Abstract
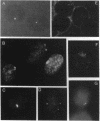
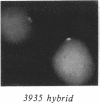
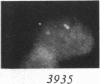
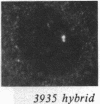
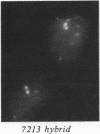
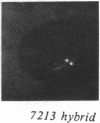
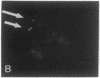
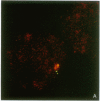
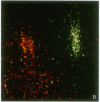
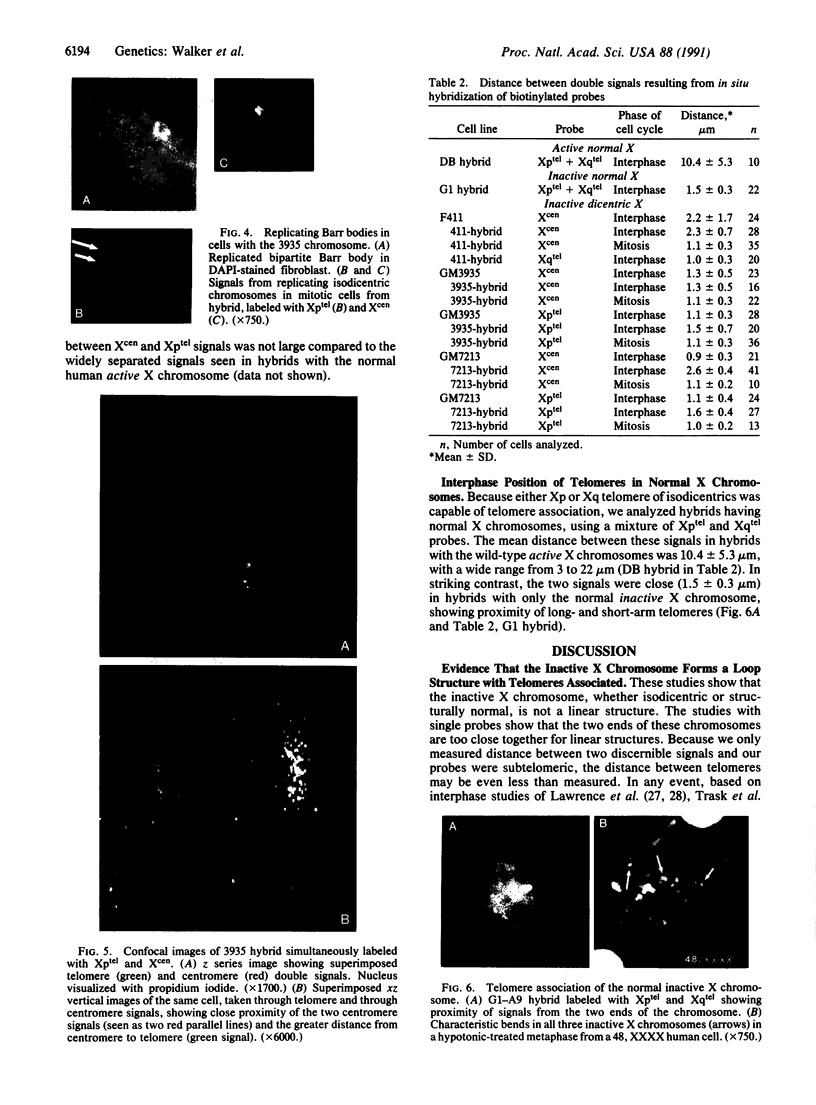
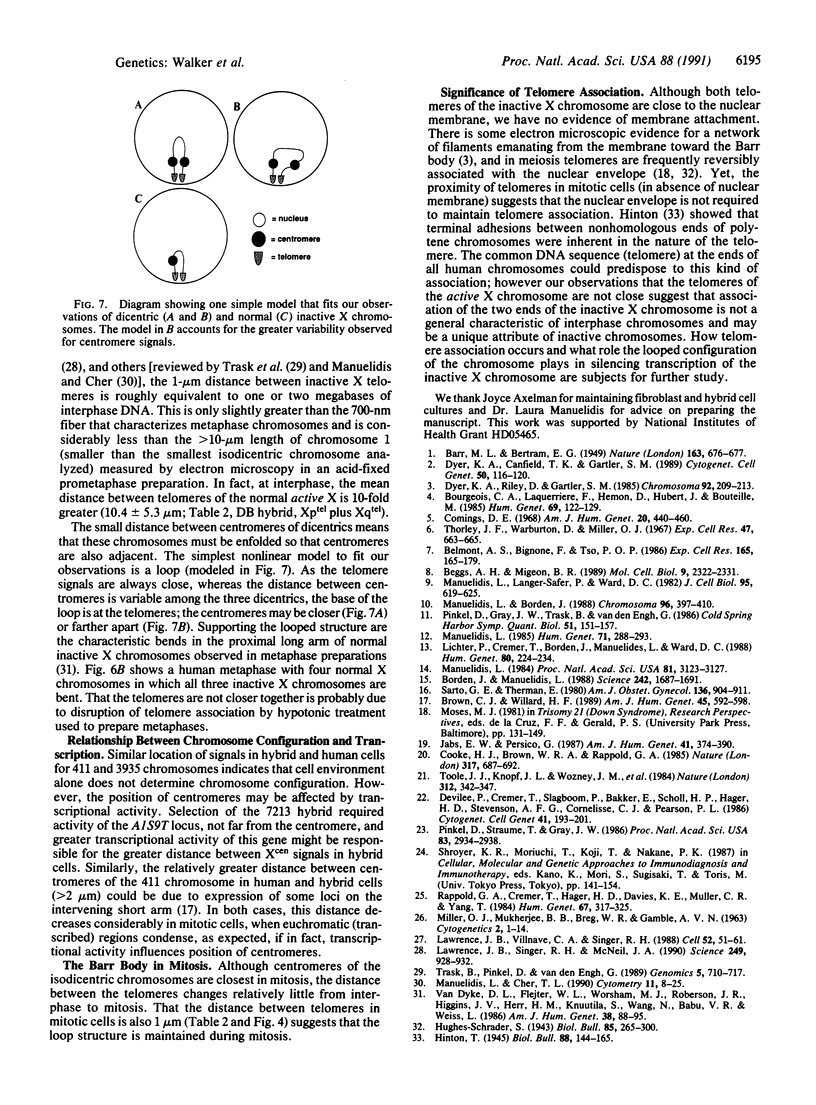
We examined Barr bodies formed by isodicentric human X chromosomes in cultured human cells and in mouse-human hybrids using confocal microscopy and DNA probes for centromere and subtelomere regions. At interphase, the two ends of these chromosomes are only a micron apart, indicating that these inactive X chromosomes are in a nonlinear configuration. Additional studies of normal X chromosomes reveal the same telomere association for the inactive X but not for the active X chromosome. This nonlinear configuration is maintained during mitosis and in a murine environment.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beggs A. H., Migeon B. R. Chromatin loop structure of the human X chromosome: relevance to X inactivation and CpG clusters. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2322–2331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmont A. S., Bignone F., Ts'o P. O. The relative intranuclear positions of Barr bodies in XXX non-transformed human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jul;165(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90541-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden J., Manuelidis L. Movement of the X chromosome in epilepsy. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1687–1691. doi: 10.1126/science.3201257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois C. A., Laquerriere F., Hemon D., Hubert J., Bouteille M. New data on the in-situ position of the inactive X chromosome in the interphase nucleus of human fibroblasts. Hum Genet. 1985;69(2):122–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00293281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Willard H. F. Noninactivation of a selectable human X-linked gene that complements a murine temperature-sensitive cell cycle defect. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):592–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. The rationale for an ordered arrangement of chromatin in the interphase nucleus. Am J Hum Genet. 1968 Sep;20(5):440–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Brown W. R., Rappold G. A. Hypervariable telomeric sequences from the human sex chromosomes are pseudoautosomal. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):687–692. doi: 10.1038/317687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Cremer T., Slagboom P., Bakker E., Scholl H. P., Hager H. D., Stevenson A. F., Cornelisse C. J., Pearson P. L. Two subsets of human alphoid repetitive DNA show distinct preferential localization in the pericentric regions of chromosomes 13, 18, and 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;41(4):193–201. doi: 10.1159/000132229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer K. A., Canfield T. K., Gartler S. M. Molecular cytological differentiation of active from inactive X domains in interphase: implications for X chromosome inactivation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;50(2-3):116–120. doi: 10.1159/000132736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer K. A., Riley D., Gartler S. M. Analysis of inactive X chromosome structure by in situ nick translation. Chromosoma. 1985;92(3):209–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00348695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Persico M. G. Characterization of human centromeric regions of specific chromosomes by means of alphoid DNA sequences. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;41(3):374–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., McNeil J. A. Interphase and metaphase resolution of different distances within the human dystrophin gene. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):928–932. doi: 10.1126/science.2203143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Villnave C. A., Singer R. H. Sensitive, high-resolution chromatin and chromosome mapping in situ: presence and orientation of two closely integrated copies of EBV in a lymphoma line. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Borden J., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Delineation of individual human chromosomes in metaphase and interphase cells by in situ suppression hybridization using recombinant DNA libraries. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):224–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01790090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER O. J., MUKHERJEE B. B., BREG W. R., GAMBLE A. V. NON-RANDOM DISTRIBUTION OF CHROMOSOMES IN METAPHASE FIGURES FROM CULTURED HUMAN LEUCOCYTES. I. THE PERIPHERAL LOCATION OF THE Y CHROMOSOME. Cytogenetics. 1963;2:1–14. doi: 10.1159/000129760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Borden J. Reproducible compartmentalization of individual chromosome domains in human CNS cells revealed by in situ hybridization and three-dimensional reconstruction. Chromosoma. 1988;96(6):397–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00303033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Chen T. L. A unified model of eukaryotic chromosomes. Cytometry. 1990;11(1):8–25. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990110104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Different central nervous system cell types display distinct and nonrandom arrangements of satellite DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3123–3127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Individual interphase chromosome domains revealed by in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1985;71(4):288–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00388453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Langer-Safer P. R., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of satellite DNA using biotin-labeled DNA probes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):619–625. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Gray J. W., Trask B., van den Engh G., Fuscoe J., van Dekken H. Cytogenetic analysis by in situ hybridization with fluorescently labeled nucleic acid probes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):151–157. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappold G. A., Cremer T., Hager H. D., Davies K. E., Müller C. R., Yang T. Sex chromosome positions in human interphase nuclei as studied by in situ hybridization with chromosome specific DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1984;67(3):317–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00291361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarto G. E., Therman E. Replication and inactivation of a dicentric X formed by telomeric fusion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Apr 1;136(7):904–911. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley J., Warburton D., Miller O. J. Absence of somatic pairing of sex chromatin masses (inactivated X chromosomes) in cultured cells from a human XXXXY male. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Sep;47(3):663–665. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole J. J., Knopf J. L., Wozney J. M., Sultzman L. A., Buecker J. L., Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J., Brown E., Shoemaker C., Orr E. C. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding human antihaemophilic factor. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):342–347. doi: 10.1038/312342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B., Pinkel D., van den Engh G. The proximity of DNA sequences in interphase cell nuclei is correlated to genomic distance and permits ordering of cosmids spanning 250 kilobase pairs. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke D. L., Flejter W. L., Worsham M. J., Roberson J. R., Higgins J. V., Herr H. M., Knuutila S., Wang N., Babu V. R., Weiss L. A practical metaphase marker of the inactive X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;39(1):88–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]