Abstract
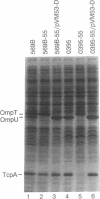
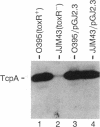
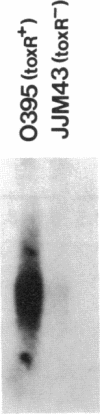
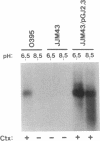
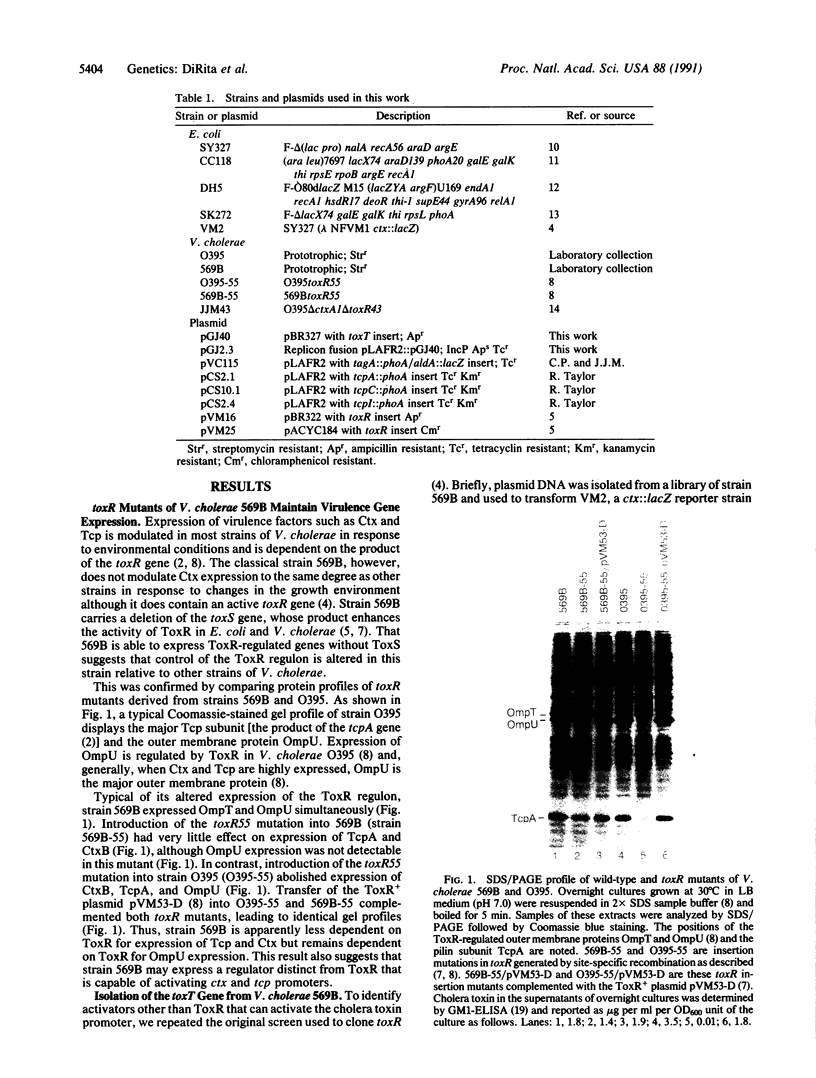
Expression of more than 17 virulence genes in Vibrio cholerae is under the coordinate control of the ToxR protein. ToxR is a transmembrane protein that binds to and activates the promoter of the operon encoding cholera toxin. As yet, the ability of ToxR to activate directly other genes in this regulon has not been demonstrated. We have cloned a gene called toxT from V. cholerae 569B; the toxT gene product, like ToxR, can activate the ctx promoter in Escherichia coli. In addition, expression of other genes identified as members of the ToxR regulon (tcpA, tcpI, aldA, and tagA) can be activated in E. coli by the toxT gene product but not by ToxR. When expressed from a constitutive promoter, the toxT gene product partially suppresses the ToxR- phenotype of a toxR deletion mutant of V. cholerae. The level of toxT mRNA is greatly reduced in a toxR mutant of V. cholerae. In addition, growth conditions under which the ToxR regulon is not expressed also repress the synthesis of toxT mRNA. These results suggest that ToxR controls transcription of toxT, whose product in turn is directly responsible for activation of several virulence genes under ToxR control.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Gelvin S. B. Deletion analysis of the mannopine synthase gene promoter in sunflower crown gall tumors and Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):233–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00331583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic regulation of bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:455–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Periplasmic interaction between two membrane regulatory proteins, ToxR and ToxS, results in signal transduction and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90206-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Iglewski B. H. Kinetics of toxA and regA mRNA accumulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4477–4483. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4477-4483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamood A. N., Iglewski B. H. Expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxA positive regulatory gene (regA) in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):589–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.589-594.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Hall R. H., Losonsky G., Mekalanos J. J., Taylor R. K., Levine M. M. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are essential for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J. D., Clements M. B., Liang T. Y., Isberg R. R., Syvanen M. Recombination genes on the Escherichia coli sex factor specific for transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Roitsch T., Christie P. J., Nester E. W. The regulatory VirG protein specifically binds to a cis-acting regulatory sequence involved in transcriptional activation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):531–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.531-537.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The VirA protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is autophosphorylated and is essential for vir gene regulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):525–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.525-530.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Pero J. Cascades of Sigma factors. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):582–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Roy C. R., Falkow S. Analysis of Bordetella pertussis virulence gene regulation by use of transcriptional fusions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6345–6348. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6345-6348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Identification of toxS, a regulatory gene whose product enhances toxR-mediated activation of the cholera toxin promoter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1288–1293. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1288-1293.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsot C., Mekalanos J. J. Expression of ToxR, the transcriptional activator of the virulence factors in Vibrio cholerae, is modulated by the heat shock response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9898–9902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsot C., Mekalanos J. J. Expression of the Vibrio cholerae gene encoding aldehyde dehydrogenase is under control of ToxR, the cholera toxin transcriptional activator. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2842–2851. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2842-2851.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., DiRita V. J., Goldberg M. B., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J. New attenuated derivatives of Vibrio cholerae. Res Microbiol. 1990 Sep-Oct;141(7-8):893–899. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90127-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Mekalanos J. J. Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae ToxR regulon: identification of novel genes involved in intestinal colonization. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2822-2829.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson S. H. Factors influencing in vitro skin permeability factor production by Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):27–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.27-34.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch K. L., Beckwith J. An Escherichia coli mutation preventing degradation of abnormal periplasmic proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1576–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]