Abstract
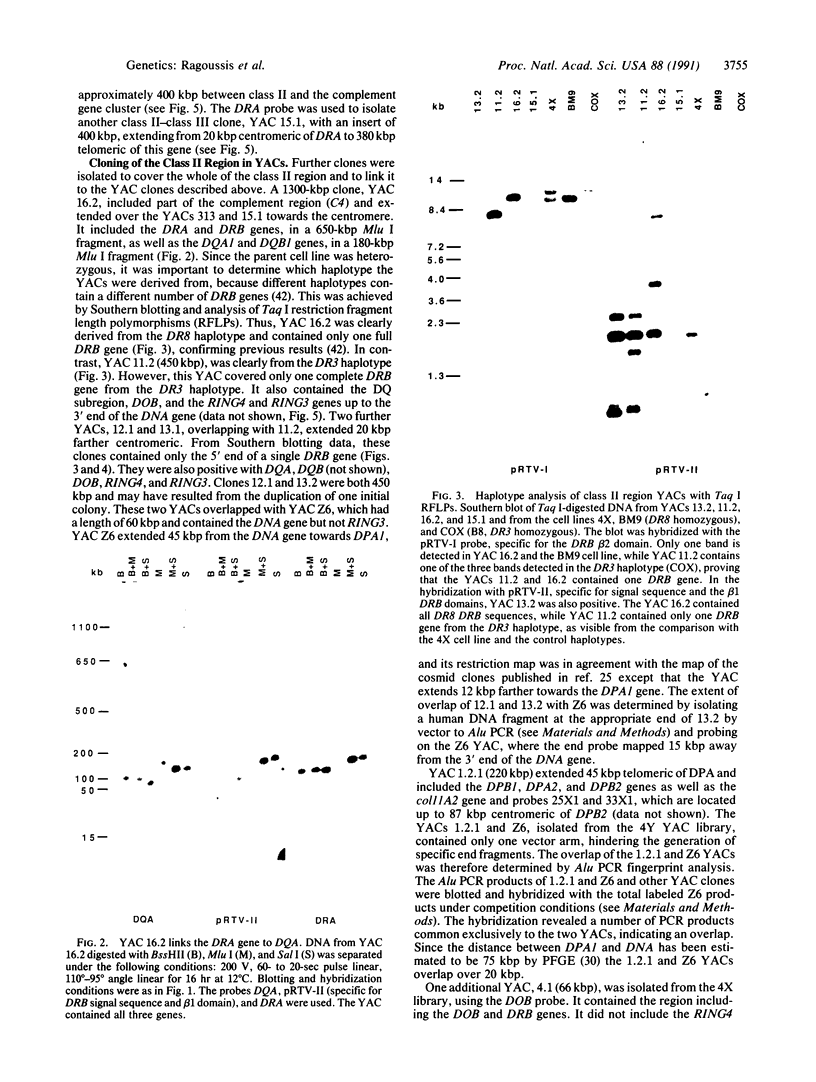
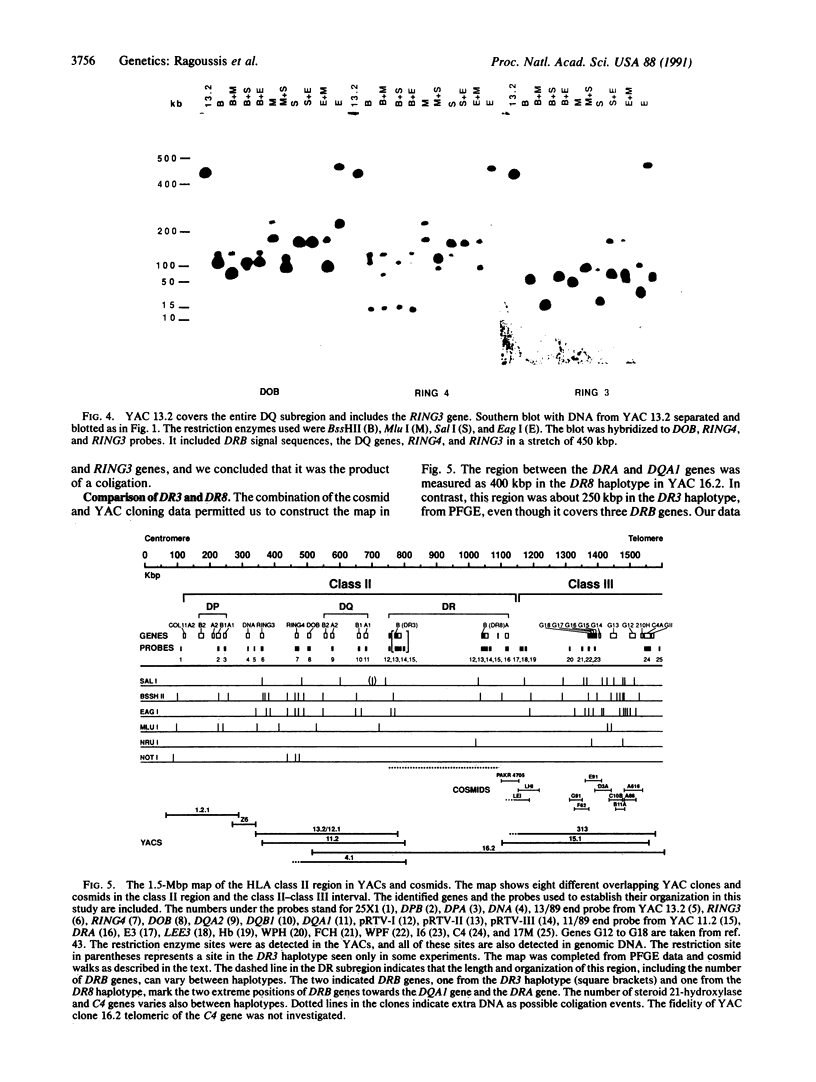
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) have been applied to clone the entire class II region of the human major histocompatibility complex (MHC), including its flanking regions, in a contig over 1.5 million base pairs (bp) long. The human DNA inserts in the YACs have a size between 60 and 1300 kbp and were isolated from two EcoRI partial digest libraries. The gaps between DRA and DRB, DRB and DQA, and DOB and DPA, which had not been cloned by other means, have been bridged with YAC clones. The contig extends through the 400 kpb of DNA between the DRA and C4 genes, thus linking the class II region with the complement gene cluster in the class III region. The cloning in YACs has been supported by a conventional cosmid walk of 290 kbp in the C4-DRA region. Restriction enzyme sites in the YAC clones were compared to the sites in the cosmid walk, to published cosmid clones, and to the already existing physical maps, leading to a detailed characterization of a region of the human genome over 1500 kbp. The YAC clones will be valuable for functional analysis of the MHC.
Full text
PDF
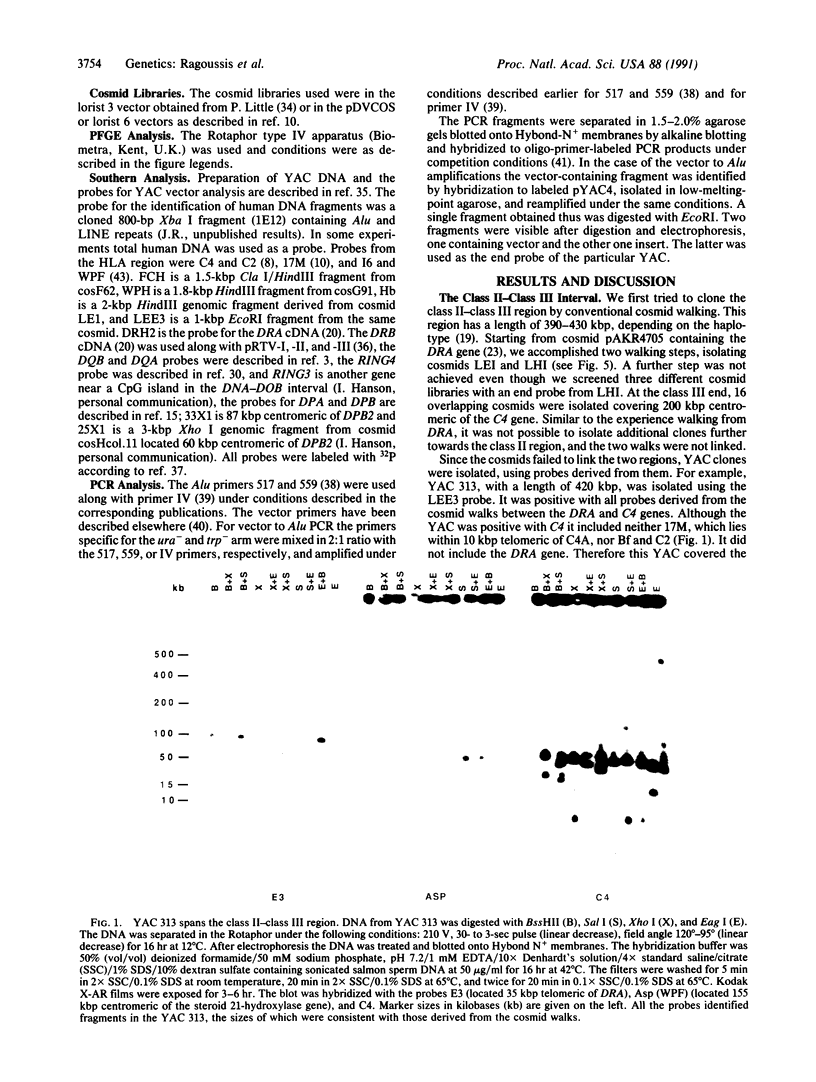

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson G., Larhammar D., Widmark E., Servenius B., Peterson P. A., Rask L. Class II genes of the human major histocompatibility complex. Organization and evolutionary relationship of the DR beta genes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8748–8758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell J. L., Jarrold E. A. HLA-DR allogenotyping using exon-specific cDNA probes and application of rapid minigel methods. Mol Immunol. 1986 Oct;23(10):1111–1116. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck G., Strominger J. L. Cosmid clones in the HLA-DZ and -DP subregions. Hum Immunol. 1990 Mar;27(3):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(90)90056-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck G., Strominger J. L. Molecular organization of the DQ subregion (DO-DX-DV-DQ) of the human MHC and its evolutionary implications. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1734–1737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks-Wilson A. R., Goodfellow P. N., Povey S., Nevanlinna H. A., de Jong P. J., Goodfellow P. J. Rapid cloning and characterization of new chromosome 10 DNA markers by Alu element-mediated PCR. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90207-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme J., Andersson M., Andersson G., Möller E., Peterson P. A., Rask L. HLA-DR beta genes vary in number between different DR specificities, whereas the number of DQ beta genes is constant. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2149–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. A molecular map of the human major histocompatibility complex class III region linking complement genes C4, C2 and factor B. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):237–241. doi: 10.1038/307237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Katzman P., Alicot E. M., Koller B. H., Geraghty D. E., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L., Spies T. Linkage map of the human major histocompatibility complex including the tumor necrosis factor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerundolo V., Alexander J., Anderson K., Lamb C., Cresswell P., McMichael A., Gotch F., Townsend A. Presentation of viral antigen controlled by a gene in the major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):449–452. doi: 10.1038/345449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chimini G., Pontarotti P., Nguyen C., Toubert A., Boretto J., Jordan B. R. The chromosome region containing the highly polymorphic HLA class I genes displays limited large scale variability in the human population. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):395–400. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier S., Sinnott P. J., Dyer P. A., Price D. A., Harris R., Strachan T. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis identifies a high degree of variability in the number of tandem 21-hydroxylase and complement C4 gene repeats in 21-hydroxylase deficiency haplotypes. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1393–1402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. H., Little P. F. A cosmid vector for systematic chromosome walking. Gene. 1986;49(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham I., Sargent C. A., Dawkins R. L., Campbell R. D. An analysis of variation in the long-range genomic organization of the human major histocompatibility complex class II region by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham I., Sargent C. A., Kendall E., Campbell R. D. Characterization of the class III region in different MHC haplotypes by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(3):175–182. doi: 10.1007/BF02114970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham I., Sargent C. A., Trowsdale J., Campbell R. D. Molecular mapping of the human major histocompatibility complex by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson I. M., Gorman P., Lui V. C., Cheah K. S., Solomon E., Trowsdale J. The human alpha 2(XI) collagen gene (COL11A2) maps to the centromeric border of the major histocompatibility complex on chromosome 6. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):925–931. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. A., Bell J. I., Long E. O., Lindsten T., McDevitt H. O. Mapping of the class II region of the human major histocompatibility complex by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):453–455. doi: 10.1038/323453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Aota S. Global variation in G+C content along vertebrate genome DNA. Possible correlation with chromosome band structures. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Wada K., Aota S. Giant G+C% mosaic structures of the human genome found by arrangement of GenBank human DNA sequences according to genetic positions. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90273-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai J., Ando A., Sato T., Nakatsuji T., Tsuji K., Inoko H. Analysis of gene structure and antigen determinants of DR2 antigens using DR gene transfer into mouse L cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):312–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall E., Sargent C. A., Campbell R. D. Human major histocompatibility complex contains a new cluster of genes between the HLA-D and complement C4 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7251–7257. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin Z., Lehrach H. Yeast artificial chromosomes: an alternative approach to the molecular analysis of mouse developmental mutations. Genet Res. 1990 Oct-Dec;56(2-3):203–208. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300035308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrance S. K., Smith C. L. Megabase scale restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the human major histocompatibility complex. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):394–399. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90299-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrance S. K., Smith C. L., Srivastava R., Cantor C. R., Weissman S. M. Megabase-scale mapping of the HLA gene complex by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1387–1390. doi: 10.1126/science.3029868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter S. A., Nelson D. L., Warren S. T., Ledbetter D. H. Rapid isolation of DNA probes within specific chromosome regions by interspersed repetitive sequence polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):475–481. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90477-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellins E., Smith L., Arp B., Cotner T., Celis E., Pious D. Defective processing and presentation of exogenous antigens in mutants with normal HLA class II genes. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):71–74. doi: 10.1038/343071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olerup O., Smith C. I., Hammarström L. Different amino acids at position 57 of the HLA-DQ beta chain associated with susceptibility and resistance to IgA deficiency. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):289–290. doi: 10.1038/347289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachnis V., Pevny L., Rothstein R., Costantini F. Transfer of a yeast artificial chromosome carrying human DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5109–5113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavan W. J., Hieter P., Reeves R. H. Generation of deletion derivatives by targeted transformation of human-derived yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1300–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragoussis J., Bloemer K., Pohla H., Messer G., Weiss E. H., Ziegler A. A physical map including a new class I gene (cda12) of the human major histocompatibility complex (A2/B13 haplotype) derived from a monosomy 6 mutant cell line. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley J., Butler R., Ogilvie D., Finniear R., Jenner D., Powell S., Anand R., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. A novel, rapid method for the isolation of terminal sequences from yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2887–2890. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollini P., Mach B., Gorski J. Linkage map of three HLA-DR beta-chain genes: evidence for a recent duplication event. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7197–7201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubock M. J., Larin Z., Cook M., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R., Lehrach H. A yeast artificial chromosome containing the mouse homeobox cluster Hox-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4751–4755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Campbell R. D. Identification of multiple HTF-island associated genes in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Blanck G., Bresnahan M., Sands J., Strominger J. L. A new cluster of genes within the human major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):214–217. doi: 10.1126/science.2911734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Sorrentino R., Boss J. M., Okada K., Strominger J. L. Structural organization of the DR subregion of the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan T. Molecular genetics and polymorphism of class I HLA antigens. Br Med Bull. 1987 Jan;43(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. A molecular basis for genetic susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Trends Genet. 1988 May;4(5):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90135-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Saueracker G., Kay P. H., Christiansen F. T., Anand R., Dawkins R. L. Extensive deletions and insertions in different MHC supratypes detected by pusled field gel electrophoresis. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):933–940. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J. Genetics and polymorphism: class II antigens. Br Med Bull. 1987 Jan;43(1):15–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Hanson I., Mockridge I., Beck S., Townsend A., Kelly A. Sequences encoded in the class II region of the MHC related to the 'ABC' superfamily of transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):741–744. doi: 10.1038/348741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]