Abstract
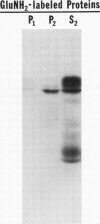
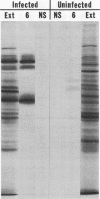
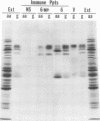
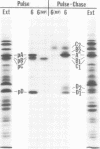
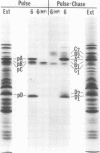
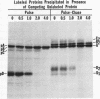
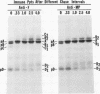
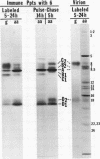
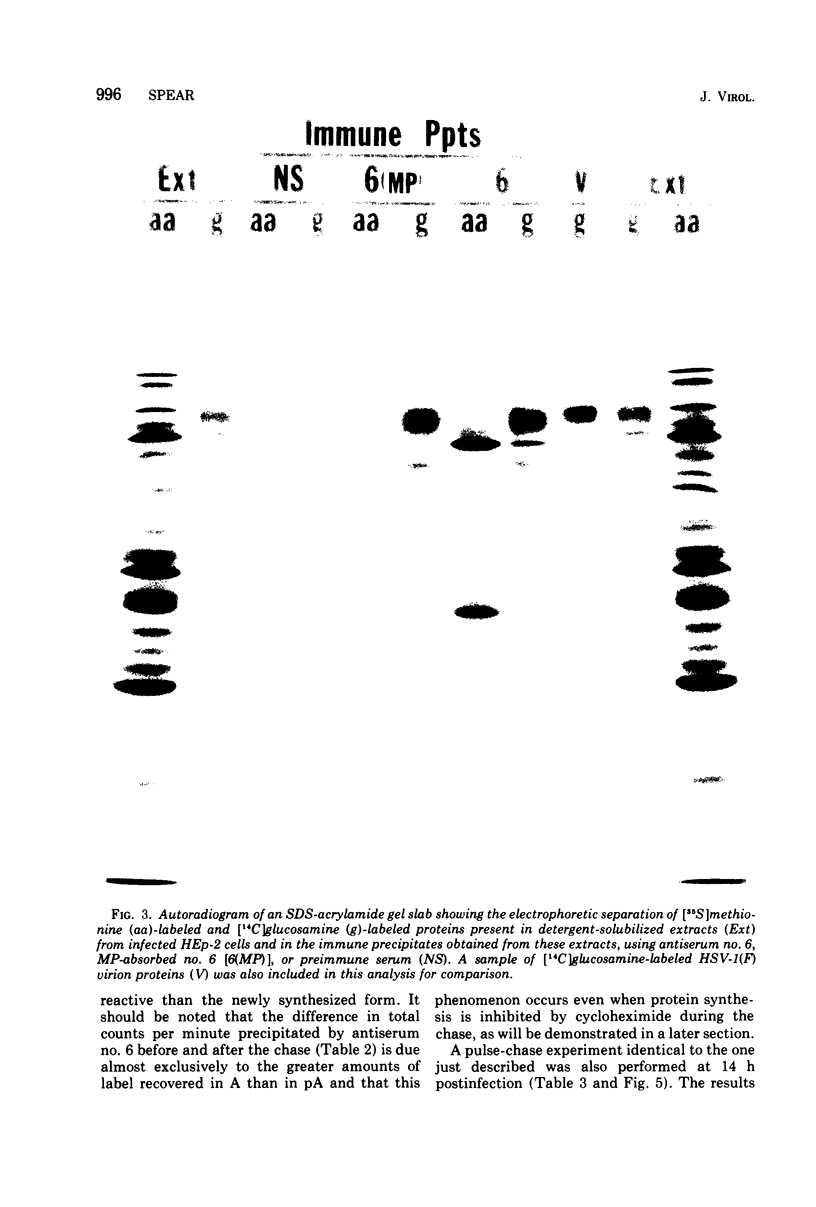
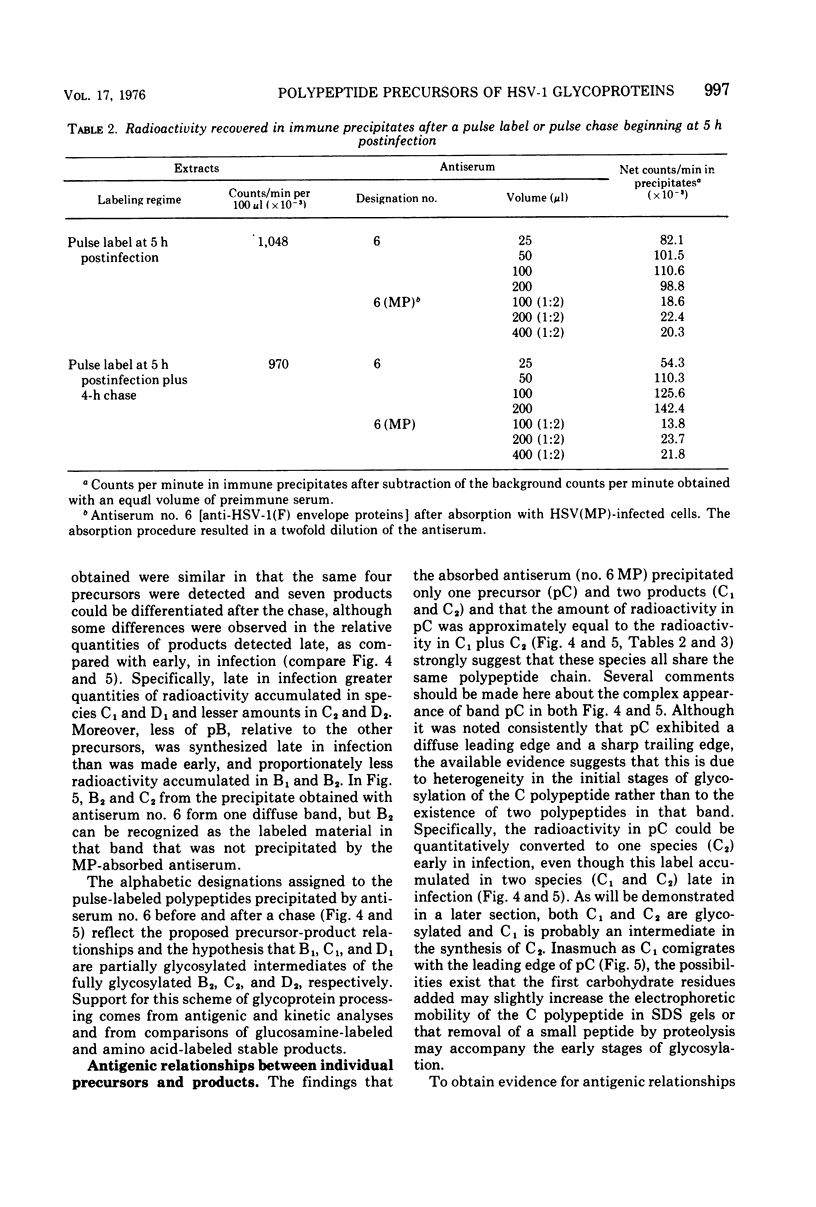
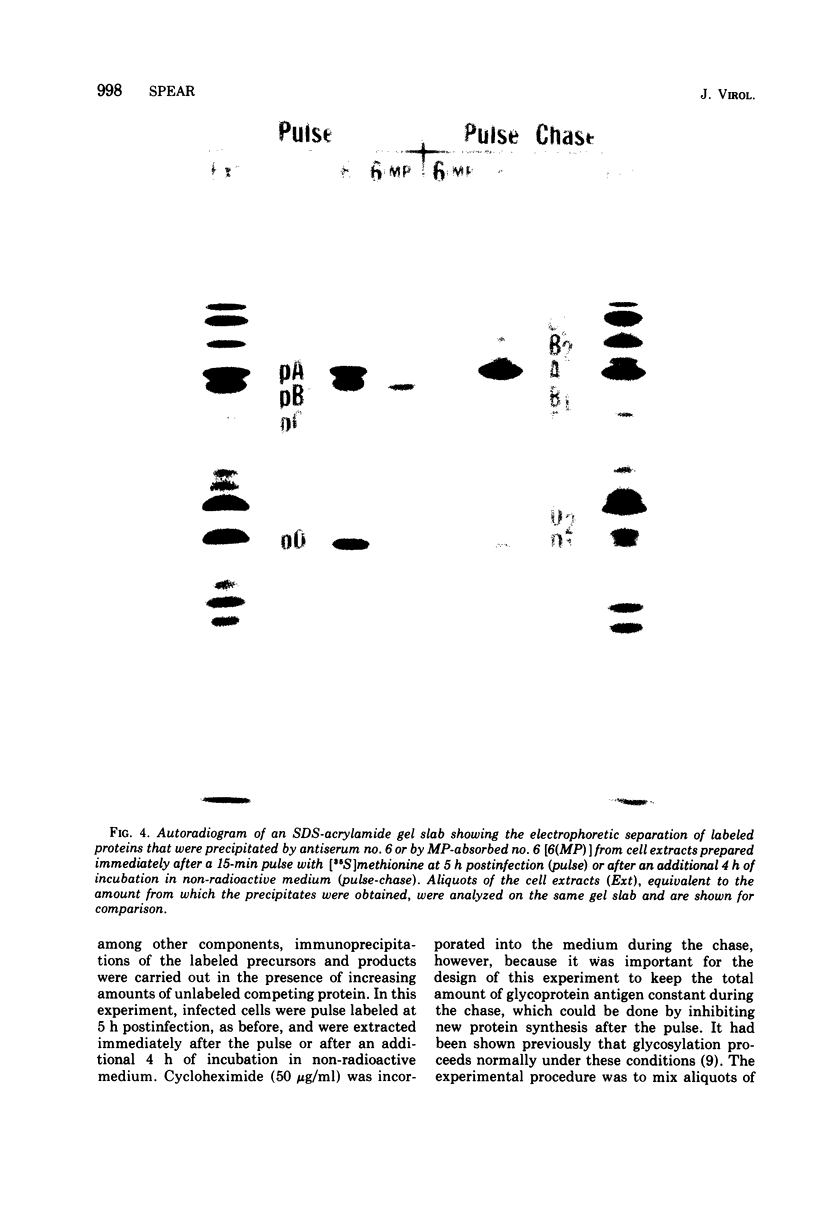
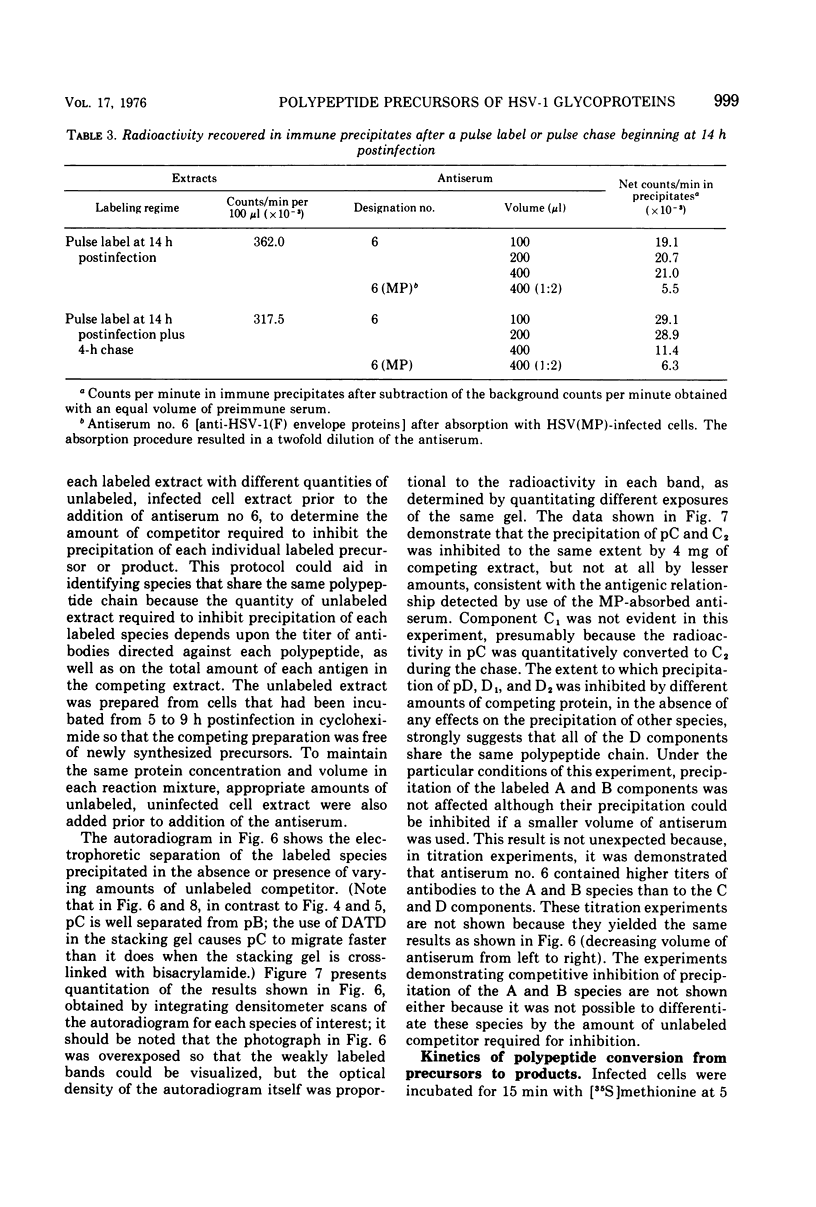
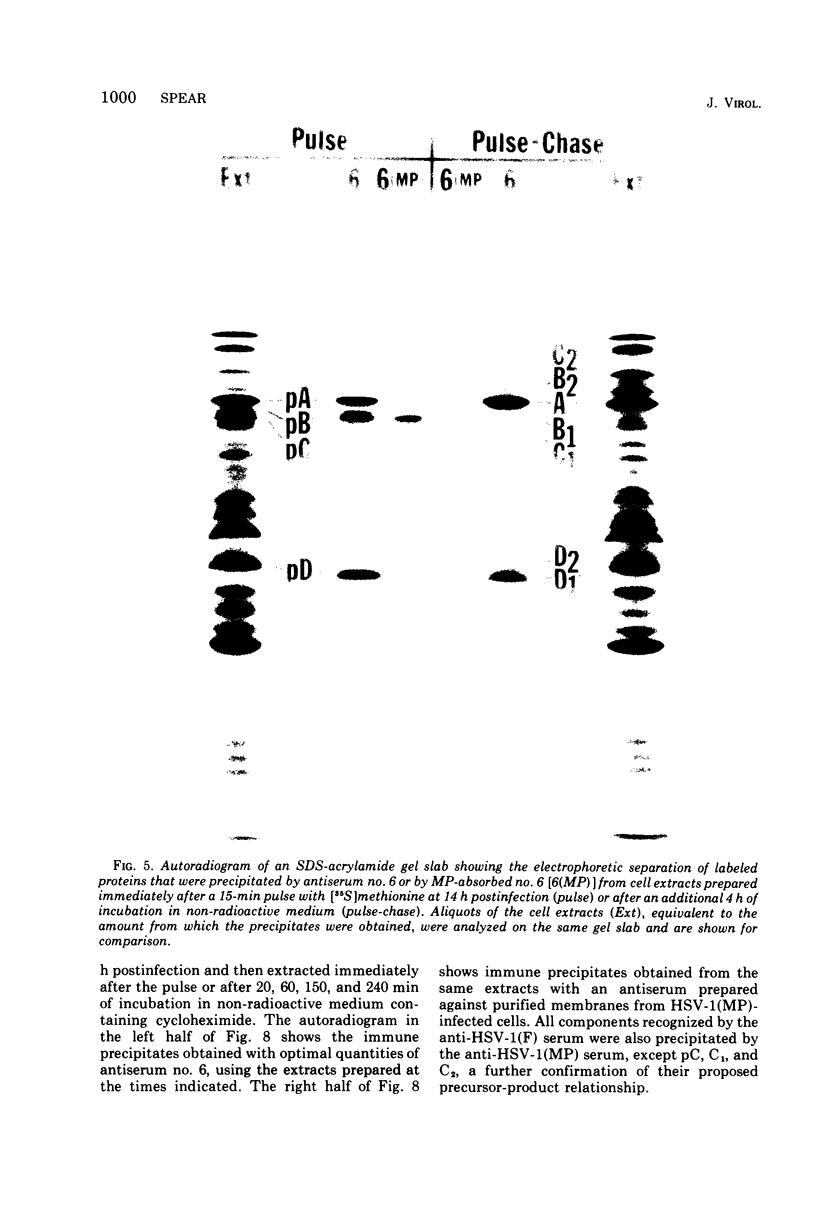
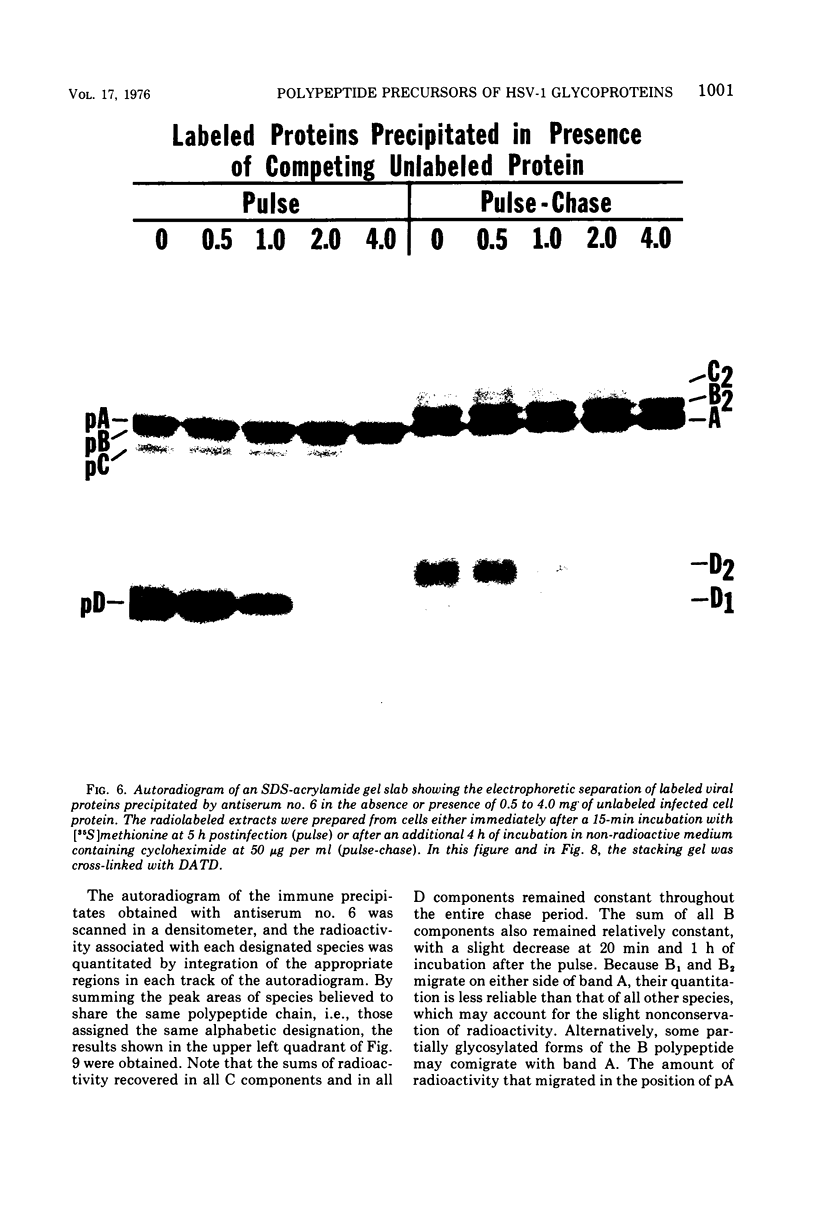
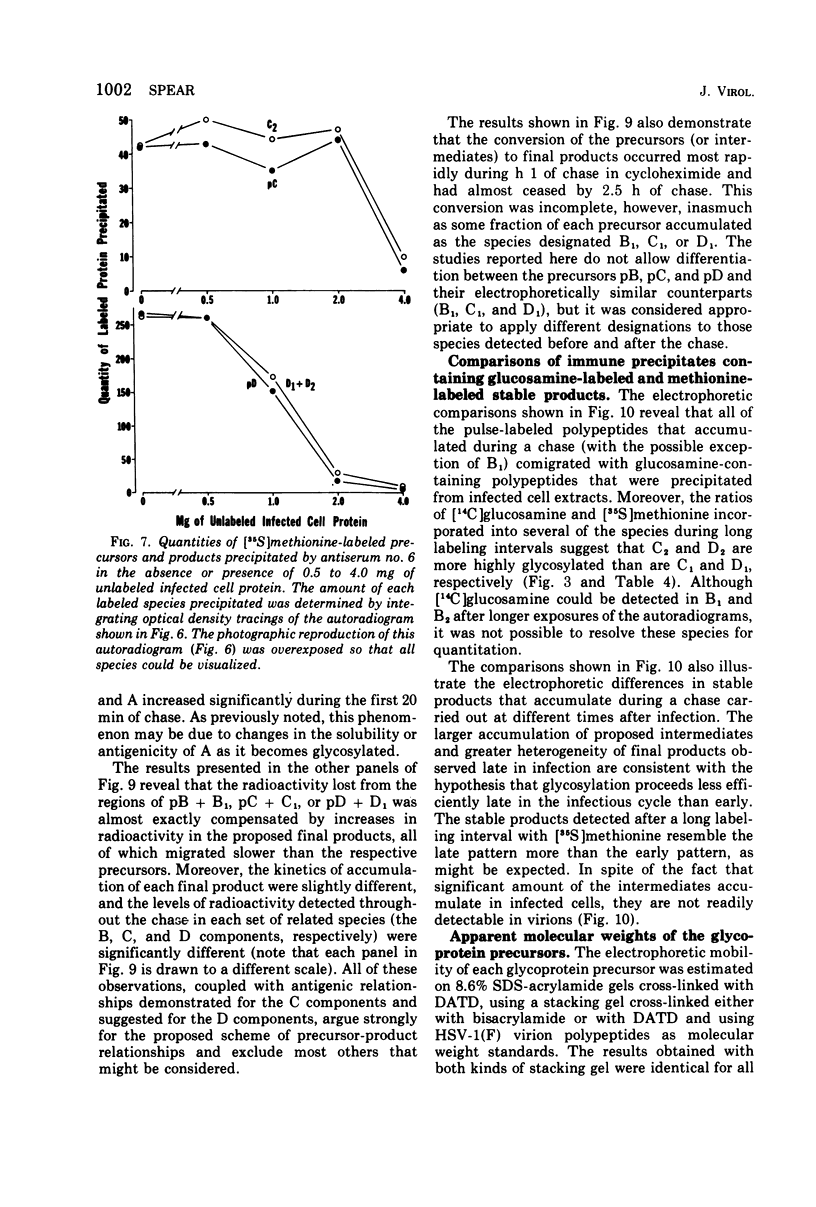
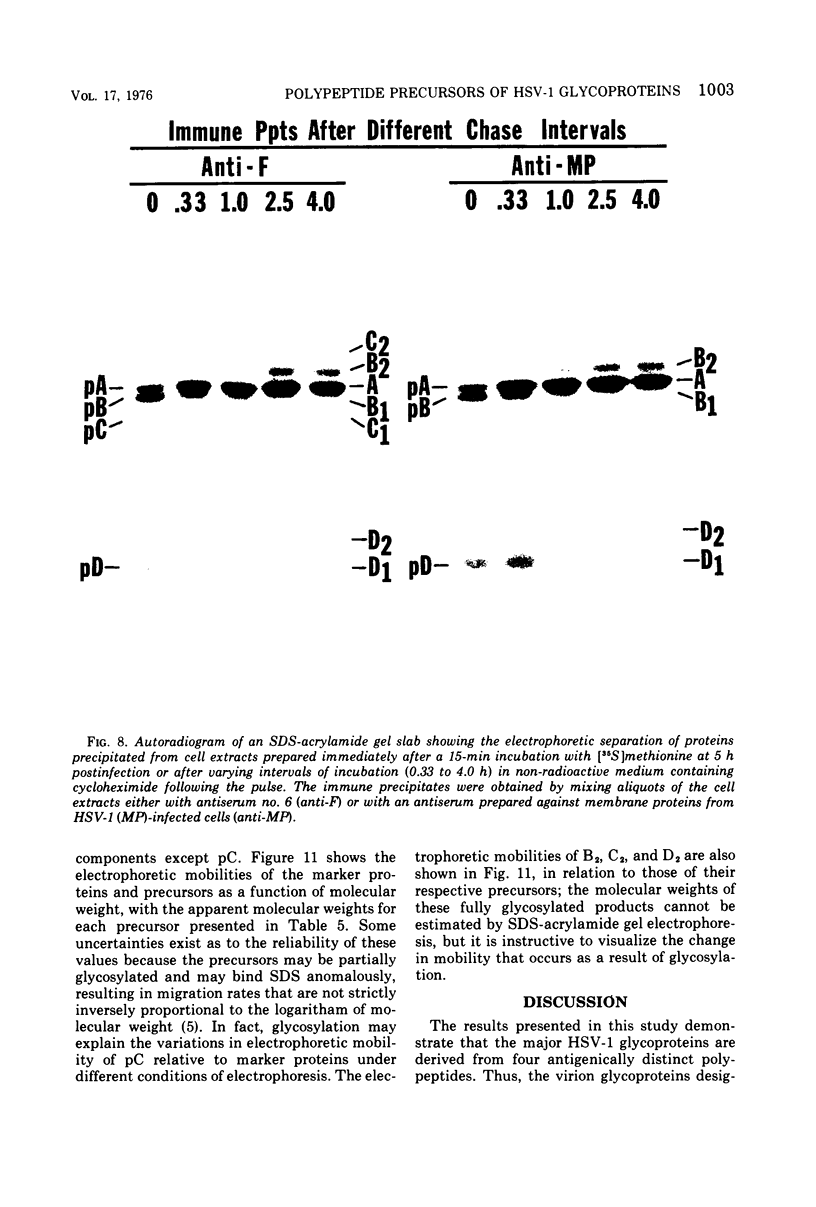
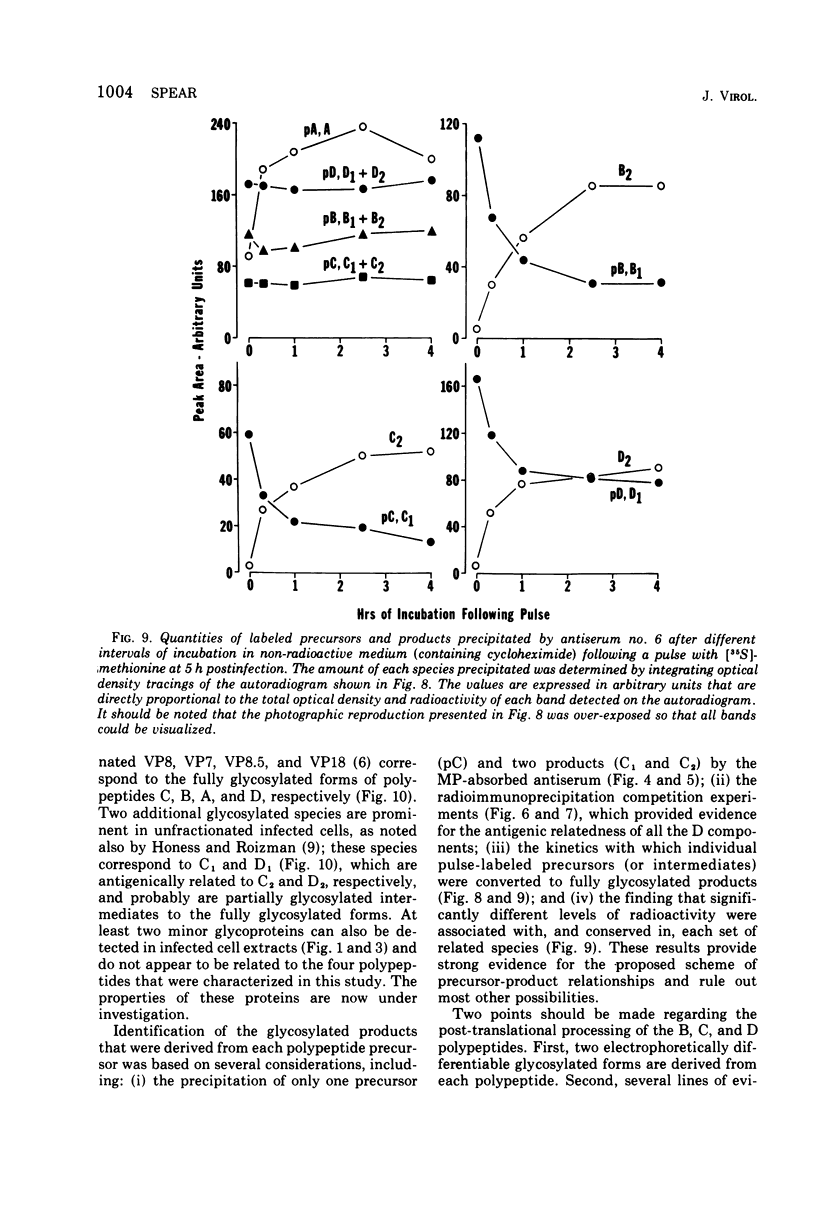
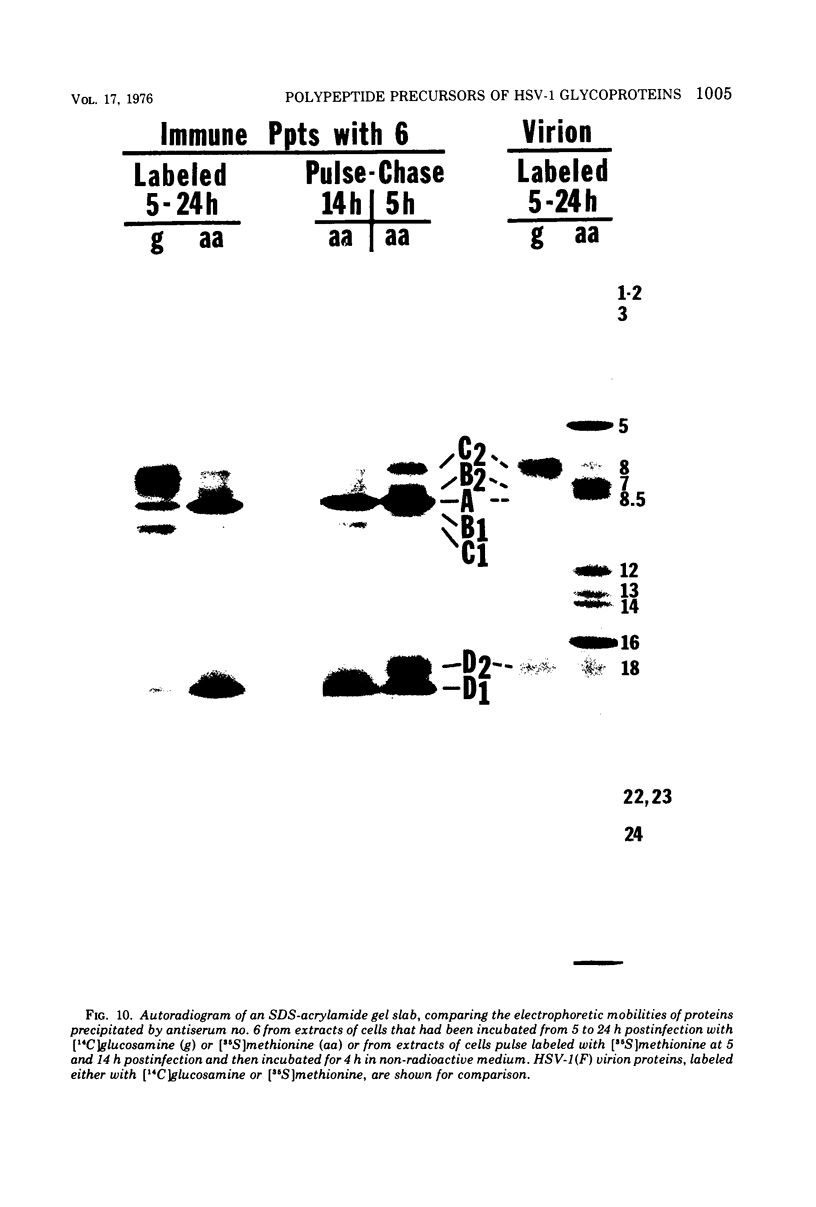
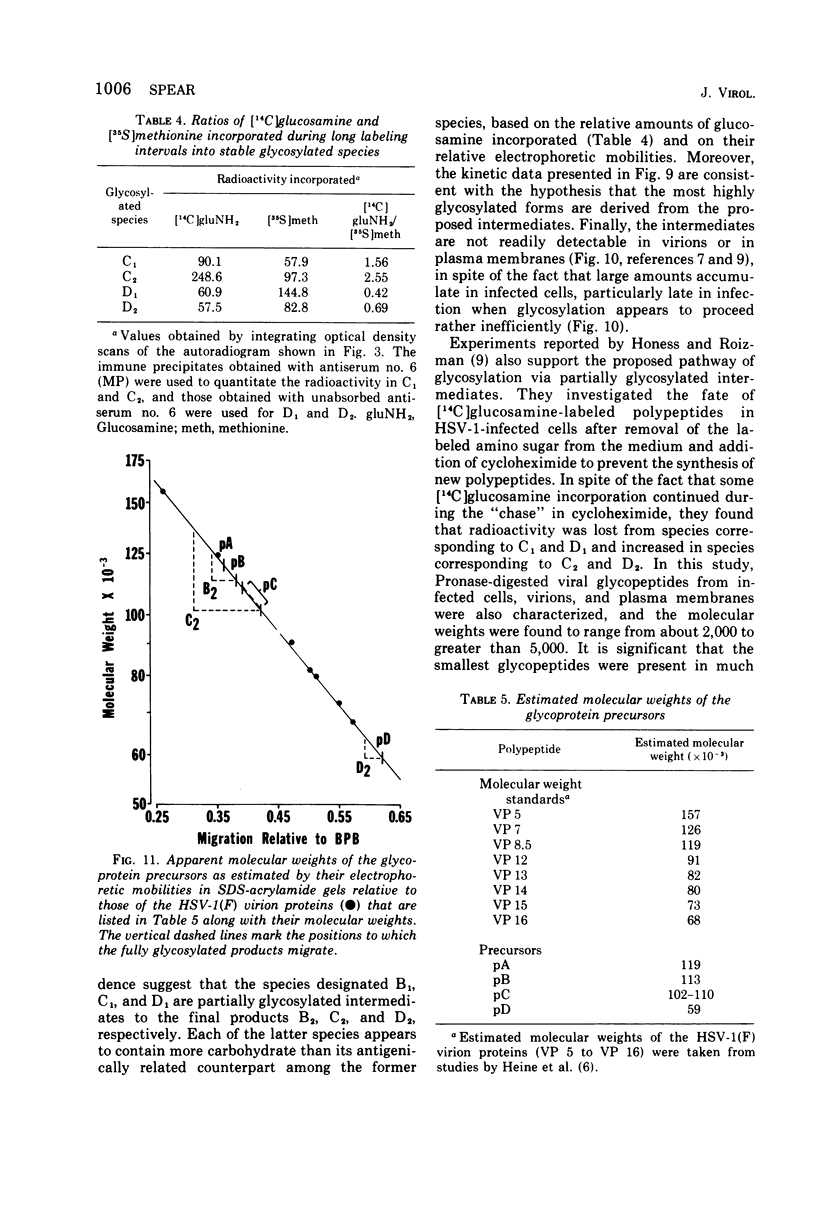
Polypeptide precursors to the major glycoproteins specified by herpes simplex virus type 1 were identified in immunoprecipitation experiments using antisera that reacted specifically with the viral glycoproteins and their precursors. The results demonstrate that the major glycosylated proteins detected in infected cells are derived from four antigenically distinct polypeptides. Three of these polypeptides become glycosylated in two discrete stages, yielding partially glycosylated intermediates and fully glycosylated products. The final products are the predominant species detected in cytoplasmic virions and in plasma membranes. The fourth polypeptide precursor appears to acquire very little carbohydrate and differs in several respects from the other three precursors.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behrens N. H., Carminatti H., Staneloni R. J., Leloir L. F., Cantarella A. I. Formation of lipid-bound oligosaccharides containing mannose. Their role in glycoprotein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3390–3394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 8. Characterization and composition of multiple capsid forms of subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1044–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1044-1052.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grefrath S. P., Reynolds J. A. The molecular weight of the major glycoprotein from the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3913–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. VI. Viral proteins in the plasma membrane. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):431–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.431-439.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XIII. Glycosylation of viral polypeptides. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1308–1326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1308-1326.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 3. Viruses differing in their effects on the social behavior of infected cells specify different membrane glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):865–871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olshevsky U., Becker Y. Herpes simplex virus structural proteins. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):948–960. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B. Polykaryocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:327–342. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Schlesinger M. J. Formation of Sindbis virus proteins: identification of a precursor for one of the envelope proteins. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):925–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.925-932.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Burge B. W. Biosynthesis of the Sindbis virus carbohydrates. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1366–1374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1366-1374.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Kellejmroian B. Proteins spcified by herpes simplex virus. II. Viral glycoprotins associated with cellular membranes. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):123–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.123-131.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]