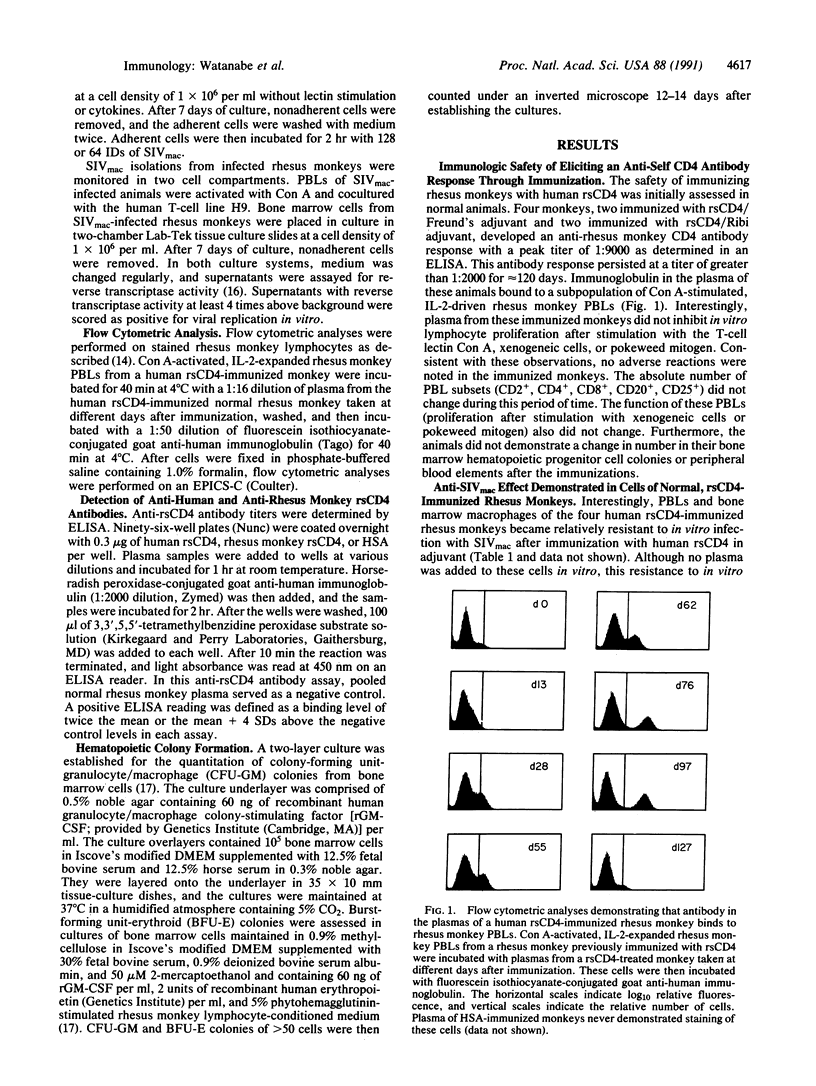
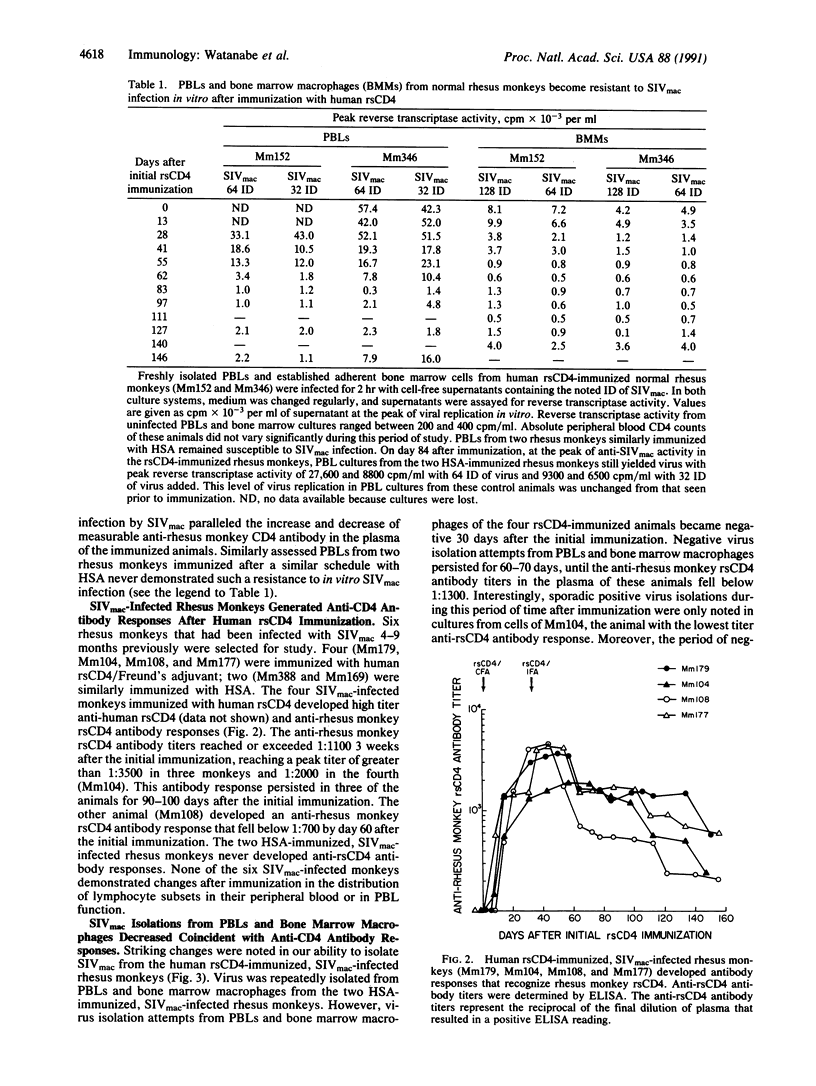
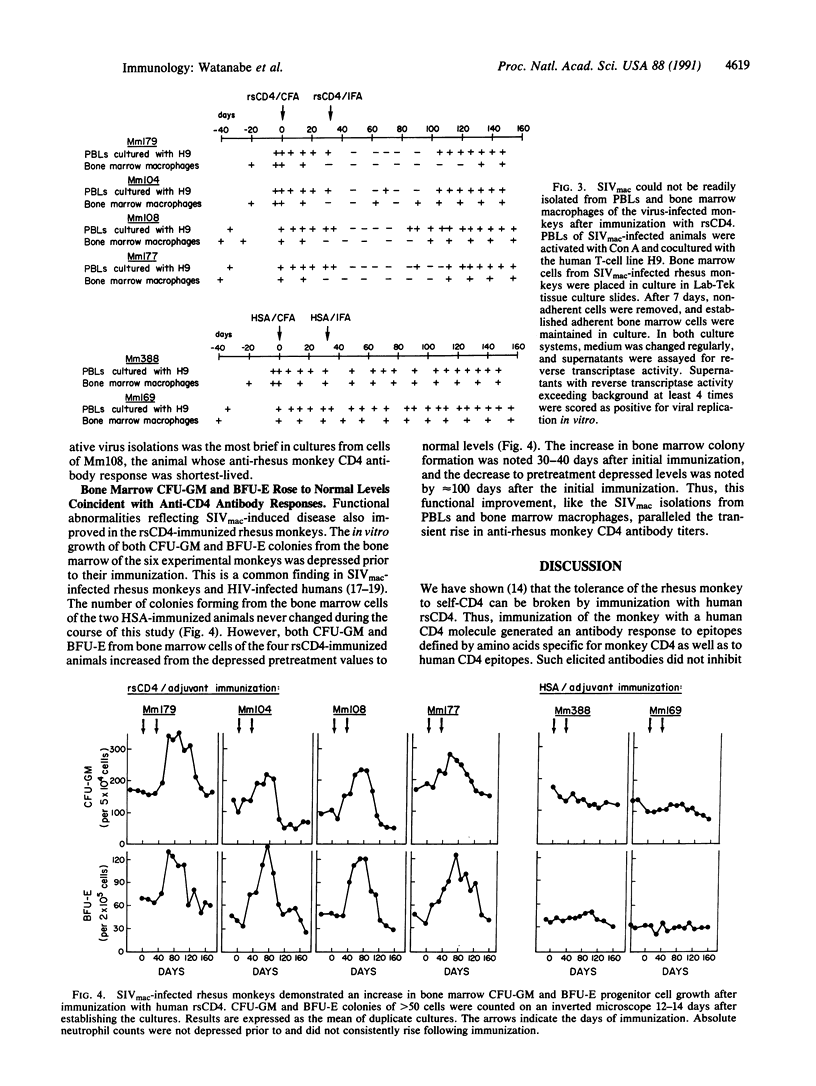
Abstract
Since the CD4 molecule is a high-affinity cell-surface receptor for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), it has been suggested that a soluble truncated form of CD4 may compete with cell-surface CD4 for HIV binding and thus be of use in the therapy of AIDS. We have utilized the simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques (SIVmac)-infected rhesus monkeys to explore another possible therapeutic application of CD4 in AIDS--the use of recombinant soluble CD4 (rsCD4) as an immunogen. SIVmac-infected rhesus monkeys immunized with human rsCD4 developed not only an anti-human CD4 but also an anti-rhesus monkey CD4 antibody response. Coincident with the generation of this antibody response, SIVmac could not be isolated easily from peripheral blood lymphocytes and bone marrow macrophages of these animals. Furthermore, the decreased number of both granulocyte/macrophage and erythrocyte colonies grown from the bone marrow of these immunized monkeys rose to normal levels. These findings suggest that a modified human CD4 molecule serving as an immunogen might elicit an antibody response in man that could induce a beneficial therapeutic response in HIV-infected individuals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger E. A., Clouse K. A., Chaudhary V. K., Chakrabarti S., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I., Moss B. CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin hybrid protein blocks the spread of human immunodeficiency virus infection in vitro and is active against cells expressing the envelope glycoproteins from diverse primate immunodeficiency retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9539–9543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Mizukami T., Fuerst T. R., FitzGerald D. J., Moss B., Pastan I., Berger E. A. Selective killing of HIV-infected cells by recombinant human CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin hybrid protein. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):369–372. doi: 10.1038/335369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen K. C., McDougal J. S., Inacker R., Folena-Wasserman G., Arthos J., Rosenberg J., Maddon P. J., Axel R., Sweet R. W. A soluble form of CD4 (T4) protein inhibits AIDS virus infection. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):82–84. doi: 10.1038/331082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Bertonis J. M., Meier W., Johnson V. A., Costopoulos D. S., Liu T., Tizard R., Walker B. D., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T. HIV infection is blocked in vitro by recombinant soluble CD4. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):76–78. doi: 10.1038/331076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey R. E., Richardson N. E., Kowalski M., Brown N. R., Chang H. C., Siliciano R. F., Dorfman T., Walker B., Sodroski J., Reinherz E. L. A soluble CD4 protein selectively inhibits HIV replication and syncytium formation. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):78–81. doi: 10.1038/331078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. O., Allan J. D., Hodges T. L., Kaplan L. D., Arri C. J., Fitch H. F., Izu A. E., Mordenti J., Sherwin J. E., Groopman J. E. The safety and pharmacokinetics of recombinant soluble CD4 (rCD4) in subjects with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. A phase 1 study. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Feb 15;112(4):254–261. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-4-. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi M., Yetz J. M., Letvin N. L. In vitro growth characteristics of simian T-lymphotropic virus type III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7053–7057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. W., Chalifoux L. V., Ringler D. J., Wyand M. S., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., Desrosiers R. C., Blake B. J., Hunt R. D. Comparative biology of natural and experimental SIVmac infection in macaque monkeys: a review. J Med Primatol. 1990;19(2):109–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiderman I. Z., Greenberg M. L., Adelsberg B. R., Siegal F. P. A glycoprotein inhibitor of in vitro granulopoiesis associated with AIDS. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1267–1272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Daniel M. D., Sehgal P. K., Desrosiers R. C., Hunt R. D., Waldron L. M., MacKey J. J., Schmidt D. K., Chalifoux L. V., King N. W. Induction of AIDS-like disease in macaque monkeys with T-cell tropic retrovirus STLV-III. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2412295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann K. A., Turner S., Lambert J. M., Reed M. H., Schlossman S. F., Letvin N. L. In vivo administration of lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in nonhuman primates. V. Evidence that humoral immune response to monoclonal antibodies and immunotoxin conjugates abrogates their cytotoxic activity. Transplantation. 1989 Dec;48(6):906–912. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198912000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley R. T., Merigan T. C., Gaut P., Hirsch M. S., Holodniy M., Flynn T., Liu S., Byington R. E., Henochowicz S., Gubish E. Recombinant soluble CD4 therapy in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. A phase I-II escalating dosage trial. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Feb 15;112(4):247–253. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-4-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Byrn R. A., Marsters S. A., Gregory T., Groopman J. E., Capon D. J. Blocking of HIV-1 infectivity by a soluble, secreted form of the CD4 antigen. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1704–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.3500514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stella C. C., Ganser A., Hoelzer D. Defective in vitro growth of the hemopoietic progenitor cells in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):286–293. doi: 10.1172/JCI113071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till M. A., Ghetie V., Gregory T., Patzer E. J., Porter J. P., Uhr J. W., Capon D. J., Vitetta E. S. HIV-infected cells are killed by rCD4-ricin A chain. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1166–1168. doi: 10.1126/science.2847316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traunecker A., Lüke W., Karjalainen K. Soluble CD4 molecules neutralize human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):84–86. doi: 10.1038/331084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubota H., Winkler G., Meade H. M., Jakubowski A., Thomas D. W., Letvin N. L. CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin conjugates delay but do not fully inhibit human immunodeficiency virus replication in lymphocytes in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1684–1689. doi: 10.1172/JCI114892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Chen Z. W., Tsubota H., Lord C. I., Levine C. G., Letvin N. L. Soluble human CD4 elicits an antibody response in rhesus monkeys that inhibits simian immunodeficiency virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):120–124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Reimann K. A., DeLong P. A., Liu T., Fisher R. A., Letvin N. L. Effect of recombinant soluble CD4 in rhesus monkeys infected with simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):267–270. doi: 10.1038/337267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Ringler D. J., Nakamura M., DeLong P. A., Letvin N. L. Simian immunodeficiency virus inhibits bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor cell growth. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.656-663.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


