Abstract
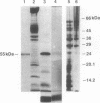
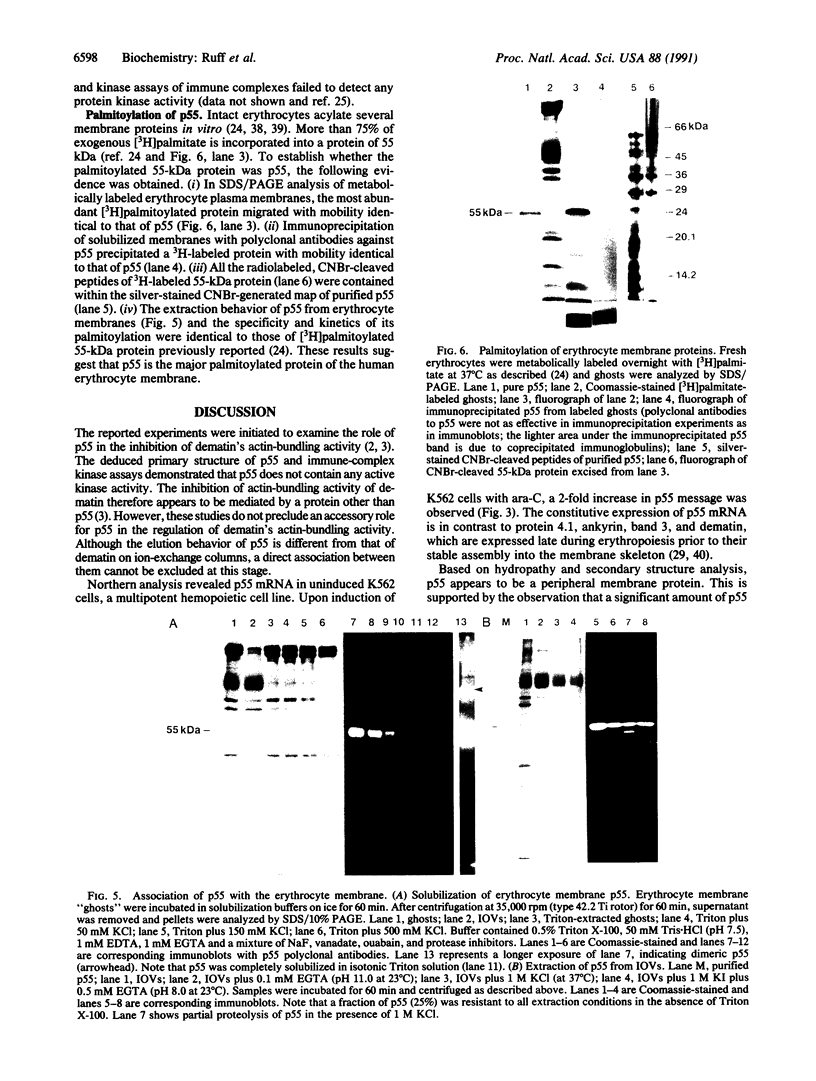
The complete amino acid sequence of a 55-kDa erythrocyte membrane protein was deduced from cDNA clones isolated from a human reticulocyte library. This protein, p55, is copurified during the isolation of dematin, an actin-bundling protein of the erythrocyte membrane cytoskeleton. Fractions enriched in p55 also contain protein kinase activity that completely abolishes the actin-bundling property of purified dematin in vitro. The predicted amino acid sequence of p55 does not contain any consensus sequence corresponding to the catalytic domains of protein kinases but does contain a conserved sequence found in the noncatalytic domains of oncogene-encoded tyrosine kinases. This conserved src homology 3 (SH-3) motif appears to suppress the tyrosine kinase activity of various oncoproteins and has also been found in several plasma membrane associated proteins involved in signal transduction. Northern blot analysis indicated that p55 mRNA was constitutively expressed during erythropoiesis and underwent 2-fold amplification after induction of K562 erythroleukemia cells toward the erythropoietic lineage. The abundant expression of p55 mRNA, along with protein 4.1 mRNA, was evident in terminally differentiated human reticulocytes. Although p55 has many features consistent with known peripheral membrane proteins, its tight association with the plasma membrane is reminiscent of an integral membrane protein. This fact may be partly explained by the observation that p55 is the most extensively palmitoylated protein of the erythrocyte membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. The spectrin-actin junction of erythrocyte membrane skeletons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi Scarrà G. L., Romani M., Coviello D. A., Garrè C., Ravazzolo R., Vidali G., Ajmar F. Terminal erythroid differentiation in the K-562 cell line by 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine: accompaniment by c-myc messenger RNA decrease. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6327–6332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Mulholland J., Zhu Z. M., Botstein D. Homology of a yeast actin-binding protein to signal transduction proteins and myosin-I. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):288–290. doi: 10.1038/343288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil R. R., Byers T. J., Sillman A. L., Bar-Zvi D., Goldstein L. S., Branton D. The complete sequence of Drosophila alpha-spectrin: conservation of structural domains between alpha-spectrins and alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2197–2205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faquin W. C., Husain-Chishti A., Branton D. Expression of dematin (protein 4.9) during avian erythropoiesis. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;53(1):48–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz W. M., Berger P., Wang J. Y. Deletion of an N-terminal regulatory domain of the c-abl tyrosine kinase activates its oncogenic potential. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):137–147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens M., Kan Y. Y. DNA analysis in the diagnosis of hemoglobin disorders. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:805–817. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanspal M., Palek J. Synthesis and assembly of membrane skeletal proteins in mammalian red cell precursors. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1417–1424. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann F. M., Fresco L. D., Hoffman-Falk H., Shilo B. Z. Nucleotide sequences of the Drosophila src and abl homologs: conservation and variability in the src family oncogenes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain-Chishti A., Faquin W., Wu C. C., Branton D. Purification of erythrocyte dematin (protein 4.9) reveals an endogenous protein kinase that modulates actin-bundling activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8985–8991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain-Chishti A., Levin A., Branton D. Abolition of actin-bundling by phosphorylation of human erythrocyte protein 4.9. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):718–721. doi: 10.1038/334718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain A., Branton D. Purification of erythrocyte band 4.1 and other cytoskeletal components using hydroxyapatite-Ultrogel. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):206–211. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Baltimore D. N-terminal mutations activate the leukemogenic potential of the myristoylated form of c-abl. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):449–456. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Greengard P. A quantitative dot-immunobinding assay for proteins using nitrocellulose membrane filters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1684–1687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G., Korn E. D., Hammer J. A., 3rd The heavy chain of Acanthamoeba myosin IB is a fusion of myosin-like and non-myosin-like sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6720–6724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G., Saxe C. L., 3rd, Kimmel A. R., Hammer J. A., 3rd Dictyostelium discoideum contains a gene encoding a myosin I heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6186–6190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren C., Cohen C. M. Purification and properties of human erythrocyte band 4.2. Association with the cytoplasmic domain of band 3. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Wasenius V. M., Salvén P., Saraste M. Transforming and membrane proteins. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):388–388. doi: 10.1038/334388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leto T. L., Lomax K. J., Volpp B. D., Nunoi H., Sechler J. M., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Cloning of a 67-kD neutrophil oxidase factor with similarity to a noncatalytic region of p60c-src. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):727–730. doi: 10.1126/science.1692159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maretzki D., Mariani M., Lutz H. U. Fatty acid acylation of membrane skeletal proteins in human erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80033-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Mathey-Prevot B., Bernards A., Baltimore D. Neuronal pp60c-src contains a six-amino acid insertion relative to its non-neuronal counterpart. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):411–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2440106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Non-catalytic domains of cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases: regulatory elements in signal transduction. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth P., Röhrkasten A., Biel M., Bosse E., Regulla S., Meyer H. E., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Primary structure of the beta subunit of the DHP-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1115–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.2549640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahr K. E., Laurila P., Kotula L., Scarpa A. L., Coupal E., Leto T. L., Linnenbach A. J., Winkelmann J. C., Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T. The complete cDNA and polypeptide sequences of human erythroid alpha-spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4434–4443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Miki S., Tachibana H., Hayashi F., Akiyama T., Fukami Y. A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues 137 to 157 of p60v-src inhibits tyrosine-specific protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1152–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90805-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F. Fatty acylation of proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):411–426. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90013-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D. L., Branton D. Partial purification and characterization of an actin-bundling protein, band 4.9, from human erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):775–785. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Lazarides E. Ankyrin is fatty acid acylated in erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Hargreaves W. R., Branton D. Purification of two spectrin-binding proteins: biochemical and electron microscopic evidence for site-specific reassociation between spectrin and bands 2.1 and 4.1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]