Abstract
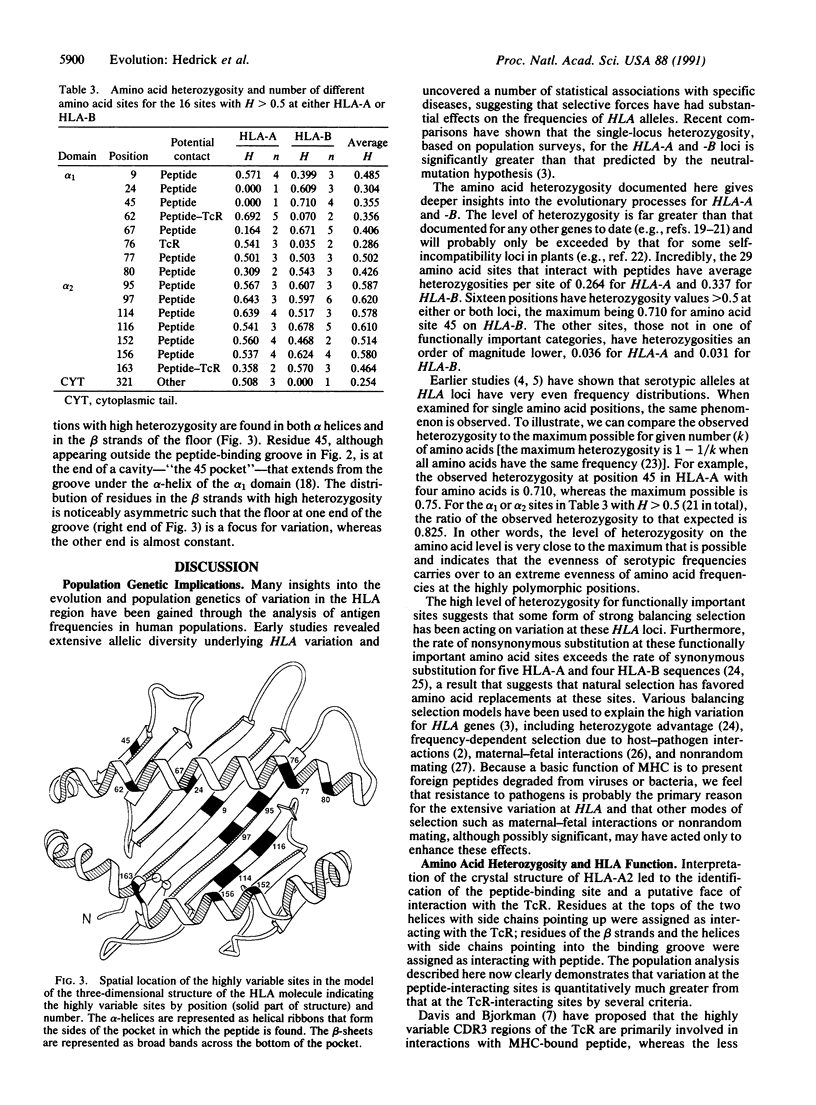
The amino acid heterozygosities per site for HLA-A and -B loci are determined to be extremely high by combining population serotypic frequencies with amino acid sequences. For the 54 amino acid sites thought to have functional importance, the average heterozygosity per site is 0.301. Sixteen positions have heterozygosities greater than 0.5 at one or both loci and the frequencies of amino acids at a given position are very even, resulting in nearly the maximum heterozygosity possible. Furthermore, the high heterozygosity is concentrated in the peptide-interacting sites, whereas the sites that interact with the T-cell receptor have lower heterozygosity. Overall, these results indicate the importance of some form of balancing selection operating at HLA loci, maybe even at the individual amino acid level.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorkman P. J., Parham P. Structure, function, and diversity of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:253–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Guagliardi L. E. The cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:707–744. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. M., Hansen T. H., Ingold A. L., Potter T. A. Recognition by CD8 on cytotoxic T lymphocytes is ablated by several substitutions in the class I alpha 3 domain: CD8 and the T-cell receptor recognize the same class I molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBose R. F., Dykhuizen D. E., Hartl D. L. Genetic exchange among natural isolates of bacteria: recombination within the phoA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7036–7040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett T. P., Saper M. A., Bjorkman P. J., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Specificity pockets for the side chains of peptide antigens in HLA-Aw68. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):692–696. doi: 10.1038/342692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick P. W., Thomson G. Evidence for balancing selection at HLA. Genetics. 1983 Jul;104(3):449–456. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick P. W., Thomson G. Maternal-fetal interactions and the maintenance of HLA polymorphism. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):205–212. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class II loci: evidence for overdominant selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):167–170. doi: 10.1038/335167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ioerger T. R., Clark A. G., Kao T. H. Polymorphism at the self-incompatibility locus in Solanaceae predates speciation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9732–9735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klitz W., Thomson G., Baur M. P. Contrasting evolutionary histories among tightly linked HLA loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Sep;39(3):340–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman M. Nucleotide polymorphism at the alcohol dehydrogenase locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):412–417. doi: 10.1038/304412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Lomen C. E., Lawlor D. A., Ways J. P., Holmes N., Coppin H. L., Salter R. D., Wan A. M., Ennis P. D. Nature of polymorphism in HLA-A, -B, and -C molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4005–4009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Benjamin R. J., Wesley P. K., Buxton S. E., Garrett T. P., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Norment A. M., Littman D. R., Parham P. A binding site for the T-cell co-receptor CD8 on the alpha 3 domain of HLA-A2. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):41–46. doi: 10.1038/345041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Norment A. M., Chen B. P., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Littman D. R., Parham P. Polymorphism in the alpha 3 domain of HLA-A molecules affects binding to CD8. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):345–347. doi: 10.1038/338345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. A., Lopez M. T., McDevitt H. O. Autoimmune diseases: the failure of self tolerance. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1380–1388. doi: 10.1126/science.1972595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. HLA disease associations: models for insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and the study of complex human genetic disorders. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:31–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., McMichael A. J. Specificity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes stimulated with influenza virus. Studies in mice and humans. Prog Allergy. 1985;36:10–43. doi: 10.1159/000409860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki K., Beauchamp G. K., Wysocki C. J., Bard J., Thomas L., Boyse E. A. Recognition of H-2 types in relation to the blocking of pregnancy in mice. Science. 1983 Jul 8;221(4606):186–188. doi: 10.1126/science.6857281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]