Abstract
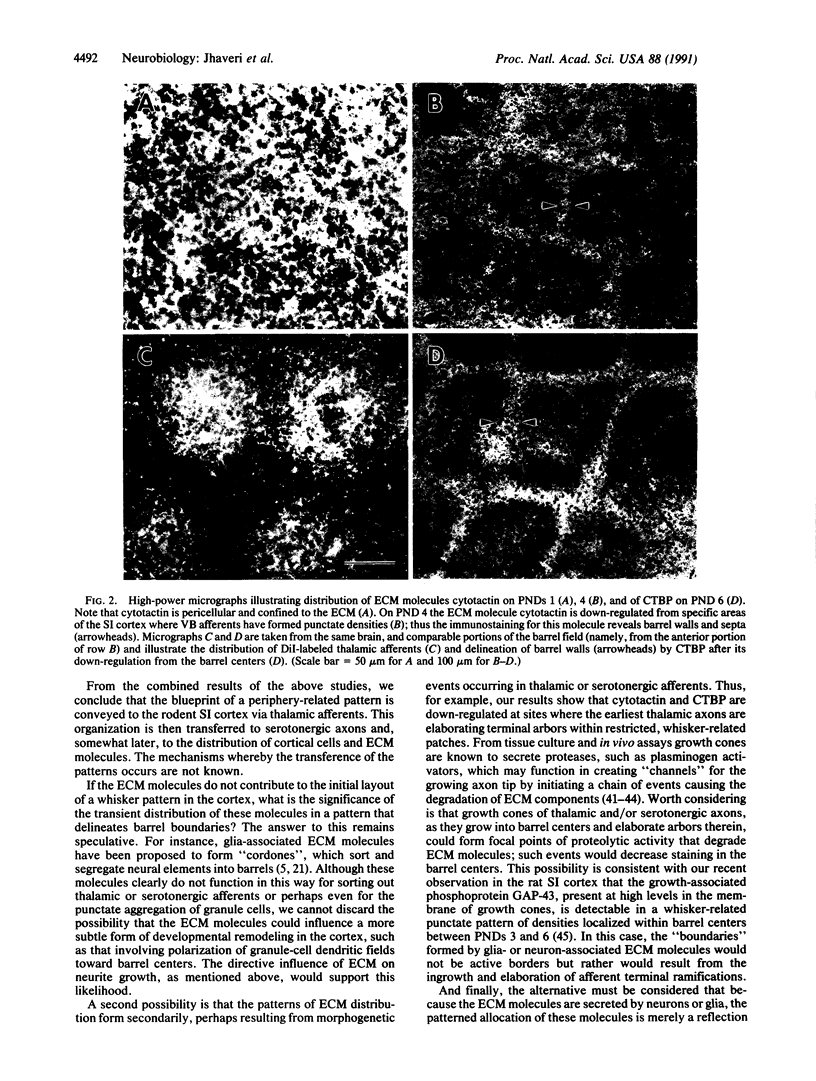
The rodent primary somatosensory cortex is characterized by aggregates of cellular and axonal elements that replicate the distribution of mystacial vibrissae on the face. The periphery-related cortical pattern ("barrels") is influenced by an amalgam of elements extrinsic (i.e., afferents) and intrinsic (i.e., neurons, glia, and their substrate) to the developing neocortex. To assign the role of some of these elements in cortical pattern formation, we have examined the temporal correlation between periphery-related patterns formed by thalamocortical axons and by extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules associated with neurons and glia in the cortex. Thalamocortical axons were labeled with the lipophilic tracer 1,1'-dioctydecyl-3,3,3',3'-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate (DiI) in aldehyde-fixed neonatal rat brains, and the same brains were also prepared for immunohistochemical localization of ECM molecules cytotactin and cytotactin-binding proteoglycan. We present evidence that thalamocortical axons form a periphery-related pattern well before such an organization is detectable in the distribution of ECM molecules. Furthermore, a patterned distribution of ECM molecules results from the down-regulation of these molecules from barrel centers, where thalamic axons have established vibrissa-specific patches. We conclude that thalamic axons convey the blueprint of the sensory periphery onto the neocortex and that ECM molecules do not participate in the initial formation of this pattern.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belford G. R., Killackey H. P. The sensitive period in the development of the trigeminal system of the neonatal rat. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Sep 15;193(2):335–350. doi: 10.1002/cne.901930203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belford G. R., Killackey H. P. Vibrissae representation in subcortical trigeminal centers of the neonatal rat. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jan 15;183(2):305–321. doi: 10.1002/cne.901830207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo K. L., Woolsey T. A. Axonal trajectories between mouse somatosensory thalamus and cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Apr 22;258(4):542–564. doi: 10.1002/cne.902580406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Mackie E. J., Pearson C. A., Sakakura T. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein involved in tissue interactions during fetal development and oncogenesis. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet M., Fambrough D. M. Chick myotendinous antigen. I. A monoclonal antibody as a marker for tendon and muscle morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1926–1936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet M. Tenascin/J1/cytotactin: the potential function of hexabrachion proteins in neural development. Dev Neurosci. 1989;11(4-5):266–275. doi: 10.1159/000111905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. G., Steindler D. A. Critical period-dependent alterations of the transient body image in the rodent cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 5;489(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. G., Steindler D. A. Lectins demarcate the barrel subfield in the somatosensory cortex of the early postnatal mouse. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 8;249(2):157–169. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. G., Steindler D. A. Monoclonal antibody to glial fibrillary acidic protein reveals a parcellation of individual barrels in the early postnatal mouse somatosensory cortex. Brain Res. 1986 Aug 20;380(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90232-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Hoffman S., Grumet M., Thiery J. P., Edelman G. M. Site-restricted expression of cytotactin during development of the chicken embryo. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1917–1930. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Hoffman S., Tan S. S., Edelman G. M. Cytotactin and its proteoglycan ligand mark structural and functional boundaries in somatosensory cortex of the early postnatal mouse. Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;136(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Prieto A. L., Hoffman S., Jones F. S., Friedlander D. R. Expression of adhesion molecules and the establishment of boundaries during embryonic and neural development. Exp Neurol. 1990 Jul;109(1):6–18. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(05)80004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato R. J., Blue M. E., Largent B. L., Lynch D. R., Ledbetter D. J., Molliver M. E., Snyder S. H. Ontogeny of the serotonergic projection to rat neocortex: transient expression of a dense innervation to primary sensory areas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erzurumlu R. S., Bates C. A., Killackey H. P. Differential organization of thalamic projection cells in the brain stem trigeminal complex of the rat. Brain Res. 1980 Oct 6;198(2):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90756-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erzurumlu R. S., Jhaveri S., Benowitz L. I. Transient patterns of GAP-43 expression during the formation of barrels in the rat somatosensory cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Feb 15;292(3):443–456. doi: 10.1002/cne.902920310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erzurumlu R. S., Jhaveri S. Thalamic axons confer a blueprint of the sensory periphery onto the developing rat somatosensory cortex. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 Nov 1;56(2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90087-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erzurumlu R. S., Killackey H. P. Development of order in the rat trigeminal system. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Feb 1;213(4):365–380. doi: 10.1002/cne.902130402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faissner A., Kruse J., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Mackie E. The high-molecular-weight J1 glycoproteins are immunochemically related to tenascin. Differentiation. 1988;37(2):104–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faissner A., Kruse J. J1/tenascin is a repulsive substrate for central nervous system neurons. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godement P., Vanselow J., Thanos S., Bonhoeffer F. A study in developing visual systems with a new method of staining neurones and their processes in fixed tissue. Development. 1987 Dec;101(4):697–713. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.4.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet M., Hoffman S., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Cytotactin, an extracellular matrix protein of neural and non-neural tissues that mediates glia-neuron interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. A proteoglycan with HNK-1 antigenic determinants is a neuron-associated ligand for cytotactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Killackey H. P. Terminal arbors of axons projecting to the somatosensory cortex of the adult rat. I. The normal morphology of specific thalamocortical afferents. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3529–3543. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03529.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Seeds N. W. Plasminogen activator release at the neuronal growth cone. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1532–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.7197054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Seeds N. W. Plasminogen activator secretion by granule neurons in cultures of developing cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7810–7814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D. Cell-derived proteases and protease inhibitors as regulators of neurite outgrowth. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Dec;11(12):541–544. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N., Ivins J. K., Buettner H. M. Neuronal plasminogen activators: cell surface binding sites and involvement in neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci. 1989 Dec;9(12):4269–4286. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-12-04269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Specification of cerebral cortical areas. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):170–176. doi: 10.1126/science.3291116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice F. L., Gomez C., Barstow C., Burnet A., Sands P. A comparative analysis of the development of the primary somatosensory cortex: interspecies similarities during barrel and laminar development. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jun 22;236(4):477–495. doi: 10.1002/cne.902360405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R. Extracellular matrix molecules that influence neural development. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:491–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steindler D. A., Cooper N. G., Faissner A., Schachner M. Boundaries defined by adhesion molecules during development of the cerebral cortex: the J1/tenascin glycoprotein in the mouse somatosensory cortical barrel field. Dev Biol. 1989 Jan;131(1):243–260. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steindler D. A., O'Brien T. F., Laywell E., Harrington K., Faissner A., Schachner M. Boundaries during normal and abnormal brain development: in vivo and in vitro studies of glia and glycoconjugates. Exp Neurol. 1990 Jul;109(1):35–56. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(05)80007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrle B., Chiquet M. Tenascin is accumulated along developing peripheral nerves and allows neurite outgrowth in vitro. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):401–415. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker C. Receptive fields of barrels in the somatosensory neocortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Mar 15;166(2):173–189. doi: 10.1002/cne.901660205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker C., Woolsey T. A. Structure of layer IV in the somatosensory neocortex of the rat: description and comparison with the mouse. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Dec 15;158(4):437–453. doi: 10.1002/cne.901580405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolsey T. A., Van der Loos H. The structural organization of layer IV in the somatosensory region (SI) of mouse cerebral cortex. The description of a cortical field composed of discrete cytoarchitectonic units. Brain Res. 1970 Jan 20;17(2):205–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]