha enhance in vitro growth of bacteria. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160: 961–967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata S, Casey M, Frank DW, Ausubel FM, Drenkard E. (2003). Use of the Galleria mellonella caterpillar as a model host to study the role of the type III secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis. Infect Immun 71: 2404–2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragman AA, Kim HB, Reilly CS, Wendt C, Isaacson RE. (2012). The lung microbiome in moderate and severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PloS one 7: e47305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch P, Steck N, Suwandi A, Seidel JA, Kunzel S, Bhullar K et al. (2015). Expression of the Blood-Group-Related Gene B4galnt2 Alters Susceptibility to Salmonella Infection. PLoS pathogens 11: e1005008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietsch A, Mekalanos JJ. (2006). Metabolic regulation of type III secretion gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 59: 807–820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley CD, Duan K, Fischer C, Parkins MD, Storey DG, Rabin HR et al. (2008. a). Discerning the complexity of community interactions using a Drosophila model of polymicrobial infections. PLoS pathogens 4: e1000184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley CD, Parkins MD, Rabin HR, Duan K, Norgaard JC, Surette MG. (2008. b). A polymicrobial perspective of pulmonary infections exposes an enigmatic pathogen in cystic fibrosis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 15070–15075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sze MA, Dimitriu PA, Hayashi S, Elliott WM, McDonough JE, Gosselink JV et al. (2012). The lung tissue microbiome in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 185: 1073–1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani R, Hastie T, Narasimhan B, Chu G. (2002). Diagnosis of multiple cancer types by shrunken centroids of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 6567–6572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heeckeren AM, Schluchter MD. (2002). Murine models of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. Lab Anim 36: 291–312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heeckeren AM, Schluchter MD, Xue W, Davis PB. (2006). Response to acute lung infection with mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173: 288–296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance RE, Rietsch A, Mekalanos JJ. (2005). Role of the type III secreted exoenzymes S, T, and Y in systemic spread of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in vivo. Infect Immun 73: 1706–1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman A, Bassis CM, Beck JM, Young VB, Curtis JL, Huffnagle GB et al. (2015). Application of a neutral community model to assess structuring of the human lung microbiome. mBio 6: e02284-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman A, Rosenbaum MA, Werner JJ, Winans SC, Angenent LT. (2014). Metabolite transfer with the fermentation product 2,3-butanediol enhances virulence by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ISME J 8: 1210–1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner JJ, Koren O, Hugenholtz P, DeSantis TZ, Walters WA, Caporaso JG et al. (2012). Impact of training sets on classification of high-throughput bacterial 16 s rRNA gene surveys. ISME J 6: 94–103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteson KL, Meinardi S, Lim YW, Schmieder R, Maughan H, Quinn R et al. (2014). Breath gas metabolites and bacterial metagenomes from cystic fibrosis airways indicate active pH neutral 2,3-butanedione fermentation. ISME J 8: 1247–1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.