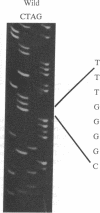
Abstract
Using an oligonucleotide hybridization assay, we studied the clinical implication of wild-type hepatitis B virus (HBV) and a HBV mutant that is unable to secrete hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) because of a translational defect due to a stop codon in the pre-C region in 106 hepatitis B surface antigen-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B. Wild-type HBV was detected in 31 of 42 (73.8%) HBeAg-positive patients, whereas a mixed viral population was present in 10 (23.8%). Significant differences in the severity and outcome of liver disease were not observed in the two groups of patients. However, the emergence of HBeAg-minus HBV in wild-type HBV carriers was associated with an exacerbation of liver disease and was followed by the presence of antibodies against HBeAg (anti-HBe) in serum in 50% of the cases. In 61 of 64 (95.3%) anti-HBe-positive patients, HBeAg-minus HBV was the predominant virus: HBeAg-minus HBV was detected in 42 patients (65.6%), whereas both wild-type and HBeAg-minus HBV were present in 19 (29.7%). HBeAg-minus HBV was associated with a course of hepatitis characterized by flare-ups of liver cell necrosis interspersed with periods of asymptomatic HBV carriage (P less than 0.01). These data support the hypothesis that genetic heterogeneity of HBV significantly influences the course and outcome of chronic hepatitis B. Wild-type HBV secreting HBeAg induces immunologic tolerance and causes chronic infection. HBeAg-minus HBV might be unable to induce chronic infection without the helper function of wild-type HBV, but it appears to be more pathogenic. Once chronic infection is established, HBeAg-minus HBV variants may prevail and displace wild-type virus.
Full text
PDF
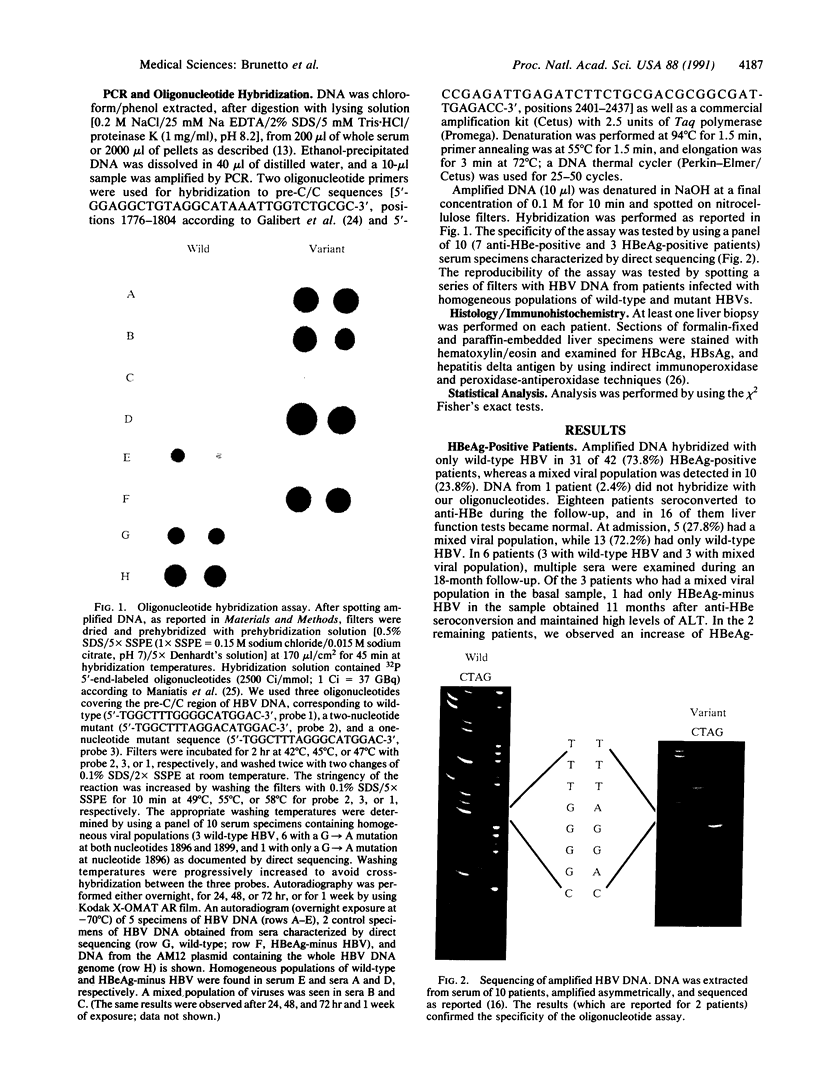


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonino F., Hoyer B., Nelson J., Engle R., Verme G., Gerin J. Hepatitis B virus DNA in the sera of HBsAg carriers: a marker of active hepatitis B virus replication in the liver. Hepatology. 1981 Sep-Oct;1(5):386–391. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonino F., Rosina F., Rizzetto M., Rizzi R., Chiaberge E., Tardanico R., Callea F., Verme G. Chronic hepatitis in HBsAg carriers with serum HBV-DNA and anti-HBe. Gastroenterology. 1986 May;90(5 Pt 1):1268–1273. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunetto M. R., Oliveri F., Rocca G., Criscuolo D., Chiaberge E., Capalbo M., David E., Verme G., Bonino F. Natural course and response to interferon of chronic hepatitis B accompanied by antibody to hepatitis B e antigen. Hepatology. 1989 Aug;10(2):198–202. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunetto M. R., Stemler M., Bonino F., Schodel F., Oliveri F., Rizzetto M., Verme G., Will H. A new hepatitis B virus strain in patients with severe anti-HBe positive chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 1990 Mar;10(2):258–261. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90062-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Jacyna M. R., Hadziyannis S., Karayiannis P., McGarvey M. J., Makris A., Thomas H. C. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):588–591. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattovich G., Brollo L., Alberti A., Giustina G., Pontisso P., Realdi G., Ruol A. Chronic persistent hepatitis type B can be a progressive disease when associated with sustained virus replication. J Hepatol. 1990 Jul;11(1):29–33. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90267-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadziyannis S. J., Lieberman H. M., Karvountzis G. G., Shafritz D. A. Analysis of liver disease, nuclear HBcAg, viral replication, and hepatitis B virus DNA in liver and serum of HBeAg Vs. anti-HBe positive carriers of hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 1983 Sep-Oct;3(5):656–662. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Shafritz D. A., Popper H. Chronic type B hepatitis and the "healthy" HBsAg carrier state. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):758–763. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Tong S., Vitvitski L., Zoulim F., Trépo C. Rapid detection and further characterization of infection with hepatitis B virus variants containing a stop codon in the distal pre-C region. J Gen Virol. 1990 Sep;71(Pt 9):1993–1998. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-9-1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok A. S., Hadziyannis S. J., Weller I. V., Karvountzis M. G., Monjardino J., Karayiannis P., Montano L., Thomas H. C. Contribution of low level HBV replication to continuing inflammatory activity in patients with anti-HBe positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gut. 1984 Nov;25(11):1283–1287. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.11.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Jones J. E., Hughes J. L., Price J., Raney A. K., McLachlan A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6599–6603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Yotsumoto S., Akahane Y., Yamanaka T., Miyazaki Y., Sugai Y., Tsuda F., Tanaka T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Hepatitis B viruses with precore region defects prevail in persistently infected hosts along with seroconversion to the antibody against e antigen. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1298–1303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1298-1303.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus gene function: the precore region targets the core antigen to cellular membranes and causes the secretion of the e antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1578–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimondo G., Schneider R., Stemler M., Smedile V., Rodino G., Will H. A new hepatitis B virus variant in a chronic carrier with multiple episodes of viral reactivation and acute hepatitis. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):64–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90274-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimondo G., Stemler M., Schneider R., Wildner G., Squadrito G., Will H. Latency and reactivation of a precore mutant hepatitis B virus in a chronically infected patient. J Hepatol. 1990 Nov;11(3):374–380. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90224-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Masiarz F. R., Rutter W. J. A signal peptide encoded within the precore region of hepatitis B virus directs the secretion of a heterogeneous population of e antigens in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8405–8409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Trépo C. Active hepatitis B virus replication in the presence of anti-HBe is associated with viral variants containing an inactive pre-C region. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):596–603. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90030-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Keshet E., Eliakim M., Shouval D. Detection and characterization of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum of HBe antigen-negative HBsAg carriers. J Med Virol. 1984;14(1):17–26. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uy A., Bruss V., Gerlich W. H., Köchel H. G., Thomssen R. Precore sequence of hepatitis B virus inducing e antigen and membrane association of the viral core protein. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R., Alexander G. J. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus-related liver disease and its relationship to serum markers of viral replication. J Hepatol. 1986;3 (Suppl 2):S3–S8. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(86)80094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada G., Takaguchi K., Matsueda K., Nishimoto H., Takahashi M., Fujiki S., Mizuno M., Kinoyama S., Tsuji T. Immunoelectron microscopic observation of intrahepatic HBeAg in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1990 Jul;12(1):133–140. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti A. R., Ferroni P., Magliano E. M., Pirovano P., Lavarini C., Massaro A. L., Gavinelli R., Fabris C., Rizzetto M. Perinatal transmission of the hepatitis B virus and of the HBV-associated delta agent from mothers to offspring in northern Italy. J Med Virol. 1982;9(2):139–148. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]