Abstract
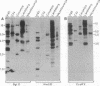
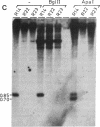
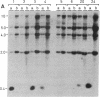
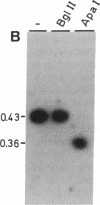
Analysis of 11 genomic clones containing the S-adenosylmethionine synthetase 1 gene (sam1) of Arabidopsis thaliana revealed the presence of a 431-base-pair (bp) insertion in the 3' end of sam1 in one of these clones. The inserted sequence, called Tat1, shows structural features of a transposon. It is flanked by a 5-bp duplication of the target site DNA and has 13-bp inverted repeats at its termini. Two highly homologous elements situated in a different genomic context were isolated from a genomic library. Genomic Southern analysis indicates that there are at least four copies of Tat1 present in the A. thaliana ecotype Columbia genome. Different hybridization patterns are observed with DNAs derived from different ecotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana, indicating that the element has moved since the divergence of these ecotypes. In two populations of A. thaliana, linear extrachromosomal Tat1-homologous DNA has been observed. The presented data are consistent with the hypothesis that Tat1 is an active transposable element.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya M. K., Smith A. M., Ellis T. H., Hedley C., Martin C. The wrinkled-seed character of pea described by Mendel is caused by a transposon-like insertion in a gene encoding starch-branching enzyme. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90721-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring H. P., Starlinger P. Molecular genetics of transposable elements in plants. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:175–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring H. P., Tillmann E., Starlinger P. DNA sequence of the maize transposable element Dissociation. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):127–130. doi: 10.1038/307127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Ish-Horowicz D. Extrachromosomal circular copies of the eukaryotic transposable element copia in cultured Drosophila cells. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):591–595. doi: 10.1038/292591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann A., Schulz W., Hahlbrock K. Two alleles of the single-copy chalcone synthase gene in parsley differ by a transposon-like element. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Apr;212(1):93–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00322449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsman A. J., Mellor J., Adams S., Rathjen P. D., Malim M. H., Fulton S. M., Wilson W., Kingsman S. M. The genetic organization of the yeast Ty element. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:155–167. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebbers E., Herdies L., De Clercq A., Seurinck J., Leemans J., Van Damme J., Segura M., Gheysen G., Van Montagu M., Vandekerckhove J. Determination of the Processing Sites of an Arabidopsis 2S Albumin and Characterization of the Complete Gene Family. Plant Physiol. 1988 Aug;87(4):859–866. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossie K. G., Young M. W., Varmus H. E. Extrachromosomal DNA forms of copia-like transposable elements, F elements and middle repetitive DNA sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. Variation in cultured cells and embryos. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam H. G., Giraudat J., Den Boer B., Moonan F., Loos WDB., Hauge B. M., Goodman H. M. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Linkage Map of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 1989 Jul;1(7):699–705. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.7.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peleman J., Boerjan W., Engler G., Seurinck J., Botterman J., Alliotte T., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Strong cellular preference in the expression of a housekeeping gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encoding S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):81–93. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peleman J., Saito K., Cottyn B., Engler G., Seurinck J., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Structure and expression analyses of the S-adenosylmethionine synthetase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90510-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman R. F., Fedoroff N. V., Messing J. The nucleotide sequence of the maize controlling element Activator. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan K., Emmons S. W. Extrachromosomal copies of transposon Tc1 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4018–4022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Klösgen R. B., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The Spm (En) transposable element controls the excision of a 2-kb DNA insert at the wx allele of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirsat A. H. A transposon-like structure in the 5' flanking sequence of a legumin gene from Pisum sativum. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Apr;212(1):129–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00322455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan V., Freeling M. An extrachromosomal form of the Mu transposons of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4924–4928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin L. O., Rhodes P. R., Goldberg R. B. cA lectin gene insertion has the structural features of a transposable element. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1023–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90560-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voytas D. F., Ausubel F. M. A copia-like transposable element family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):242–244. doi: 10.1038/336242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]