Abstract
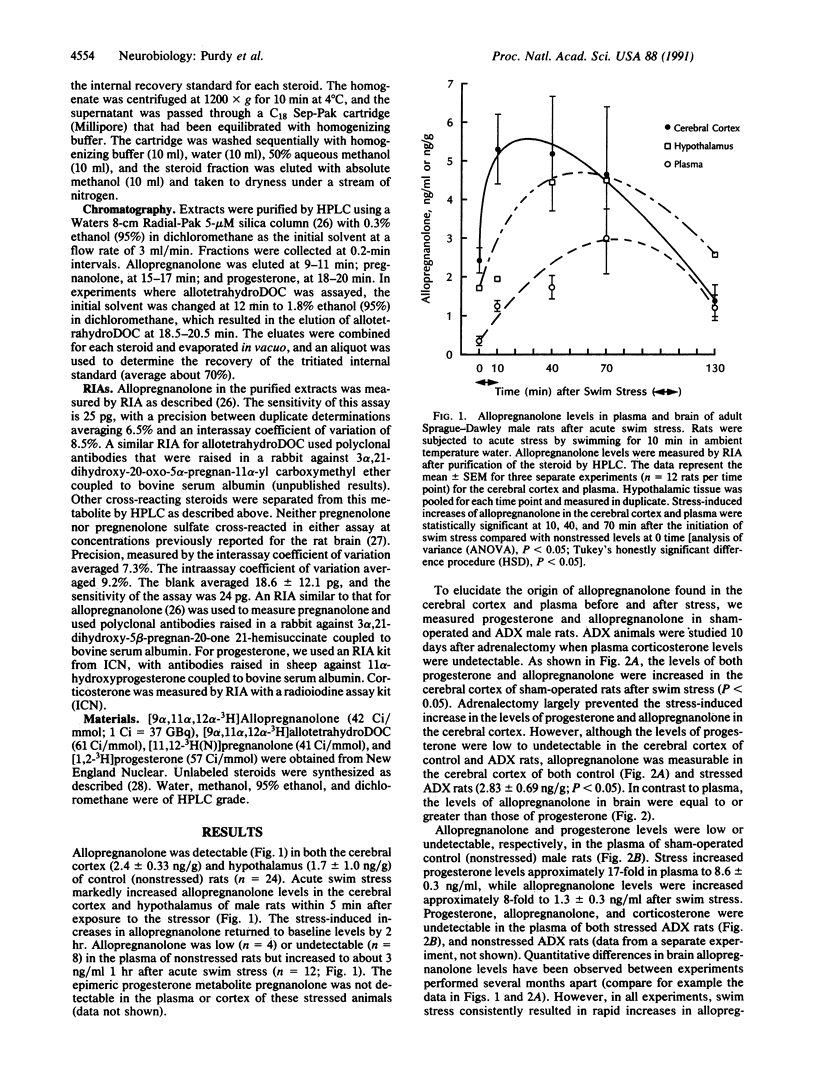
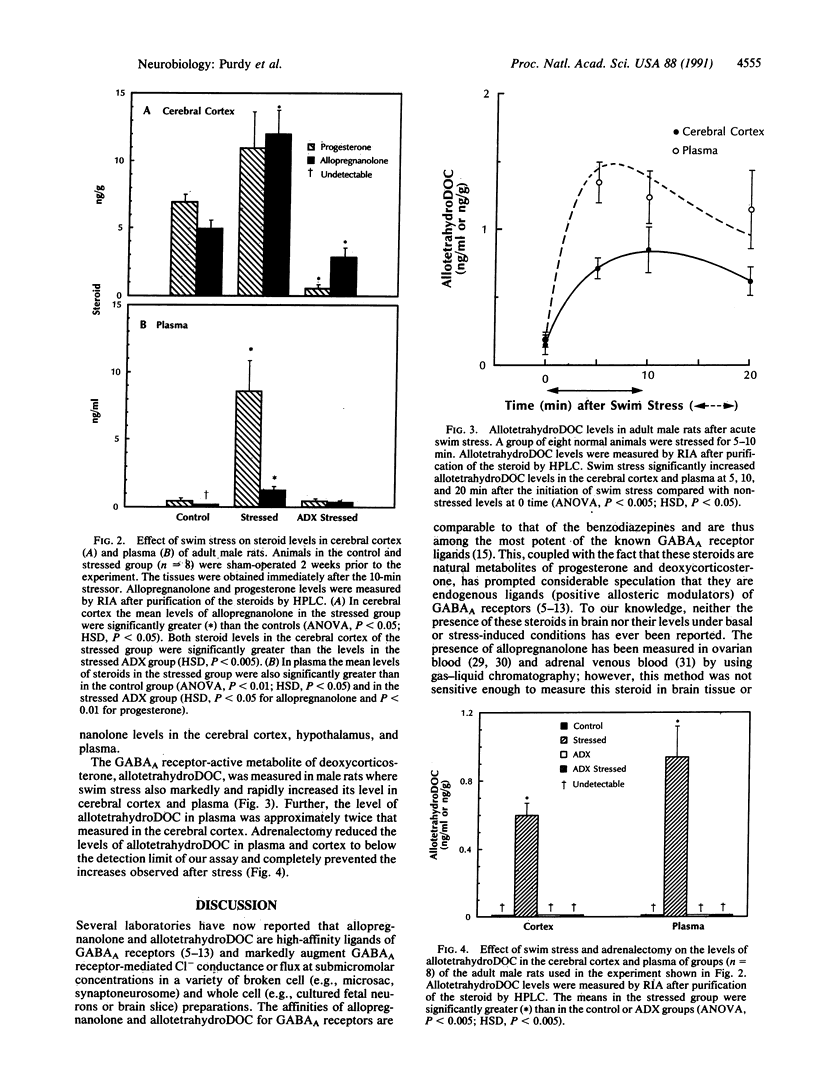
A 3 alpha-hydroxy A-ring-reduced metabolite of progesterone, 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one (allopregnanolone), and one of deoxycorticosterone (DOC), 3 alpha,21-dihydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20- one (allotetrahydroDOC), are among the most potent known ligands of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors designated GABAA in the central nervous system. With specific radioimmunoassays, rapid (less than 5 min) and robust (4- to 20-fold) increases of allopregnanolone and allotetrahydroDOC were detected in the brain (cerebral cortex and hypothalamus) and in plasma of rats after exposure to ambient temperature swin stress. Neither steroid was detectable in the plasma of adrenalectomized rats either before or after swim stress. However, allopregnanolone, but not allotetrahydroDOC, was still present in the cerebral cortex (greater than 3 ng/g) after adrenalectomy. These data demonstrate the presence of allopregnanolone and allotetrahydroDOC in brain and show that acute stress results in a rapid increase of these neuroactive steroids to levels known to modulate GABAA receptor function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker J. L., Harrison N. L., Lange G. D., Owen D. G. Potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric-acid-activated chloride conductance by a steroid anaesthetic in cultured rat spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:485–501. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnea A., Hajibeigi A., Trant J. M., Mason J. I. Expression of steroid metabolizing enzymes by aggregating fetal brain cells in culture: a model for developmental regulation of the progesterone 5 alpha-reductase pathway. Endocrinology. 1990 Jul;127(1):500–502. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-1-500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Neurosteroids: a new brain function? J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;37(3):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(90)90490-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belelli D., Bolger M. B., Gee K. W. Anticonvulsant profile of the progesterone metabolite 5 alpha-pregnan-3 alpha-ol-20-one. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul 18;166(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besman M. J., Yanagibashi K., Lee T. D., Kawamura M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Identification of des-(Gly-Ile)-endozepine as an effector of corticotropin-dependent adrenal steroidogenesis: stimulation of cholesterol delivery is mediated by the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovolin P., Schlichting J., Miyata M., Ferrarese C., Guidotti A., Alho H. Distribution and characterization of diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI) in peripheral tissues of rat. Regul Pept. 1990 Jul 30;29(2-3):267–281. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(90)90089-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callachan H., Cottrell G. A., Hather N. Y., Lambert J. J., Nooney J. M., Peters J. A. Modulation of the GABAA receptor by progesterone metabolites. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Aug 21;231(1264):359–369. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calogero A. E., Gallucci W. T., Chrousos G. P., Gold P. W. Interaction between GABAergic neurotransmission and rat hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone secretion in vitro. Brain Res. 1988 Oct 25;463(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90523-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpéchot C., Synguelakis M., Talha S., Axelson M., Sjövall J., Vihko R., Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Pregnenolone and its sulfate ester in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1983 Jun 27;270(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90797-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N., Glowa J. R., Majewska M. D., Paul S. M. Anxiolytic activity of an endogenous adrenal steroid. Brain Res. 1986 Nov 29;398(2):382–385. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91500-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee K. W., Bolger M. B., Brinton R. E., Coirini H., McEwen B. S. Steroid modulation of the chloride ionophore in rat brain: structure-activity requirements, regional dependence and mechanism of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Aug;246(2):803–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee K. W., Chang W. C., Brinton R. E., McEwen B. S. GABA-dependent modulation of the Cl- ionophore by steroids in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 29;136(3):419–423. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Forchetti C. M., Corda M. G., Konkel D., Bennett C. D., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Majewska M. D., Harrington J. W., Barker J. L. Structure-activity relationships for steroid interaction with the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor complex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Apr;241(1):346–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havoundjian H., Paul S. M., Skolnick P. Acute, stress-induced changes in the benzodiazepine/gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor complex are confined to the chloride ionophore. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):787–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbauer M., Birmingham M. K., De Nicola A. F., Oliver J. T. In vivo secretion of 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one, a potent anaesthetic steroid, by the adrenal gland of the rat. J Steroid Biochem. 1985 Jan;22(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(85)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbauer M. Physiological variations in the ovarian production of 5alpha-pregnane derivatives with sedative properties in the rat. J Steroid Biochem. 1975 Sep;6(9):1307–1310. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(75)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Z. Y., Bourreau E., Jung-Testas I., Robel P., Baulieu E. E. Neurosteroids: oligodendrocyte mitochondria convert cholesterol to pregnenolone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8215–8219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa S., Sawada T., Nakamura Y., Morioka H. Ovarian secretion of pregnane compounds during the estrous cycle and pregnancy in rats. Endocrinology. 1974 Jun;94(6):1615–1620. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-6-1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung-Testas I., Hu Z. Y., Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Neurosteroids: biosynthesis of pregnenolone and progesterone in primary cultures of rat glial cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2083–2091. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavaliers M., Wiebe J. P. Analgesic effects of the progesterone metabolite, 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one, and possible modes of action in mice. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 14;415(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger N. R., Scott R. G. Nonneuronal localization for steroid converting enzyme: 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase in olfactory tubercle of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1989 Jun;52(6):1866–1870. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger K. E., Papadopoulos V. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors mediate translocation of cholesterol from outer to inner mitochondrial membranes in adrenocortical cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15015–15022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Chen J. S., Belelli D., Pritchett D. B., Seeburg P. H., Gee K. W. A steroid recognition site is functionally coupled to an expressed GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 12;188(6):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanthier A., DiBattista J. A., Patwardhan V. V. Pregnenolone binding sites in the rat olfactory bulb. J Steroid Biochem. 1990 Mar;35(3-4):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(90)90258-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Harrison N. L., Schwartz R. D., Barker J. L., Paul S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):1004–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.2422758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melcangi R. C., Celotti F., Ballabio M., Castano P., Massarelli R., Poletti A., Martini L. 5 alpha-reductase activity in isolated and cultured neuronal and glial cells of the rat. Brain Res. 1990 May 21;516(2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90923-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Pace J. R., Purdy R. H., Paul S. M. Characterization of steroid interactions with gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-gated chloride ion channels: evidence for multiple steroid recognition sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):263–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Suzdak P. D., Paul S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites potentiate GABA receptor-mediated chloride ion flux with nanomolar potency. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 27;142(3):483–485. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhin A. G., Papadopoulos V., Costa E., Krueger K. E. Mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors regulate steroid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9813–9816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Kirkness E. F., Callachan H., Lambert J. J., Turner A. J. Modulation of the GABAA receptor by depressant barbiturates and pregnane steroids. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1257–1269. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Santi M. R., Vicini S., Pritchett D. B., Purdy R. H., Paul S. M., Seeburg P. H., Costa E. Neurosteroids act on recombinant human GABAA receptors. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90202-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy R. H., Moore P. H., Jr, Rao P. N., Hagino N., Yamaguchi T., Schmidt P., Rubinow D. R., Morrow A. L., Paul S. M. Radioimmunoassay of 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one in rat and human plasma. Steroids. 1990 Jul;55(7):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(90)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy R. H., Morrow A. L., Blinn J. R., Paul S. M. Synthesis, metabolism, and pharmacological activity of 3 alpha-hydroxy steroids which potentiate GABA-receptor-mediated chloride ion uptake in rat cerebral cortical synaptoneurosomes. J Med Chem. 1990 Jun;33(6):1572–1581. doi: 10.1021/jm00168a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. A., Karavolas H. J. Conversion of progesterone by rat anterior pituitary tissue to 5 alpha-pregnane-3,20-dione and 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one. Endocrinology. 1973 Aug;93(2):430–435. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-2-430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D., Wess M. J., Labarca R., Skolnick P., Paul S. M. Acute stress enhances the activity of the GABA receptor-gated chloride ion channel in brain. Brain Res. 1987 May 12;411(1):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90692-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick P., Paul S. M. Benzodiazepine receptors in the central nervous system. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1982;23:103–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. M., Ransom R. W., Yang J. S., Olsen R. W. Steroid anesthetics and naturally occurring analogs modulate the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor complex at a site distinct from barbiturates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):960–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincens M., Shu C., Moguilewsky M., Philibert D. A progesterone metabolite enhances the activity of the GABAA receptor complex at the pituitary level. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 1;168(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90627-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


