Abstract
Subcellular fractionation of scrapie-infected hamster brain indicated the association of the scrapie agent with a component of the endomembrane system. Characterization by equilibrium density gradient centrifugation, electron microscopy, and marker enzymes suggested a primary association with rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum and a possible incorporation into the plasma membrane. DNA polymerase activity demonstrated a direct correlation with regions of scrapie activity from the gradient fractions. A scrapie-related product was detected after (3H)TMP incorporation and analysis on 2.2% polyacrylamide gels. Analysis of nucleic acid species extracted from subcellular fractions resulted in a greater quantity from healthy brain; however, no qualitative distinctions were detected.
Full text
PDF

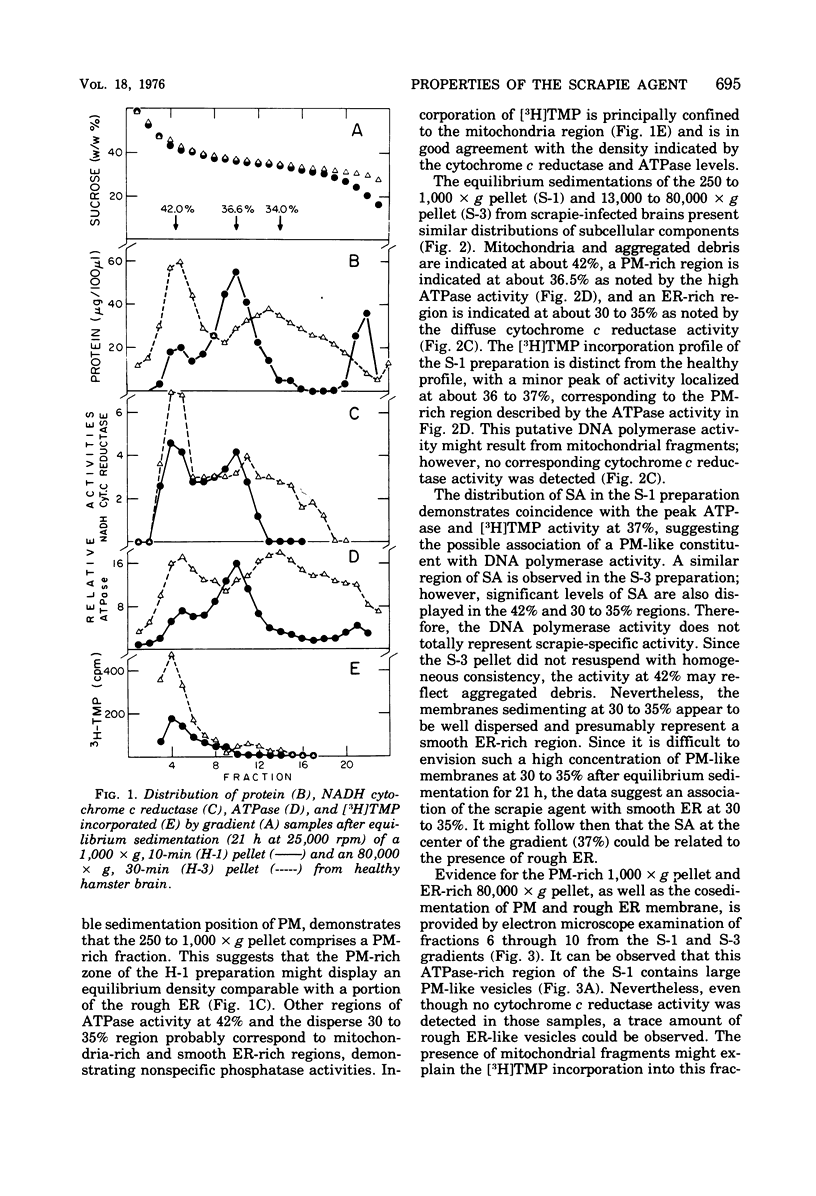
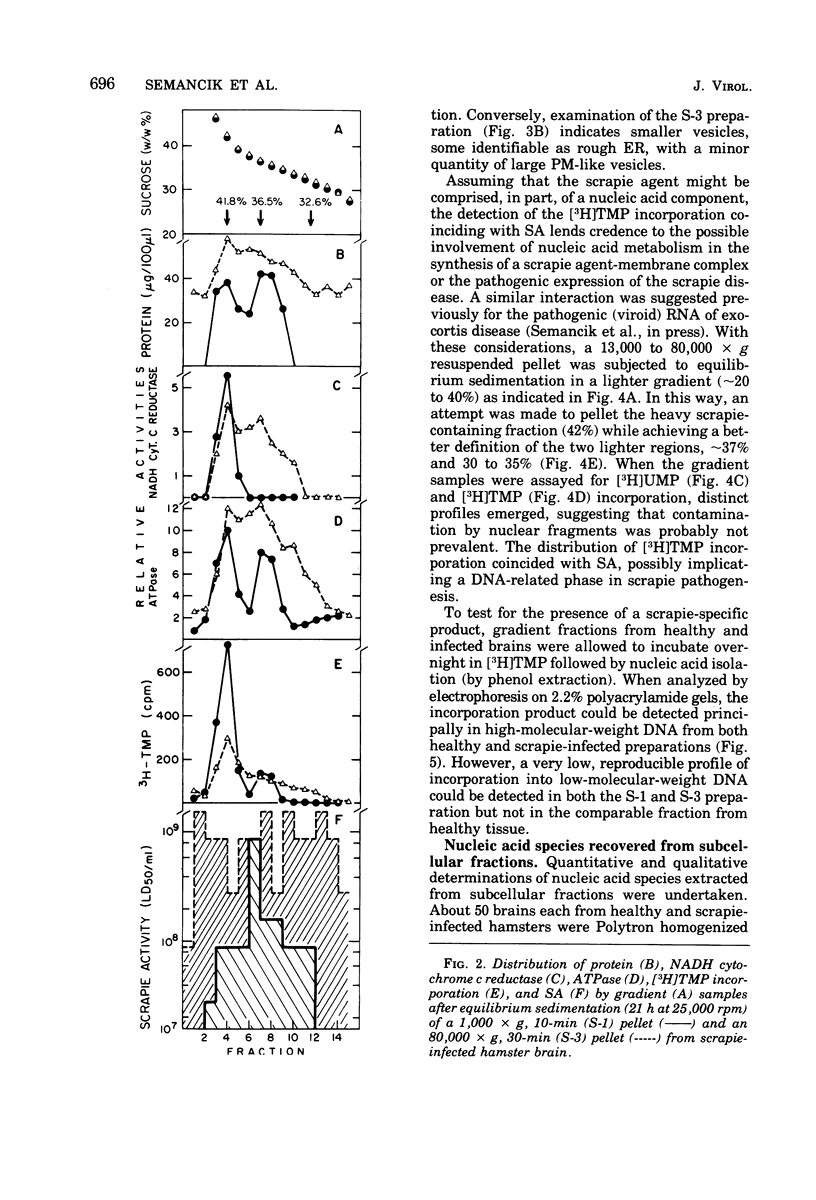

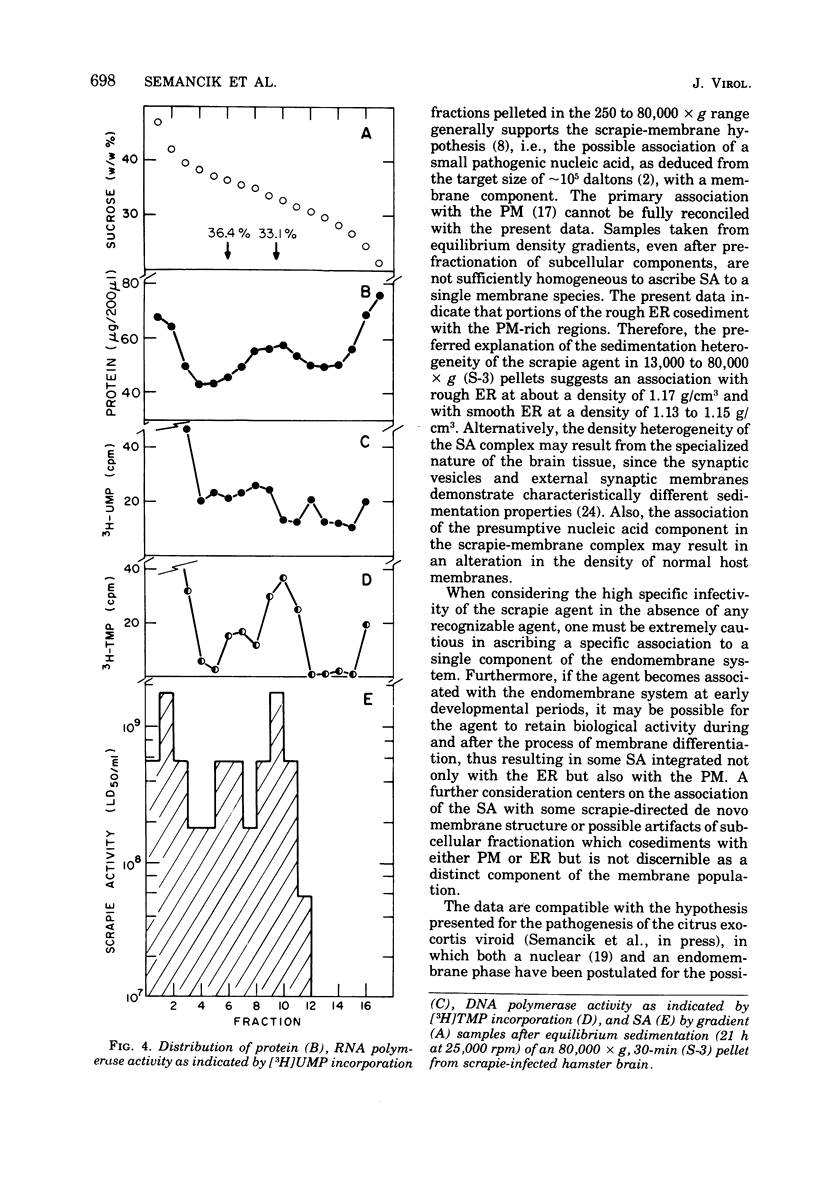
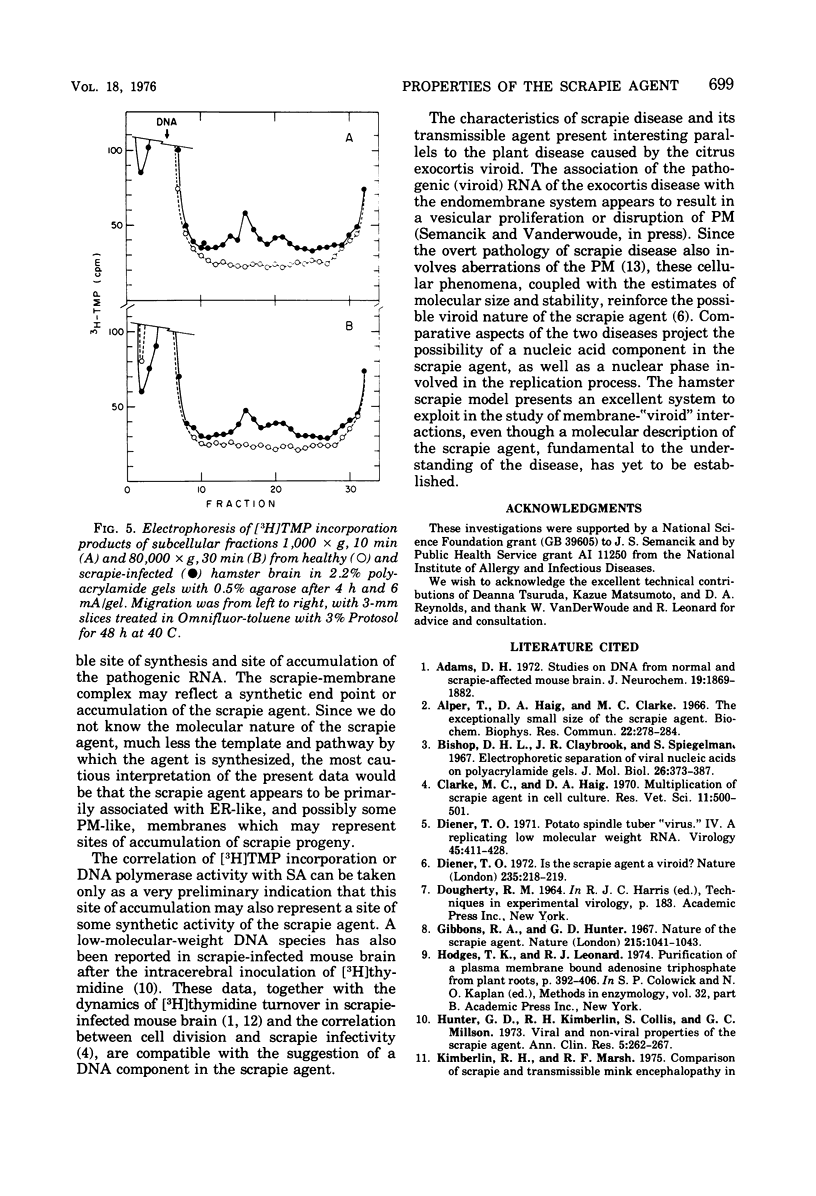

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. H. Studies on DNA from normal and scrapie-affected mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1869–1882. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper T., Haig D. A., Clarke M. C. The exceptionally small size of the scrapie agent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Feb 3;22(3):278–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90478-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. C., Haig D. A. Multiplication of scrapie agent in cell culture. Res Vet Sci. 1970 Sep;11(5):500–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener T. O. Is the scrapie agent a viroid? Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 16;235(59):218–219. doi: 10.1038/newbio235218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener T. O. Potato spindle tuber "virus". IV. A replicating, low molecular weight RNA. Virology. 1971 Aug;45(2):411–428. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90342-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. A., Hunter G. D. Nature of the scrapie agent. Nature. 1967 Sep 2;215(5105):1041–1043. doi: 10.1038/2151041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter G. D., Kimberlin R. H., Collis S., Millson G. C. Viral and non-viral properties of the scrapie agent. Ann Clin Res. 1973 Oct;5(5):262–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Shirt D. B., Collis S. C. The turnover of isotopically labelled DNA in vivo in developing, adult and Scrapie-affected mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1974 Jul;23(1):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb06940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P., Hooks J., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Altered plasma membranes in experimental scrapie. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;19(2):81–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00688486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh R. F., Kimberlin R. H. Comparison of scrapie and transmissible mink encephalopathy in hamsters. II. Clinical signs, pathology, and pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):104–110. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh R. F., Semancik J. S., Medappa K. C., Hanson R. P., Rueckert R. R. Scrapie and transmissible mink encephalopathy: search for infectious nucleic acid. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):993–996. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.993-996.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millson G. C., Hunter G. D., Kimberlin R. H. An experimental examination of the scrapie agent in cell membrane mixtures. II. The association of scrapie activity with membrane fractions. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Apr;81(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semancik J. S., Geelen J. L. Detection of DNA complementary to pathogenic viroid RNA in exocortis disease. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):753–756. doi: 10.1038/256753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semancik J. S., Morris T. J., Weathers L. G. Structure and conformation of low molecular weight pathogenic RNA from exocortis disease. Virology. 1973 Jun;53(2):448–456. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semancik J. S., Weathers L. G. Exocortis disease: evidence for a new species of "infectious" low molecular weight RNA in plants. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):242–244. doi: 10.1038/newbio237242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semancik J. S., Weathers L. G. Exocortis virus: an infectious free-nucleic acid plant virus with unusual properties. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):456–466. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Porter D. D., Stevens J. G. Nature of the scrapie agent: evidence against a viroid. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1099–1103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1099-1103.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. Some properties of synaptic membranes isolated from the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):982–998. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]