Abstract
Background
Severe mental illness (SMI) is common, chronic and difficult to treat. Sleep and circadian dysfunctions are prominent correlates of SMI, yet have been minimally studied in ways that reflect the complexity of the sleep problems experienced. Prior treatment studies have been disorder-focused—they have treated a specific sleep problem in a specific diagnostic group. However, real life sleep and circadianproblems are not so neatly categorized, particularly in SMI where features of insomnia overlap with hypersomnia, delayed sleep phase and irregular sleep-wake schedules. Accordingly, the aim of this studyprotocol is to test the hypothesis that a Transdiagnostic Intervention for Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction (TranS-C) will improve functional impairment, disorder-focused symptoms and sleep and circadian functioning. Participants across DSM diagnoses and across common sleep and circadian problems are eligible. The elements of TranS-C are efficacious across SMI in research settings with research-based providers. The next step is to test TranS-C in a community setting. Accordingly, this study is being conducted within Alameda County Behavioral Health Care Services (ACBHCS), the Community Mental Health Centre (CMHC) for Alameda County.
Methods/design
120 adults diagnosed with SMI and sleep and circadian dysfunction within ACBHCS will be randomly allocated to TranS-C (n = 60) or 6-months of Usual Care followed by Delayed Treatment with TranS-C (UC-DT; n = 60). TranS-C is modularized and delivered across eight to twelve 50-minute, weekly, individual sessions. All participants will be assessed before and immediately following treatment and again 6 months later. Primary analysis will examine whether TranS-C significantly improves functional impairment, disorder-specific symptoms and sleep and circadian functioning, relative to UC-DT. Exploratory analysis will examine whether improvements in sleep and circadian functioning predict reduction in functional impairment and disorder-specific symptoms, and whether the intervention effects are mediated by improved sleep and circadian functioning and moderated by previously reported risk factors (demographics, symptom severity, medications, psychiatric and medical comorbidity).
Discussion
This trial tests an important and understudied mechanism—dysregulated sleep and circadian rhythms—in SMI, a novel transdiagnostic treatment approach, in a community setting so as to contribute to the goal of bridging the gap between research and practice.
Trial registration
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02469233. Registered on 9 June 2015.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13063-016-1690-9) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Transdiagnostic, Sleep, circadian, Severe mental illness, Dissemination
Background
The number of people receiving a treatment for severe mental illness (SMI) has risen [1–3], and health care expenditures have skyrocketed [2]. Yet, less than half of the treatments delivered have an evidence base [4–6], and there is no evidence that available treatments decrease disability [7]. Instead, the prevalence of mental illness is increasing [8–10]. Accordingly, providing the large number of people with an SMI access to evidence-based treatments requires fundamentally new approaches [11, 12].
One relatively new approach is to target research and treatment at a transdiagnostic process. A transdiagnostic process is defined, in mental health, as a clinical feature in common across more than one mental illness [13–16]. The advantage of targeting research and treatment at a transdiagnostic process is threefold. First, if a transdiagnostic process contributes to the maintenance of symptoms across multiple disorders, then one approach is to develop treatments based on the process rather than on the large number of discrete disorders currently listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) [14]. Second, comorbidity is the norm [17, 18]. Hence, a significant clinical dilemma is which disorders to prioritize for treatment [14]. Treating transdiagnostic processes provides one path forward [13, 14]. Third, a transdiagnostic approach may reduce the heavy burden on clinicians, who must learn multiple disorder-focused protocols, by focusing on common theoretical underpinnings and interventions [13].
Sleep and circadian dysfunction has been highlighted as a biologically [19] and theoretically [20] plausible transdiagnostic contributor to SMI [13], and a transdiagnostic treatment for sleep and circadian disturbance has been proposed [21]. The present study protocol tests the hypothesis that the Transdiagnostic Intervention for Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction (TranS-C) for participants with SMI will improve functional impairment, disorder-focused symptoms, and sleep and circadian dysfunction.
Why is sleep and circadian dysfunction important in SMI?
First, sleep and circadian dysfunction coexists with, predates, and predicts SMI. Insomnia, hypersomnia, delayed sleep phase, and irregular sleep-wake schedules are commonly comorbid with SMI [22–26]. The rate of insomnia across DSM disorders is approximately 50% [25]. The rate of hypersomnia is as high as 75% across the mood disorders [26]. These problems often persist even with best practice treatment for SMI [27–31]. Across multiple longitudinal studies, sleep and circadian dysfunction predicts and predates the onset and worsening of SMI symptoms [32–41]. Second, sleep and circadian dysfunction contributes to vicious cycles of mutually reinforcing symptoms in SMI, including emotional dysfunction [42, 43], poor health [44, 45], cognitive dysfunction [46, 47], and behavior problems [48, 49]. Third, sleep and circadian dysfunction is modifiable in SMI. Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) effectively treats insomnia that is comorbid with a wide range of SMIs, including major depressive disorder [50], posttraumatic stress disorder [51–54], schizophrenia [55], bipolar disorder [56, 57], alcohol dependence [58], and mixed SMI [59–61]. There is evidence that these gains are well-maintained following the cessation of treatment [62]. There is also evidence that treating insomnia improves the symptoms of the comorbid disorder [50, 51, 55, 63]. In our study, we will test a treatment that addresses an important and understudied transdiagnostic mechanism—dysregulated sleep and circadian rhythms—in SMI. It also addresses an understudied conceptual framework, namely that sleep and circadian dysfunction contributes to vicious cycles of escalating vulnerability and increased risk in SMI.
The majority of prior studies have been disorder-focused—they have been designed to treat a specific sleep problem (e.g., insomnia) in a specific diagnostic group (e.g., depression, posttraumatic stress disorder). Real-life sleep and circadian problems are not so neatly categorized, particularly in SMI. Indeed, insomnia can overlap with hypersomnia [26, 33, 64–67], delayed sleep phase [68], and irregular sleep-wake schedules [28]. In a prior study, CBT-I was modified to address the broader range of sleep dysfunctions in SMI [56, 57], adding elements from interpersonal and social rhythm therapy [69, 70], chronotherapy [71], and motivational enhancement [72–74]. Strong results reported by other groups [75] and advice from dissemination experts [76, 77] led us to develop a modularized transdiagnostic treatment [21].
Real-world setting: community mental health centers
There has been ample testing of sleep and circadian interventions in specific disorders in research settings with research-based providers. Hence, the next step is to conduct an “efficacy in the real world” study in community settings with community-based providers while maintaining the high level of control necessary to establish internal validity. This next step is important because there is currently a 15- to 20-year lag between treatment discovery and incorporating new treatments into routine practice [12, 78]. Initial results indicate that providing CBT-I in various real-world settings is effective [79–81].
Sleep health
The sleep health framework [82] underpins and guides TranS-C. The sleep health framework prompts a shift from a singular focus on the identification and treatment of sleep disorders to a health promotion perspective, which emphasizes universal attributes of sleep that can be optimized to promote well-being. The sleep health framework encourages sleep improvement along six dimensions that have been linked to mental and physical health outcomes [82]. The dimensions are (a) regularity of sleep and waking up; (b) satisfaction with sleep or sleep quality; (c) alertness during waking hours or daytime sleepiness; (d) appropriate timing of the patient’s sleep within a 24-h day; (e) sleep efficiency (i.e., the ability to sleep for a large percentage of the time in bed), as indicated by ease of falling asleep at the beginning of the night and the ease of returning to sleep after awakenings across the night; and (f) sleep duration, which is the total amount of sleep obtained by the patient per 24 h.
The main aim of this study protocol is to evaluate the effects of TranS-C vs. usual care followed by delayed treatment with TranS-C (UC-DT) on functional impairment, disorder-focused symptoms, and sleep and circadian function in participants receiving treatment for SMI in a community mental health center. The hypothesis tested is that TranS-C will be superior to UC-DT at posttreatment and 6-month follow-up for functional impairment, disorder-focused symptoms, and sleep and circadian function.
In exploratory analyses, we will address (a) whether improved sleep and circadian functioning predicts reduced functional impairment and disorder-focused symptoms, regardless of treatment condition; (b) whether improved sleep and circadian functioning mediates the intervention effects (TranS-C vs. UC-DT) on functional impairment and disorder-focused symptoms; and (c) whether intervention effects are moderated by previously reported risk factors.
Methods/design
Study design and setting
We are conducting a prospective randomized controlled study. Adults (n = 120) who meet criteria for SMI and sleep and circadian dysfunction will be randomly assigned, in a 1:1 parallel-group design, to undergo TranS-C (n = 60) or UC-DT (n = 60) (see Fig. 1 for study design flowchart). Randomization is stratified by psychosis (yes or no) and age (older or younger than 49 years). Participants will receive a battery of outcome measures pretreatment and again at posttreatment (i.e., 9–14 weeks later) and at 6-month follow-up. Those in the UC-DT group will receive two additional assessments: 9–14 weeks and 6 months into UC-DT. An additional assessment of sleep and circadian function will take place in session 4 for the mediation analysis.
Fig. 1.
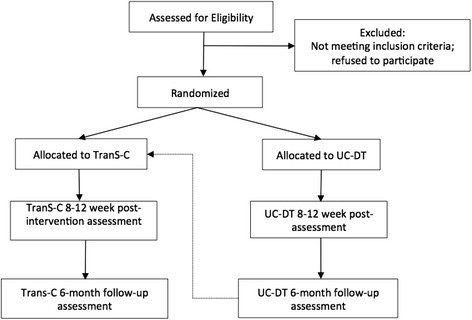
Flowchart of study design
The assessment and therapy teams are blinded to treatment allocation. Randomization will be conducted using a computerized random number generator where the planned stratification randomization is part of the allocation sequence. Only the statistician (LD), the project coordinator, and the assigned therapist know the treatment allocation of each participant. Participants are financially compensated for their time. A Data and Safety Monitoring Board will review the study every 6 months during the active treatment phase. A Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials (SPIRIT 2013) checklist (see Additional file 1) and figure (see Table 1) are provided [83].
Table 1.
SPIRIT checklist
| Time point | Study period | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrollment | Pretreatment assessment | Allocation | Postallocation | |||
| Intervention | Post-Treatment Assessment | 6-Month follow-up | ||||
| Enrollment | ||||||
| Eligibility screen | X | |||||
| Informed consent | X | X | ||||
| Allocation | X | |||||
| Intervention | ||||||
| TranS-C | X | |||||
| UC-DT1 | ||||||
| Data collection | ||||||
| Demographics | X | X | X | |||
| Primary outcomes | X | X | X | |||
| Secondary outcomes | X | X | X | |||
| Diagnostic measures | X | X | X | |||
| Sleep/insomnia history | X | |||||
| Medication tracking | X | X | X | X | ||
| Credibility/expectancy | X | |||||
Abbreviations: TranS-C Transdiagnostic Intervention for Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction, UC-DT Usual care followed by delayed treatment with Transdiagnostic Intervention for Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction.1Allocation to TranS-C after 6-months of usual care.
For participants who discontinue, the assessment team will endeavor to collect all assessment data, prioritizing the primary outcomes.
Participants
A total of 120 adults who meet criteria for SMI and sleep and circadian dysfunction are recruited from multiple sites within Alameda County Behavioral Health Care Services (ACBHCS; Alameda County, CA, USA). To date, these sites are Oakland Community Support Center (Oakland), Eden Mental Health Services (San Leandro), Tri City Community Support Center (Fremont), Alameda Support Center (Alameda), Axis Community Health (Pleasanton), La Familia Counseling (Hayward), and multiple board and care homes. Participants are referred via ACBHCS case managers and doctors. The inclusion and exclusion criteria are presented below. To enhance representativeness and generalizability, the inclusion and exclusion criteria are kept to a minimum.
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria are as follows:
Aged 18+ years
English language fluency
Presence of at least one DSM-5 mental disorder for 12 months
-
One or more of the following sleep or circadian problems for 3 months assessed with the
Sleep and Circadian Problems Interview:- ≥30 minutes to get to sleep on three or more nights per week
- Waking in the middle of the night for ≥30 minutes on three or more nights per week
- Obtaining <6 h of sleep per night on three or more nights per week. Obtaining more than 9 hours of sleep per 24 hour period (i.e., nighttime sleep plus daytime napping), 3 or more nights per week
- More than 2.78 h of variability in sleep-wake schedule across 1 week
- Bedtime later than 2:00 a.m. on three or more nights per week
Having a guaranteed bed to sleep in for 3 months
Receiving care for SMI at ACBHCS and consent to regular communications between research team and psychiatrist and/or case manager
Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria are as follows:
Presence of an active and progressive physical illness or neurological degenerative disease and/or substance abuse/dependence making participation in the study infeasible
Current serious suicide risk (assessed by our staff, a case manager, or a psychiatrist) or homicide risk (assessed by our staff, a case manager, or a psychiatrist)
Night shift work >2 nights per week in the past 3 months
Pregnancy or breastfeeding
Not able/willing to participate in and/or complete the pretreatment assessments
For the present study protocol, SMI is operationalized according to U.S. Public Law 102-321 and previous research [84–86] as the presence, for 12 months, of at least one DSM-5-defined mental disorder that leads to substantial interference with one or more major life activities [87].
Sleep apnea and periodic limb movement disorder are often comorbid with insomnia [88, 89], and individuals with these sleep disorders typically have poor sleep habits. Hence, we elected to include these individuals. Indeed, there is already some evidence that these participants benefit from CBT-I [63, 90].
Pharmacotherapy for SMI is a complex undertaking guided both by empirical evidence and by the specific experiences and responses of individual participants. Excluding participants whose medications need to be changed is neither feasible nor representative of clinical practice [91]. Medication use and changes will be recorded. All medication decisions will ultimately rest with the treating physican and participant.
Measures
In addition to demographics (age, contact information, sex, race/ethnicity, family, education, employment, living arrangements, government assistance, housing), the measures described in the subsections below will be administered.
Primary outcomes
Functional impairment is assessed with the Sheehan Disability Scale [92], which is a widely used brief measure. The DSM-5 Cross-Cutting Measure is used as a measure of disorder-focused symptoms. Sleep and circadian function is assessed with the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System–Sleep Disturbance (PROMIS-SD) [93, 94] and the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System–Sleep-Related Impairment (PROMIS-SRI) [93, 94], which are brief, comprehensive, and well-validated. The PROMIS scales are also administered at session 4 for the mediation analysis.
Secondary outcomes
Impairment is assessed with the self-administered version of the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0 and the 4-question healthy days core module developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [95]. Disorder-focused symptoms are assessed using the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptoms [96]; the Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test [97]; and the Psychotic Symptoms Rating Scales [98]. Sleep and circadian function is assessed with the daily sleep diary and actigraphy, collected for 7 days at each assessment point. The outcomes to be analyzed using the sleep diary are the mean and variability in sleep efficiency (total sleep time/time in bed × 100), total sleep time (TST), total wake time (TWT), bedtime, wake time, and rise time. In addition, nap duration will be calculated. The actigraphy outcomes to be analyzed are the means and variability for TST and TWT, as well as the daytime activity count. In addition, we will calculate a composite sleep health score [82], which is defined as the sum of scores on six sleep health dimensions: regularity (midpoint fluctuation across the 7-day sleep diary), satisfaction (sleep quality question on PROMIS-SD), alertness (daytime sleepiness question on PROMIS-SRI), timing (mean midpoint across the 7-day sleep diary), efficiency (sleep efficiency based on the 7-day sleep diary), and duration (TST based on 7-day sleep diary). This measure is proposed to capture the complexity of the sleep problems covered by TranS-C.
Other measures
The diagnostic measure used for mental disorders is the M.I.N.I. International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) (version 7.0.0, including schizophrenia and psychotic disorders). The MINI is included as an evaluation of the presence of current and past SMI. The MINI was developed to meet the need for a simple, short, but accurate structured psychiatric interview. Its validity has been well-supported [99–101]. At each assessment, we will report the number of DSM-5 diagnoses derived from the MINI. The diagnostic measure we will use for sleep disorders is the Duke Structured Interview for Sleep Disorders (DUKE) [102].
Sleep/insomnia history is obtained with the Sleep and Circadian Problems Interview, which is an adapted version of the Insomnia Interview Schedule [103]. To improve our ability to identify obstructive sleep apnea, we will supplement the proposed DUKE assessment with the STOP-BANG Questionnaire [104], which is an 8-item screen for obstructive sleep apnea. Both measures are well-validated and widely used. Those suspected to have another sleep disorder will receive nonstudy evaluation/treatment and will not be excluded. At each assessment, we will report the number of sleep diagnoses derived from the DUKE. The medication tracking log will be used to record the treatments patients are receiving. Treatment credibility/expectancy is administered at session 2 via the Credibility/Expectancy Questionnaire [105, 106].
Treatments
TranS-C
TranS-C is administered by master’s-level therapists hired within the University of California, Berkeley, for this study, who travel between the ACBHCS clinic sites. As participants move through the treatment at different rates, TranS-C is provided in eight weekly 50-minute sessions. If patients need additional sessions to cover the treatment, up to four additional sessions may be offered (i.e., maximum of 12 sessions). TranS-C includes four cross-cutting interventions featured in every session; four core modules that apply to the vast majority of participants; and seven optional modules used less commonly, depending on the presentation. Table 2 summarizes the approach.
Table 2.
Summary of the Transdiagnostic Intervention for Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction
| Cross-cutting modules introduced in sessions 1-3 (and featured in all sessions thereafter) | Module Topics in TranS-C | Treatment module |
|---|---|---|
| Case formulation | Establishing regular sleep-wake times | Core module 1, part a |
| Education | Learning a wind-down routine | Core module 1, part b |
| Behavior change and motivation | Learning a wake-up routine | Core module 1, part c |
| Goal-setting | Improving daytime functioning | Core module 2 |
| Correcting unhelpful sleep-related beliefs | Core module 3 | |
| Improving sleep efficiency | Optional module 1 | |
| Reducing time in bed | Optional module 2 | |
| Dealing with delayed or advanced phase | Optional module 3 | |
| Reducing sleep-related worry/vigilance | Optional module 4 | |
| Promoting compliance with CPAP/exposure therapy for claustrophobic reactions to CPAP | Optional module 5 | |
| Negotiating sleep in a complicated environment | Optional module 6 | |
| Reducing nightmares | Optional module 7 | |
| Maintenance of behavior change | Core module 4 |
Abbreviations: CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure, SMI Severe mental illness, TranS-C Transdiagnostic Intervention for Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction
Usual care followed by delayed treatment with TranS-C
The aim of the choice to compare TranS-C with UC-DT is to strike a balance between (a) including a comparison group to test the effectiveness of TranS-C in community settings, information critical to determining the potential of TranS-C for broader dissemination; and (b) ensuring that all participants receive what is hypothesized to be a more active treatment (TranS-C). Usual care in ACBHCS starts with a case manager who coordinates care and refers each client for a medication review and to various rehabilitation programs (e.g., health care, housing, nutrition, physical activity, finding a job, meditation group, tobacco cessation group, peer monitoring). The content of usual care will be monitored using the medication and other treatment tracking logs. As depicted in Fig. 1, at the end of 8 months in UC-DT, the participants will receive 8 to 12 sessions of TranS-C.
Treatment implementation and monitoring
Clinicians attend a one-day workshop, use a treatment manual and receive weekly supervision to standardize treatment administration. Treatment sessions are audiotaped, and a random selection are rated using the Cognitive Therapy Scale [107], which is a measure of general intervention skills and CBT-specific skills.
Data analysis
Preliminary data evaluation
Missing or aberrant data will be verified. Data will be audited for quality and completeness. We will detect outliers by evaluation of distributions and ensure that assumptions of planned analyses are met. Prior to hypothesis testing, appropriate statistical tests will be used to examine baseline differences between groups (e.g., race/ethnicity, age, sex, education, employment, psychiatric and medical comorbidities). These tests will not be used to select covariates in the primary intention-to-treat analysis [108–110]. Instead, the potential influences of baseline differences will be evaluated as moderators (described below).
Management of missing data
Recruiting 120 participants allows for attrition as per the power calculation below. In longitudinal analyses, we will use all available data and produce valid inferences if attrition depends on treatment group or on previous outcomes for the same participant [111]. If dropout is related to other variables, these data will be included as predictors to reduce any bias due to nonrandom missing data.
Main aim
TranS-C will be superior to UC-DT for reducing functional impairment and disorder-focused symptoms, and for improving sleep and circadian functioning, at posttreatment and 6-month follow-up on primary outcomes. To address these aims, we will test whether there are differences in the mean trajectories across time points between TranS-C and UC-DT using hierarchical linear modeling (HLM) [112–114]. The first-level equation will represent within-person variation and will include time indicators (or dummy variables) as predictors (posttreatment, 6-month follow-up assessment, with baseline as a reference). The second-level equation represents between-person variation in the intercept and coefficients of the time indicators, and will include a dummy variable for arm (TranS-C vs. UC-DT) as the predictor variable. Interactions between arm and time indicators will be retained only if found to be significant at the 5% level. A significant interaction between arm and a time indicator suggests that there are different trajectories of change in outcome across time for each arm, and will be displayed as a graph to interpret the interaction.
Exploratory analyses
For the exploratory analyses, we will use only the primary outcome measures for impairment, disorder-focused symptoms, and sleep and circadian function:
Do improved sleep and circadian functioning predict reduced functional impairment and disorder-focused symptoms from baseline to posttreatment? We will use HLM to test whether changes in sleep and circadian functioning predict changes in functional impairment and disorder-focused symptoms from baseline to posttreatment.
Do improved sleep and circadian functioning mediate intervention effects on primary outcomes? We will conduct mediation analysis using product of coefficients, a powerful method for estimating indirect effects [115]. The mediator will be sleep and circadian functioning measured at session 4, and outcomes will be functional impairment and disorder-focused symptoms measured at posttreatment.
Are intervention effects moderated by risk factors, including demographics, symptom severity, medications, and psychiatric and medical comorbidities? We will conduct moderation analysis by testing a three-way interaction of treatment arm, time, and the moderator variable in the second-level equation using the HLM model described above [116, 117]. A significant coefficient for the arm × time × moderator interaction would indicate a moderating effect and will be followed with graphs to interpret the modification [116].
A statistical significance level of 0.05 will be used throughout.
Power analysis
Average effect size across outcomes akin to those proposed were drawn from prior research [56, 79, 80] (0.60). Using G*Power 3.1.7 software, 80% power, and a two-tailed alpha of 5%, we will need 92 participants to detect group differences. An additional 30% to account for potential attrition yields 120 participants.
Discussion
The study protocol addresses several research priorities. First, this study provides a test of a treatment that addresses an important and understudied mechanism—dysregulated sleep and circadian rhythms—in SMI. It also addresses an understudied conceptual framework, namely that sleep and circadian dysfunction contributes to vicious cycles of escalating symptoms, vulnerability, and risk in SMI. Second, this study provides a test of a transdiagnostic treatment designed to treat a wide range of sleep and circadian problems experienced by adults with a wide range of SMIs. As such, the study contributes to the goal of developing interventions that use broad, dimensional approaches to assessment and intervention [118, 119]. Third, the sleep health framework [82] that underpins the approach is relatively new. This approach emphasizes the identification and treatment of sleep disorders as well as the universal attributes of sleep that can be optimized to promote well-being. Fourth, the modular design of TranS-C, as well as the personalized behavioral “prescriptions,” are responsive to the calls to “develop a personalized approach to the diverse needs and circumstances of people with mental illness” [120, page 128]. Finally, this study will be conducted in a community setting. Conducting the study in a community setting contributes to the goal of bridging the gap between research and practice and testing treatments in the community. If the study is successful, this research will establish the potential for widespread dissemination of TranS-C to improve SMI outcomes in the community.
Trial status
The trial is funded for 4 years. A ‘skeleton’ research staff team started setting up the study in February 2015. Patients began to be randomized in July 2015. The treatment phase will be completed in July 2018. Final outcome assessments will be complete by January 2019. As of November 2016, 70 participants of the required 120 had been enrolled.
Acknowledgements
The DSMB is composed of three members: Descartes Li, MD; Rachel Loewy, PhD; and Philip Gehrman, PhD. The DSMB reviews the progress and safety of study procedures twice per year and is responsible for safeguarding the interests of study participants. This committee is independent of the sponsor. We are deeply grateful to Dr. Alan Chapman; Faith Fuller; Adina Hemley-Bronstein; and the therapists (Kerry Kulstad-Thomas, Hanna Mark, Michael Dolsen, Niki Gumport, Caitlin Eggleston, and Jorin Bukosky) and the staff, case managers, and physicians at ACBHCS (Dr. Amanda Bachuss, Erin Bliss, Algernol Boozer, Dr. Floyd Brown, Andrea Christian, Dr. Alan Cohen, Gil Cortes, Maureen Costello, Breton Courtney, Carla Danby, Sam Davis, Marc Diamond, Kim Flores, Dr. Lori Glassie, Dr. Shana Green, Mark Gross, Karen Hamayadan, Beau Heath, Nandita Hegde, Vermeille Hill, Dr. James Hinson, Manton Hurd, Madilyn Johnson, Denise Kennedy, Lorraine Lilley, Tony Limperopulos, Dr. Nia Lozano, Susannah MacKaye, Michelle Nelson-Lewis, Corani Robles, Dr. Luisito Roxas, Susie Saechao, Courtney Sage, Tiffany Sarrach, Sandra Smith, Todd Stephenson, Kenya Sullivan, Dr. Sui-Kwong Sung, Colleen Timpane, Remy Wax, Shawan Worsley, and Sadaya Zimmerle).
Funding
This study is funded by the National Institute of Mental Health (grant MH105513). The funding agency has/had no role in the design, collection, management, analysis, or interpretation of data; the writing of the manuscript; or the decision to submit the study protocol for publication. The funding agency has no ultimate authority over any of these activities.
Availability of data and materials
Other than the authors and compliance with data-sharing agreements stipulated by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), no other entities have contractual agreements with regard to access to the final dataset.
Authors’ contributions
AGH, DJB, KH, FLS, ML, and SRH conceived of and designed the study and acquired the funding. AGH, KH, LD, and SY are responsible for the acquisition of data. LD and SRH are responsible for the analysis and interpretation of data. AGH drafted the manuscript. All authors were involved in revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
DJB has served as a paid consultant to the following (<$5000 per year for each): BeHealth Solutions LLC, Bayer, Janssen,Cereve, Emmi Solutions, Merck, CME Outfitters, and Medscape; has received licensing royalties for the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, the Insomnia Symptom Questionnaire, the Consensus Sleep Diary (intellectual property rights), and BeHealth Solutions, LLC; and has received payment from Astellas Pharma for continuing medical education lectures. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The University of California, Berkeley, Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects (CPHS) approved the study (protocol 2014-07-6508). As depicted in Table 1, verbal informed consent is obtained during the initial eligibility assessment, which is typically conducted over the telephone. This is followed by written informed consent obtained at the beginning of the preassessment, which confirms eligibility, by a member of the assessment team. See Additional file 2. Adverse events and other unintended effects will be report to the CPHS and the NIH, following the rules stipulated by these two oversight bodies. If important protocol modifications are made, these will be reviewed by the CPHS and reported on the trial’s ClinicalTrials.gov registration web page.
Abbreviations
- ACBHCS
Alameda County Behavioral Health Care Services
- CBT-I
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia
- CPAP
Continuous positive airway pressure
- DSM-5
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition
- DUKE
Duke Structured Interview for Sleep Disorders
- HLM
Hierarchical linear modeling
- MINI
M.I.N.I. International Neuropsychiatric Interview
- PROMIS-SD
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System–Sleep Disturbance
- PROMIS-SRI
Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System–Sleep-Related Impairment
- QIDS
Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology
- SMI
Severe mental illness
- SPIRIT
Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials
- TAU
Treatment as usual
- TranS-C
Transdiagnostic Intervention for Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction
- TST
Total sleep time
- TWT
Total wake time
- UC-DT
Usual care followed by delayed treatment with Transdiagnostic Intervention for Sleep and Circadian Dysfunction
Additional files
Completed SPIRIT checklist of recommended items to address in a clinical trial protocol. (PDF 109 kb)
Consent form. (PDF 63 kb)
Contributor Information
Allison G. Harvey, Phone: (510) 642-7138, Email: aharvey@berkeley.edu
Kerrie Hein, Email: kerriehein@berkeley.edu.
Lu Dong, Email: lu.dong@berkeley.edu.
Freddie L. Smith, Email: fsmith@acbhcs.org
Michael Lisman, Email: mlisman@acbhcs.org.
Stephanie Yu, Email: stephanieyu@berkeley.edu.
Sophia Rabe-Hesketh, Email: sophiarh@berkeley.edu.
Daniel J. Buysse, Email: buyssedj@upmc.edu
References
- 1.Kessler RC, Demler O, Frank RG, Olfson M, Pincus HA, Walters EE, et al. Prevalence and treatment of mental disorders, 1990 to 2003. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2515–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa043266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services . National health expenditure tables. Baltimore: Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Olfson M, Marcus SC. National patterns in antidepressant medication treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(8):848–56. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Koretz D, Merikangas KR, et al. The epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R) JAMA. 2003;289:3095–105. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.23.3095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wang PS, Lane M, Olfson M, Pincus HA, Wells KB, Kessler RC. Twelve-month use of mental health services in the United States: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:629–40. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shafran R, Clark DM, Fairburn CG, Arntz A, Barlow DH, Ehlers A, et al. Mind the gap: improving the dissemination of CBT. Behav Res Ther. 2009;47(11):902–9. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2009.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Insel TR. Translating scientific opportunity into public health impact: a strategic plan for research on mental illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(2):128–33. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2008.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2013;380(9859):2197–223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2013;380(9859):2163–96. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2013;380(9859):2095–128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kazdin AE, Blase SL. Rebooting psychotherapy research and practice to reduce the burden of mental illness. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2011;6:21–37. doi: 10.1177/1745691610393527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kazdin AE, Rabbitt SM. Novel models for delivering mental health services and reducing the burdens of mental illness. Clin Psychol Sci. 2013;1(2):170–91. doi: 10.1177/2167702612463566. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Harvey AG, Watkins E, Mansell W, Shafran R. Cognitive behavioural processes across psychological disorders: a transdiagnostic approach to research and treatment. New York: Oxford University Press; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mansell W, Harvey A, Watkins E, Shafran R. Conceptual foundations of the transdiagnostic approach to CBT. J Cogn Psychother. 2009;23(1):6–19. doi: 10.1891/0889-8391.23.1.6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fairburn CG, Cooper Z, Shafran R. Cognitive behaviour therapy for eating disorders: a “transdiagnostic” theory and treatment. Behav Res Ther. 2003;41:509–28. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7967(02)00088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Barlow DH, Allen LB, Choate ML. Toward a unified treatment for emotional disorders. Behav Ther. 2004;35:205–30. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7894(04)80036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:617–27. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kessler RC, Merikangas KR, Wang PS. Prevalence, comorbidity, and service utilization for mood disorders in the United States at the beginning of the twenty-first century. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2007;3:137–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.3.022806.091444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Harvey AG, Murray G, Chandler RA, Soehner A. Sleep disturbance as transdiagnostic: consideration of neurobiological mechanisms. Clin Psychol Rev. 2011;31:225–35. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Harvey AG. Insomnia, psychiatric disorders, and the transdiagnostic perspective. Curr Direct Psychol Sci. 2008;17:299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8721.2008.00594.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Harvey AG. A transdiagnostic approach to treating sleep disturbance in psychiatric disorders. Cogn Behav Ther. 2009;38:35–42. doi: 10.1080/16506070903033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Benca RM, Obermeyer WH, Thisted RA, Gillin JC. Sleep and psychiatric disorders: a meta-analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992;49:651–70. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820080059010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institutes of Health State of the Science Conference Statement: manifestations and management of chronic insomnia in adults June 13–15, 2005. Sleep. 2005;28:1049–57. doi: 10.1093/sleep/28.9.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Smith MT, Huang MI, Manber R. Cognitive behavior therapy for chronic insomnia occurring within the context of medical and psychiatric disorders. Clin Psychol Rev. 2005;25:559–92. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2005.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Roth T, Jaeger S, Jin R, Kalsekar A, Stang PE, Kessler RC. Sleep problems, comorbid mental disorders, and role functioning in the national comorbidity survey replication. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60(12):1364–71. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.05.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kaplan KA, Harvey AG. Hypersomnia across mood disorders: a review and synthesis. Sleep Med Rev. 2009;13(4):275–85. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2008.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sachs GS, Thase ME, Otto MW, Bauer M, Miklowitz D, Wisniewski SR, et al. Rationale, design, and methods of the Systematic Treatment Enhancement Program for Bipolar Disorder (STEP-BD) Biol Psychiatry. 2003;53:1028–42. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(03)00165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gruber J, Harvey AG, Wang PW, Brooks JO, 3rd, Thase ME, Sachs GS, et al. Sleep functioning in relation to mood, function, and quality of life at entry to the Systematic Treatment Enhancement Program for Bipolar Disorder (STEP-BD) J Affect Disord. 2009;114:41–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2008.06.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gruber J, Miklowitz DJ, Harvey AG, Frank E, Kupfer D, Thase ME, et al. Sleep matters: sleep functioning and course of illness in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. 2011;134:416–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nierenberg AA, Husain MM, Trivedi MH, Fava M, Warden D, Wisniewski SR, et al. Residual symptoms after remission of major depressive disorder with citalopram and risk of relapse: a STAR*D report. Psychol Med. 2010;40(1):41–50. doi: 10.1017/S0033291709006011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nierenberg AA, Keefe BR, Leslie VC, Alpert JE, Pava JA, Worthington JJ, III, et al. Residual symptoms in depressed patients who respond acutely to fluoxetine. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60:221–5. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v60n0403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ford DE, Kamerow DB. Epidemiologic study of sleep disturbances and psychiatric disorders: an opportunity for prevention? JAMA. 1989;262:1479–84. doi: 10.1001/jama.1989.03430110069030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Breslau N, Roth T, Rosenthal L, Andreski P. Sleep disturbance and psychiatric disorders: a longitudinal epidemiological study of young adults. Biol Psychiatry. 1996;39:411–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(95)00188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Johnson EO, Roth T, Breslau N. The association of insomnia with anxiety disorders and depression: exploration of the direction of risk. J Psychiatry Res. 2006;40(8):700–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2006.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bryant RA, Creamer M, O’Donnell M, Silove D, McFarlane AC. Sleep disturbance immediately prior to trauma predicts subsequent psychiatric disorder. Sleep. 2010;33(1):69–74. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Perlis ML, Smith LJ, Lyness JM, Matteson SR, Pigeon WR, Jungquist C, et al. Insomnia as a risk factor for onset of depression in the elderly. Behav Sleep Med. 2006;4:104–13. doi: 10.1207/s15402010bsm0402_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.McLay RN, Klam WP, Volkert SL. Insomnia is the most commonly reported symptom and predicts other symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder in US service members returning from military deployments. Mil Med. 2010;175(10):759–62. doi: 10.7205/MILMED-D-10-00193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chang PP, Ford DE, Mead LA, Cooper-Patrick L, Klag MJ. Insomnia in young men and subsequent depression: the Johns Hopkins Precursors Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;146:105–14. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jansson-Fromark M, Lindblom K. A bidirectional relationship between anxiety and depression, and insomnia? A prospective study in the general population. J Psychosom Res. 2008;64(4):443–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Perlis ML, Giles DE, Buysse DJ, Tu X, Kupfer DJ. Self-reported sleep disturbance as a prodromal symptom in recurrent depression. J Affect Disord. 1997;42:209–12. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0327(96)01411-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sivertsen B, Harvey AG, Lundervold AJ, Hysing M. Sleep problems and depression in adolescence: results from a large population-based study of Norwegian adolescents aged 16–18 years. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;23(8):681–9. doi: 10.1007/s00787-013-0502-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Perlis ML, Nielsen TA. Mood regulation, dreaming and nightmares: evaluation of a desensitization function for REM sleep. Dreaming. 1993;3:243–57. doi: 10.1037/h0094383. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cartwright R, Luten A, Young M, Mercer P, Bears M. Role of REM sleep and dream affect in overnight mood regulation: a study of normal volunteers. Psychiatry Res. 1998;81:1–8. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1781(98)00089-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Roth T, Coulouvrat C, Hajak G, Lakoma MD, Sampson NA, Shahly V, et al. Prevalence and perceived health associated with insomnia based on DSM-IV-TR; International Statistical Classification of Diseases and related health problems, Tenth Revision; and Research Diagnostic Criteria/International Classification of Sleep Disorders, Second Edition criteria: results from the America Insomnia Survey. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69:592–600. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.10.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Buysse D, Grunstein R, Horne J, Lavie P. Can an improvement in sleep positively impact on health? Sleep Med Rev. 2010;14:405–10. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2010.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Van Dongen HP, Maislin G, Mullington JM, Dinges DF. The cumulative cost of additional wakefulness: dose-response effects on neurobehavioral functions and sleep physiology from chronic sleep restriction and total sleep deprivation. Sleep. 2003;26:117–26. doi: 10.1093/sleep/26.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Goel N, Rao H, Durmer JS, Dinges DF. Neurocognitive consequences of sleep deprivation. Semin Neurol. 2009;29:320–39. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1237117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Adan A, Natale V, Caci H, Prat G. Relationship between circadian typology and functional and dysfunctional impulsivity. Chronobiol Int. 2010;27:606–19. doi: 10.3109/07420521003663827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Medeiros M, Carvalho LB, Silva TA, Prado LB, Prado GF. Sleep disorders are associated with impulsivity in school children aged 8 to 10 years. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2005;63(3B):761–5. doi: 10.1590/S0004-282X2005000500008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Manber R, Edinger JD, Gress JL, San Pedro-Salcedo MG, Kuo TF, Kalista T. Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia enhances depression outcome in patients with comorbid major depressive disorder and insomnia. Sleep. 2008;31:489–95. doi: 10.1093/sleep/31.4.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Germain A, Shear MK, Hall M, Buysse DJ. Effects of a brief behavioral treatment for PTSD-related sleep disturbances: a pilot study. Behav Res Ther. 2007;45:627–32. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2006.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ulmer CS, Edinger JD, Calhoun PS. A multi-component cognitive-behavioral intervention for sleep disturbance in veterans with PTSD: a pilot study. J Clin Sleep Med. 2011;7(1):57–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Germain A, Richardson R, Moul DE, Mammen O, Haas G, Forman SD, et al. Placebo-controlled comparison of prazosin and cognitive-behavioral treatments for sleep disturbances in US military veterans. J Psychosom Res. 2012;72(2):89–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2011.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Margolies SO, Rybarczyk B, Vrana SR, Leszczyszyn DJ, Lynch J. Efficacy of a cognitive‐behavioral treatment for insomnia and nightmares in Afghanistan and Iraq veterans With PTSD. J Clin Psychol. 2013;69(10):1026–42. doi: 10.1002/jclp.21970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Myers E, Startup H, Freeman D. Cognitive behavioural treatment of insomnia in individuals with persistent persecutory delusions: a pilot trial. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2011;42:330–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jbtep.2011.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Harvey AG, Soehner AM, Kaplan KA, Hein K, Lee J, Kanady J, et al. Treating insomnia improves sleep, mood and functioning in bipolar disorder: a pilot randomized controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015;83(3):564–77. doi: 10.1037/a0038655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kaplan KA, Harvey AG. Behavioral treatment of insomnia in bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170(7):716–20. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12050708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Arnedt JT, Conrov D, Rutt J, Aloia MS, Brower KJ, Armitage R. An open trial of cognitive-behavioral treatment for insomnia comorbid with alcohol dependence. Sleep Med. 2007;8:176–80. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2006.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lichstein KL, Wilson NM, Johnson CT. Psychological treatment of secondary insomnia. Psychol Aging. 2000;15:232–40. doi: 10.1037/0882-7974.15.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Perlis ML, Sharpe M, Smith MT, Greenblatt D, Giles D. Behavioral treatment of insomnia: treatment outcome and the relevance of medical and psychiatric morbidity. J Behav Med. 2001;24:281–96. doi: 10.1023/A:1010770807823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Edinger JD, Olsen MK, Stechuchak KM, Means MK, Lineberger MD, Kirby A, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for patients with primary insomnia or insomnia associated predominantly with mixed psychiatric disorders: a randomized clinical trial. Sleep. 2009;32(4):499–510. doi: 10.1093/sleep/32.4.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Morin CM, Bootzin RR, Buysse DJ, Edinger JD, Espie CA, Lichstein KL. Psychological and behavioral treatment of insomnia: an update of recent evidence (1998–2004) Sleep. 2006;29:1396–406. doi: 10.1093/sleep/29.11.1398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wu JQ, Appleman ER, Salazar RD, Ong JC. Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia comorbid with psychiatric and medical conditions: a meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(9):1461–72. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.3006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kaplan KA, Gruber J, Eidelman P, Talbot LS, Harvey AG. Hypersomnia in inter-episode bipolar disorder: does it have prognostic significance? J Affect Disord. 2011;132(3):438–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Liu X, Buysse DJ, Gentzler AL, Kiss E, Mayer L, Kapornai K, et al. Insomnia and hypersomnia associated with depressive phenomenology and comorbidity in childhood depression. Sleep. 2007;30:83–90. doi: 10.1093/sleep/30.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Roberts RE, Shema SJ, Kaplan GA, Strawbridge WJ. Sleep complaints and depression in an aging cohort: a prospective perspective. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157(1):81–8. doi: 10.1176/ajp.157.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ohayon MM. Determining the level of sleepiness in the American population and its correlates. J Psychiatr Res. 2012;46(4):422–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Giglio LM, Magalhães P, Andersen ML, Walz JC, Jakobson L, Kapczinski F. Circadian preference in bipolar disorder. Sleep Breath. 2010;14:153–5. doi: 10.1007/s11325-009-0301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Frank E, Kupfer DJ, Thase ME, Mallinger A, Swartz H, Fagioli A, et al. Two year outcomes for interpersonal and social rhythm therapy in individuals with bipolar I disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:996–1004. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.9.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Frank E, Swartz HA, Kupfer DJ. Interpersonal and social rhythm therapy: managing the chaos of bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;48:593–604. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(00)00969-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wirz-Justice A, Benedetti F, Terman M. Chronotherapeutics for affective disorders: a clinician’s manual for light & wake therapy. Basel, Switzerland: Karger; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational interviewing: preparing people for change. 2. New York: Guilford Press; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Keller PA, Harlam B, Loewenstein G, Volpp KG. Enhanced active choice: a new method to motivate behavior change. J Consum Psychol. 2011;21:376–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jcps.2011.06.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Pearson ES. Goal setting as a health behavior change strategy in overweight and obese adults: a systematic literature review examining intervention components. Patient Educ Couns. 2012;87:32–42. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2011.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Weisz JR, Chorpita BF, Palinkas LA, Schoenwald SK, Miranda J, Bearman SK, et al. Testing standard and modular designs for psychotherapy treating depression, anxiety, and conduct problems in youth: a randomized effectiveness trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(3):274–82. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Chorpita BF, Daleiden EL, Weisz JR. Modularity in the design and application of therapeutic interventions. Appl Prevent Psychol. 2005;11(3):141–56. doi: 10.1016/j.appsy.2005.05.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Kilbourne AM, Neumann MS, Pincus HA, Bauer MS, Stall R. Implementing evidence-based interventions in health care: application of the replicating effective programs framework. Implement Sci. 2007;2:42. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-2-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Sundararaman R. The U.S. mental health delivery system infrastructure: a primer. Washington, DC: Congressional Research Service; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Espie CA, MacMahon KM, Kelly HL, Broomfield NM, Douglas NJ, Engleman HM, et al. Randomized clinical effectiveness trial of nurse-administered small-group cognitive behavior therapy for persistent insomnia in general practice. Sleep. 2007;30:574–84. doi: 10.1093/sleep/30.5.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Espie CA, Fleming L, Cassidy J, Samuel L, Taylor LM, White CA, et al. Randomized controlled clinical effectiveness trial of cognitive behavior therapy compared with treatment as usual for persistent insomnia in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(28):4651–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.9006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Karlin BE, Trockel M, Taylor CB, Gimeno J, Manber R. National dissemination of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia in veterans: therapist- and patient-level outcomes. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2013;81(5):912–7. doi: 10.1037/a0032554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Buysse DJ. Sleep health: can we define it? Does it matter? Sleep. 2014;37(1):9–17. doi: 10.5665/sleep.3298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Chan AW, Tetzlaff JM, Gøtzsche PC, Altman DG, Mann H, Berlin JA, et al. SPIRIT 2013 explanation and elaboration: guidance for protocols of clinical trials. BMJ. 2013;346:e7586. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e7586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Wang PS, Demler O, Kessler RC. Adequacy of treatment for serious mental illness in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2002;92(1):92–8. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.92.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kessler RC, Barker PR, Colpe LJ, Epstein JF, Gfroerer JC, Hiripi E, et al. Screening for serious mental illness in the general population. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60(2):184–9. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.60.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kessler RC, Berglund PA, Bruce ML, Koch JR, Laska EM, Leaf PJ, et al. The prevalence and correlates of untreated serious mental illness. Health Serv Res. 2001;36(6 Pt 1):987–1007. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Luyster FS, Buysse DJ, Strollo PJ., Jr Comorbid insomnia and obstructive sleep apnea: challenges for clinical practice and research. J Clin Sleep Med. 2010;6(2):196–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hornyak M, Feige B, Riemann D, Voderholzer U. Periodic leg movements in sleep and periodic limb movement disorder: prevalence, clinical significance and treatment. Sleep Med Rev. 2006;10(3):169–77. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2005.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Edinger JD, Fins AI, Sullivan RJ, Marsh GR, Dailey DS, Young M. Comparison of cognitive-behavioral therapy and clonazepam for treating periodic limb movement disorder. Sleep. 1996;19(5):442–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Daumit GL, Dickerson FB, Wang NY, Dalcin A, Jerome GJ, Anderson CA, et al. A behavioral weight-loss intervention in persons with serious mental illness. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(17):1594–602. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Sheehan DV, Harnett-Sheehan K, Raj BA. The measurement of disability. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1996;11(Suppl 3):89–95. doi: 10.1097/00004850-199606003-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Yu L, Buysse DJ, Germain A, Moul D. Development of short forms from the PROMIS Sleep Disturbance and Sleep-Related Impairment item banks. Behav Sleep Med. 2012;10:6–24. doi: 10.1080/15402002.2012.636266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Buysse DJ, Yu L, Moul DE, Germain A, Stover A, Dodds NE, et al. Development and validation of patient-reported outcome measures for sleep disturbance and sleep-related impairments. Sleep. 2010;33:781–92. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.6.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Moriarty DG, Zack MM, Kobau R. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Healthy Days Measures – population tracking of perceived physical and mental health over time. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2003;1:37. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-1-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Ibrahim HM, Carmody TJ, Arnow B, Klein DN, et al. The 16-item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (QIDS), clinician rating (QIDS-C), and self-report (QIDS-SR): a psychometric evaluation in patients with chronic major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54:573–83. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(02)01866-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.WHO ASSIST Working Group The Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST): development, reliability and feasibility. Addiction. 2002;97(9):1183–94. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Haddock G, McCarron J, Tarrier N, Faragher EB. Scales to measure dimensions of hallucinations and delusions: the Psychotic Symptom Rating Scales (PSYRATS) Psychol Med. 1999;29(4):879–89. doi: 10.1017/S0033291799008661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Sheehan D, Lecrubier Y, Harnett Sheehan K, Janavs J, Weiller E, Keskiner A, et al. The validity of the Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) according to the SCID-P and its reliability. Eur Psychiatry. 1997;12(5):232–41. doi: 10.1016/S0924-9338(97)83297-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E, et al. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998;59:22–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Schmitz N, Kruse J, Heckrath C, Alberti L, Tress W. Diagnosing mental disorders in primary care: the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ) and the Symptom Check List (SCL-90-R) as screening instruments. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 1999;34(7):360–6. doi: 10.1007/s001270050156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Edinger JD, Wyatt JK, Olsen MK, Stechuchak KM, Carney CE, Chiang A, et al. Reliability and validity of the Duke Structured Interview for Sleep Disorders for insomnia screening [abstract 0810] Sleep. 2009;32(Suppl):A265. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Morin CM. Insomnia: psychological assessment and management. New York: Guilford Press; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Farney RJ, Walker BS, Farney RM, Snow GL, Walker JM. The STOP-Bang equivalent model and prediction of severity of obstructive sleep apnea: relation to polysomnographic measurements of the apnea/hypopnea index. J Clin Sleep Med. 2011;7(5):459–65B. doi: 10.5664/JCSM.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Devilly GJ, Borkovec TD. Psychometric properties of the credibility/expectancy questionnaire. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2000;31:73–86. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7916(00)00012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Devilly GJ, Spence SH. The relative efficacy and treatment distress of EMDR and a cognitive-behavior trauma treatment protocol in the amelioration of posttraumatic stress disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 1999;13:131–57. doi: 10.1016/S0887-6185(98)00044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Young JE, Beck AT. The development of the Cognitive Therapy Scale. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania; 1980. [Google Scholar]
- 108.Beach ML, Meier P. Choosing covariates in the analysis of clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1989;10(4 Suppl):161S–175S. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(89)90055-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Canner PL. Covariate adjustment of treatment effects in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1991;12:359–66. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(91)90016-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Senn SJ. Covariate imbalance and random allocation in clinical trials. Stat Med. 1989;8:467–75. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780080410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Little RJ, Rubin DB. Statistical analysis with missing data. 2. New York: Wiley; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Raudenbush S, Bryk A. Hierarchical linear models. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 113.Goldstein H. Multilevel statistical models. 4. Chichester: Wiley; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Hox J. Multilevel analysis: techniques and applications. New York: Routledge; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 115.MacKinnon D, Lockwood C, Hoffman J, West S, Sheets V. A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychol Methods. 2002;7:83–104. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.7.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Cohen J, Cohen P, West SG, Aiken LS. Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. 3. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Jaccard J, Wan CK, Turrisi R. The detection and interpretation of interaction effects between continuous variables in multiple regression. Multivariate Behav Res. 1990;25(4):467–78. doi: 10.1207/s15327906mbr2504_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Kupfer DJ. Dimensional models for research and diagnosis: a current dilemma. J Abnorm Psychol. 2005;114:557–9. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.114.4.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Insel TR, Cuthbert BN, Garvey MA, Heinssen RK, Pine DS, Quinn KJ, et al. Research domain criteria (RDoC): toward a new classification framework for research on mental disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2010;167:748–51. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.09091379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Other than the authors and compliance with data-sharing agreements stipulated by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), no other entities have contractual agreements with regard to access to the final dataset.


