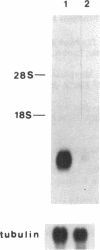
Abstract
Extracts of the bovine tracheal mucosa have an abundant peptide with potent antimicrobial activity. The 38-amino acid peptide, which we have named tracheal antimicrobial peptide (TAP), was isolated by a sequential use of size-exclusion, ion-exchange, and reverse-phase chromatographic fractionations using antimicrobial activity as a functional assay. The yield was approximately 2 micrograms/g of wet mucosa. The complete peptide sequence was determined by a combination of peptide and cDNA analysis. The amino acid sequence of TAP is H-Asn-Pro-Val-Ser-Cys-Val-Arg-Asn-Lys-Gly-Ile-Cys-Val-Pro-Ile-Arg-Cys-Pr o- Gly-Ser-Met-Lys-Gln-Ile-Gly-Thr-Cys-Val-Gly-Arg-Ala-Val-Lys-Cys-Cys-Arg- Lys-Lys - OH. Mass spectral analysis of the isolated peptide was consistent with this sequence and indicated the participation of six cysteine residues in the formation of intramolecular disulfide bonds. The size, basic charge, and presence of three intramolecular disulfide bonds is similar to, but clearly distinct from, the defensins, a well-characterized class of antimicrobial peptides from mammalian circulating phagocytic cells. The putative TAP precursor is predicted to be relatively small (64 amino acids), and the mature peptide resides at the extreme carboxyl terminus and is bracketed by a short putative propeptide region and an inframe stop codon. The mRNA encoding this peptide is more abundant in the respiratory mucosa than in whole lung tissue. The purified peptide had antibacterial activity in vitro against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In addition, the peptide was active against Candida albicans, indicating a broad spectrum of activity. This peptide appears to be, based on structure and activity, a member of a group of cysteine-rich, cationic, antimicrobial peptides found in animals, insects, and plants. The isolation of TAP from the mammalian respiratory mucosa may provide insight into our understanding of host defense of this vital tissue.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevins C. L., Zasloff M. Peptides from frog skin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:395–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlmann H., Clausen S., Behnke S., Giese H., Hiller C., Reimann-Philipp U., Schrader G., Barkholt V., Apel K. Leaf-specific thionins of barley-a novel class of cell wall proteins toxic to plant-pathogenic fungi and possibly involved in the defence mechanism of plants. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1559–1565. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Hultmark D. Cell-free immunity in insects. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B., Fink J., Merrifield R. B., Mauzerall D. Channel-forming properties of cecropins and related model compounds incorporated into planar lipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5072–5076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duclohier H., Molle G., Spach G. Antimicrobial peptide magainin I from Xenopus skin forms anion-permeable channels in planar lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82746-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Imai J., Fujiwara M., Yaeshima T., Kawashima T., Kobayashi K. A potent antibacterial protein in royal jelly. Purification and determination of the primary structure of royalisin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11333–11337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay J. E., Scott R. W., Campanelli D., Griffith J., Wilde C., Marra M. N., Seeger M., Nathan C. F. Antibiotic proteins of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Rayner J. R., Valore E. V., Tumolo A., Talmadge K., Fuller F. The structure of the rabbit macrophage defensin genes and their organ-specific expression. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1358–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Eur J Haematol. 1990 Jan;44(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1990.tb00339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini M. G., Poulter L., Gibson B. W., Williams D. H. Biosynthesis and degradation of peptides derived from Xenopus laevis prohormones. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):113–120. doi: 10.1042/bj2430113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W., Richter K., Kreil G. A novel peptide designated PYLa and its precursor as predicted from cloned mRNA of Xenopus laevis skin. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):711–714. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Selsted M. E., Ganz T., Lehrer R. I. Antimicrobial defensin peptides form voltage-dependent ion-permeable channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J., Keppi E., Dimarcq J. L., Wicker C., Reichhart J. M., Dunbar B., Lepage P., Van Dorsselaer A., Hoffmann J., Fothergill J. Insect immunity: isolation from immune blood of the dipteran Phormia terranovae of two insect antibacterial peptides with sequence homology to rabbit lung macrophage bactericidal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T. Neutrophils and host defense. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 15;109(2):127–142. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Limited N-terminal sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:602–613. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Purification of three antibacterial proteins from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17112–17116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Furunaka H., Miyata T., Tokunaga F., Muta T., Iwanaga S., Niwa M., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). Isolation and chemical structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16709–16713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson T., Samuelsson G. The amino acid sequence of viscotoxin A2 from the European mistletoe (Viscum album L., Loranthaceae). Acta Chem Scand. 1972;26(2):585–595. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.26-0585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette A. J., Greco R. M., James M., Frederick D., Naftilan J., Fallon J. T. Developmental regulation of cryptdin, a corticostatin/defensin precursor mRNA in mouse small intestinal crypt epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1687–1695. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Wada K., Hase T., Matsubara H., Nakanishi T., Yoshizumi H. Amino acid sequence of a purothionin homolog from barley flour. J Biochem. 1980 Feb;87(2):549–555. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Skerlavaj B., Bolognesi M., Gennaro R. Structure and bactericidal activity of an antibiotic dodecapeptide purified from bovine neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9573–9575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samakovlis C., Kimbrell D. A., Kylsten P., Engström A., Hultmark D. The immune response in Drosophila: pattern of cecropin expression and biological activity. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2969–2976. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Zimmermann R. Import of frog prepropeptide GLa into microsomes requires ATP but does not involve docking protein or ribosomes. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):699–703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antibacterial activity of antimicrobial peptides of rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):150–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.150-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soravia E., Martini G., Zasloff M. Antimicrobial properties of peptides from Xenopus granular gland secretions. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 15;228(2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H., Hultmark D., Engström A., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):246–248. doi: 10.1038/292246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade D., Boman A., Wåhlin B., Drain C. M., Andreu D., Boman H. G., Merrifield R. B. All-D amino acid-containing channel-forming antibiotic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhoff H. V., Juretić D., Hendler R. W., Zasloff M. Magainins and the disruption of membrane-linked free-energy transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6597–6601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. G., Griffith J. E., Marra M. N., Snable J. L., Scott R. W. Purification and characterization of human neutrophil peptide 4, a novel member of the defensin family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11200–11203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin: isolation, characterization of two active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]