Abstract
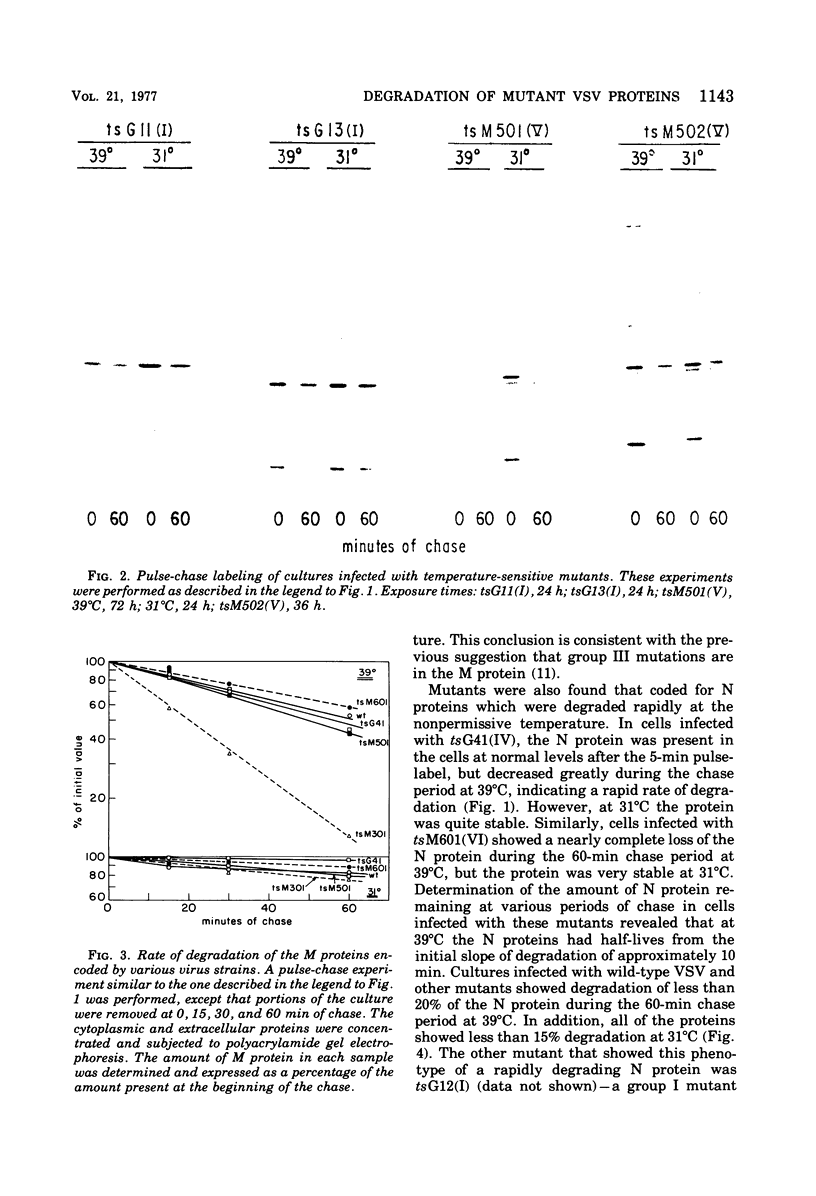
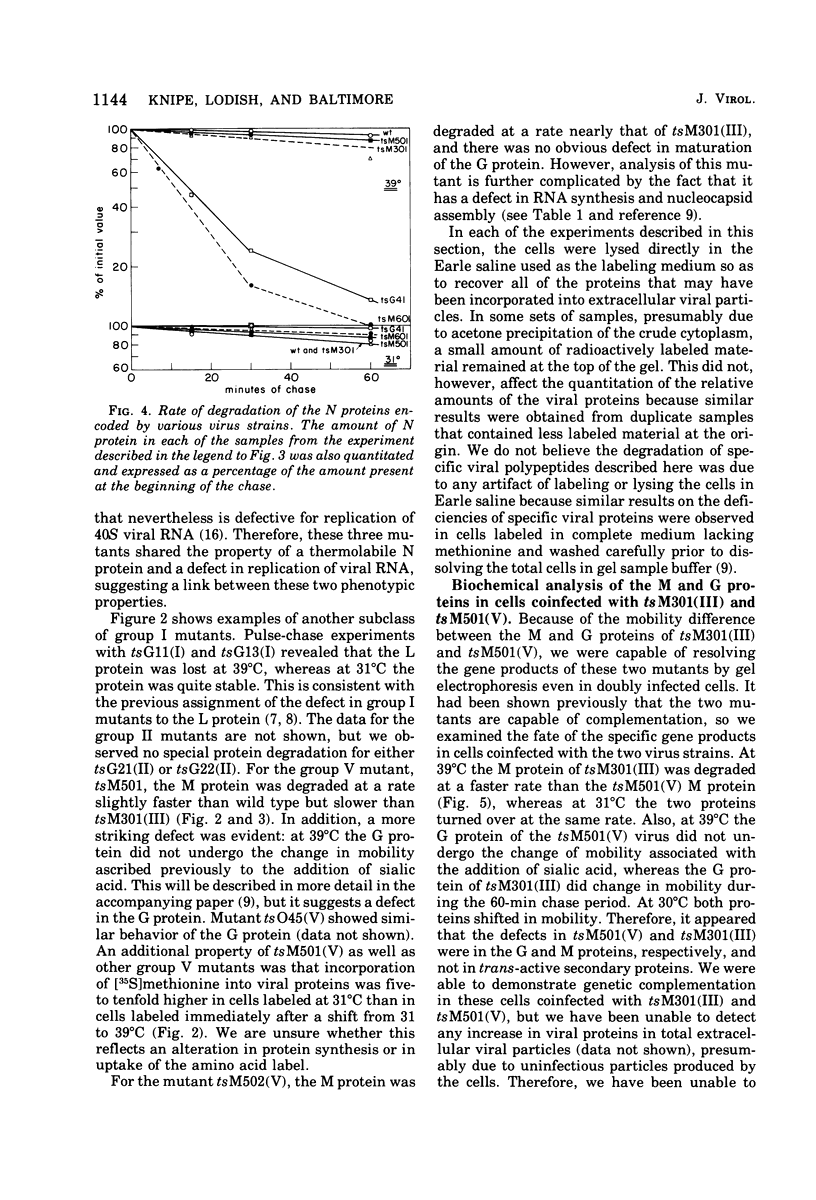
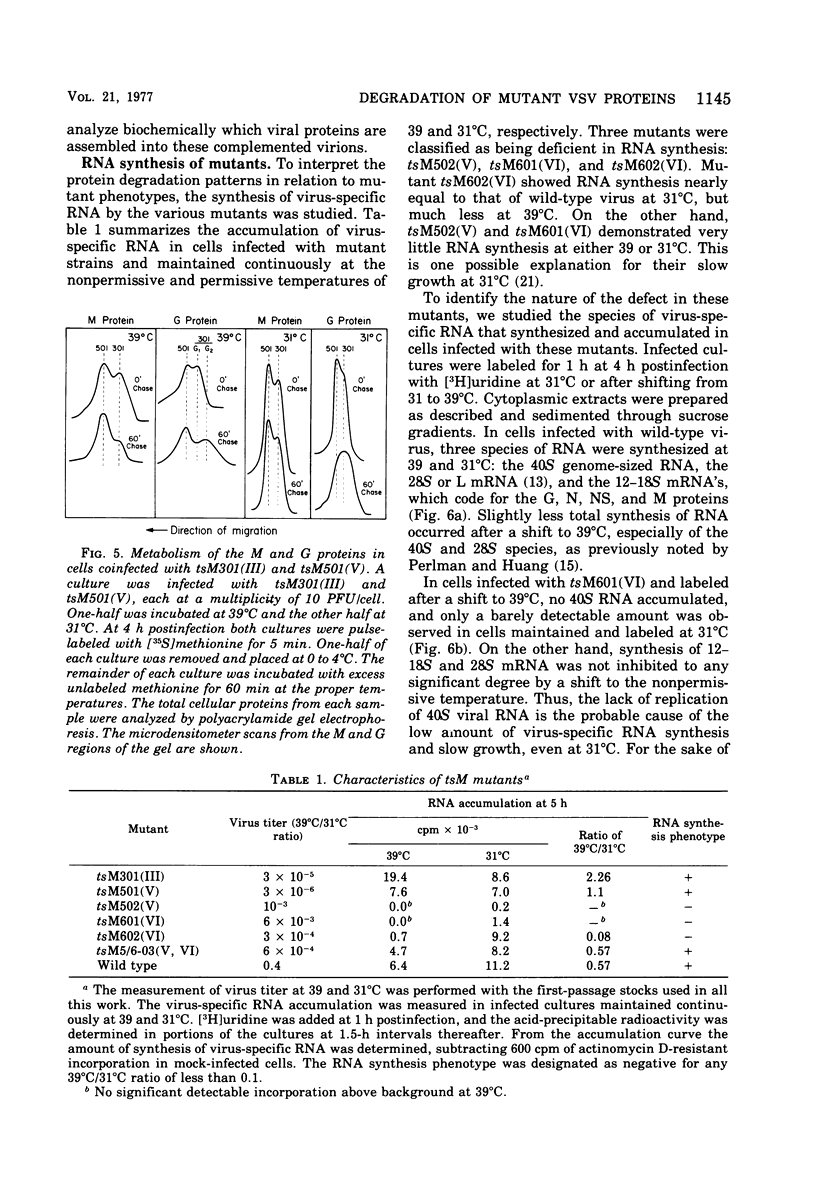
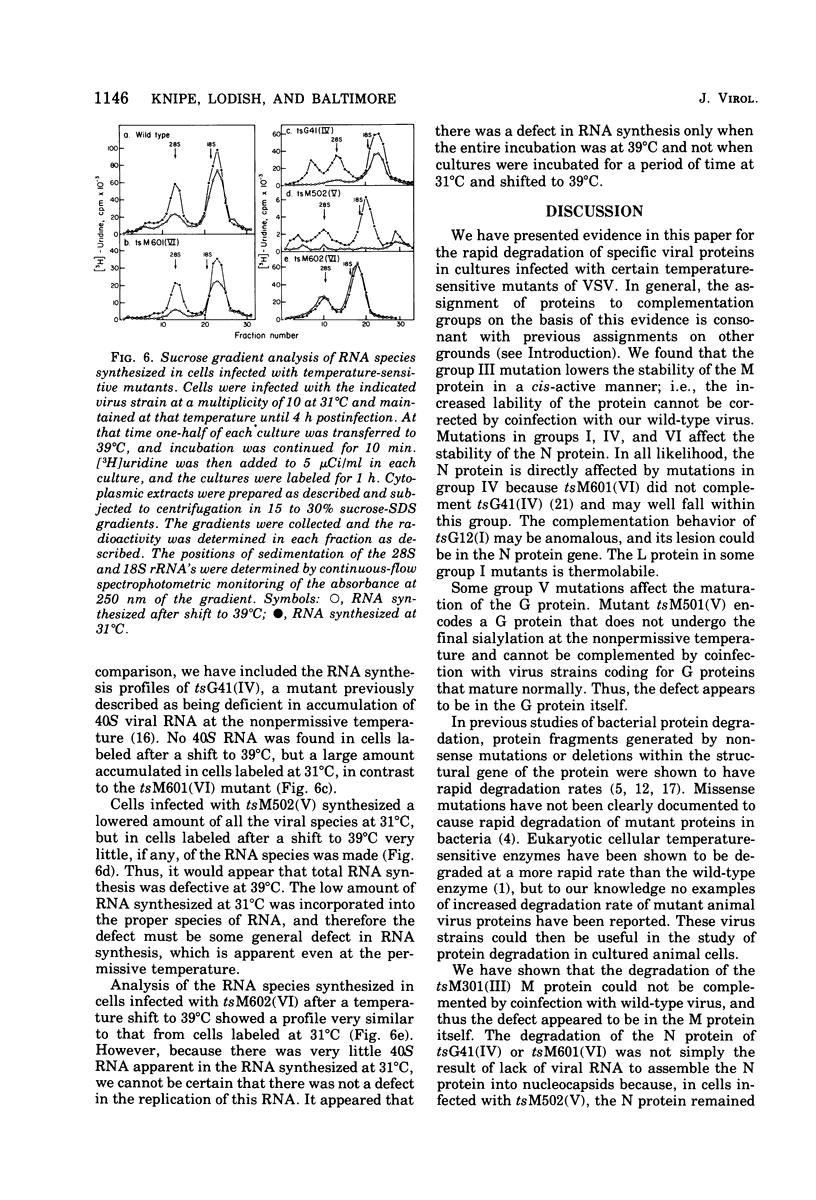
The metabolism of viral RNA and proteins has been studied in cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutant strains of vesicular stomatitis virus. Certain viral proteins encoded by the mutant strains, usually the putative mutant protein for the assigned complementation group, were shown to be degraded more rapidly at the nonpermissive temperature than were the wild-type proteins. Group III mutants (tsG33, tsM301) encode M proteins which are degraded three- to fourfold faster than the wild-type protein. This defect cannot be fully rescued by coinfection with wild-type virus, and thus the defect appears to be in the M protein itself. Mutants tsM601 (VI) and tsG41(IV) encode N proteins which are degraded much faster than the wild-type protein and also share the property of being defective in replication of viral RNA, suggesting a correlation between these phenotypic properties. Furthermore, the L proteins of tsG11(I) and tsG13(I) are more labile than the wild-type protein at the nonpermissive temperature. The G protein of tsM501(V) did not undergo the change in electrophoretic mobility previously shown to be the result of sialylation, suggesting that it is defective in maturation or glycosylation at the nonpermissive temperature. Three of the mutants previously isolated in this laboratory, tsM502(V), tsM601(VI), and tsM602(VI), were shown to be defective in viral RNA synthesis at the nonpermissive temperature. Mutant tsM601(VI) was defective mainly in viral RNA replication, whereas tsM502(V) appeared to be totally defective for viral RNA transcription and replication at the nonpermissive temperature.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capecchi M. R., Capecchi N. E., Hughes S. H., Wahl G. M. Selective degradation of abnormal proteins in mammalian tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4732–4736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A. Etude des mutants thermosensibles du virus de la stomatite vésiculaire. Mise au point d'un test de complémentation. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 May 5;268(18):2305–2308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A. Etude génétique du virus de la stomatite vésiculaire: classement de mutants thermosensibles spontanés en groupes de complémentation. J Gen Virol. 1970 Sep;8(3):187–195. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-3-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Dice J. F. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):835–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt R. In vivo degradation of nonsense fragments in E. coli. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1151–1154. doi: 10.1038/2281151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway A. F., Wong P. K., Cormack D. V. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):917–926. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M., Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. RNA- temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus: L-protein thermosensitivity accounts for transcriptase restriction of group I mutants. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):596–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.596-603.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M., Wagner R. R. Location of the transcription defect in group I temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):28–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.28-35.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Maturation of viral proteins in cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1149-1158.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Localization of two cellular forms of the vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1121–1127. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1121-1127.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafay F. Envelope proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: effect of temperature-sensitive mutations in complementation groups III and V. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1220-1228.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Zabin I. Beta-galactosidase. Rates of synthesis and degradation of incomplete chains. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2205–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Translation of vesicular stomatitis messenger RNA by extracts from mammalian and plant cells. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):62–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.62-72.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngan J. S., Holloway A. F., Cormack D. V. Temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus: comparison of the in vitro RNA polymerase defects of group I and group IV mutants. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):765–772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.765-772.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman S. M., Huang A. S. RNA synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. V. Interactions between transcription and replication. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1395–1400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1395-1400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Miller J. H., Weber K. In vivo degradation of mutant lac repressor. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1154–1156. doi: 10.1038/2281154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. Genetic characteristics of conditional lethal mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus induced by 5-fluorouracil, 5-azacytidine, and ethyl methane sulfonate. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):559–567. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.559-567.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Printz-Ané C., Combard A., Martinet C. Study of the transcription and the replication of vesicular stomatitis virus by using temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):889–895. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.889-895.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Dumont R., Baltimore D. Screening procedure for complementation-dependent mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.41-49.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger J. T., Reichmann M. E. RNA synthesis in temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.570-578.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Závada J. Pseudotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus with the coat of murine leukaemia and of avian myeloblastosis viruses. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jun;15(3):183–191. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-15-3-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]