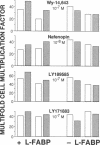
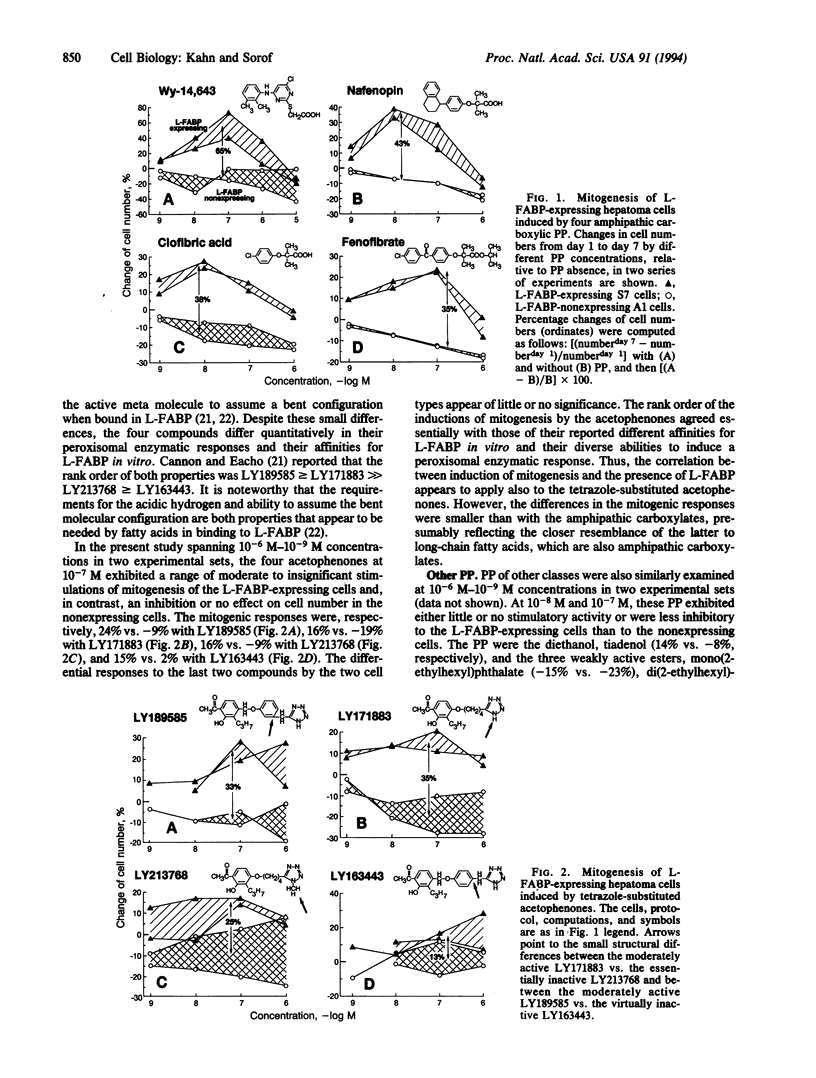
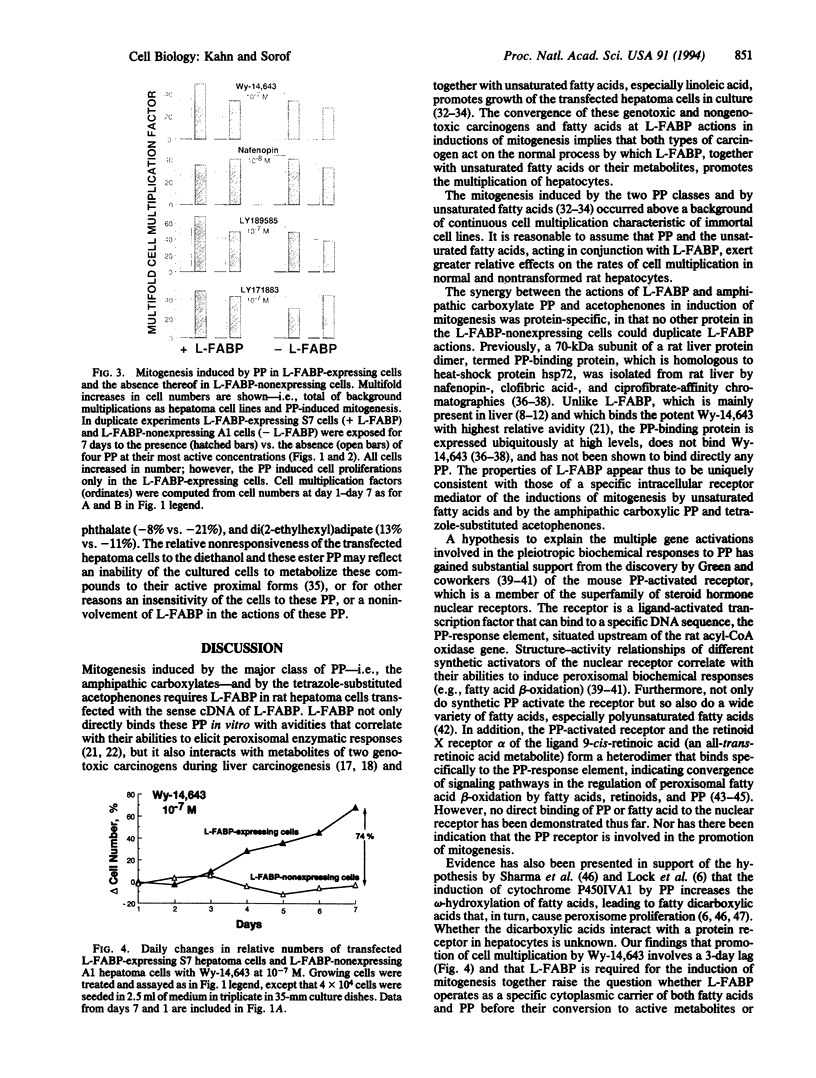
Abstract
Peroxisome proliferators (PP) are a diverse group of chemicals that induce dramatic increases in peroxisomes in rodent hepatocytes, followed by hypertrophy, hepatomegaly, alterations in lipid metabolism, mitogenesis, and finally hepatocarcinomas. Termed nongenotoxic carcinogens, they do not interact with DNA, are not mutagenic in bacterial assays, and fail to elicit many of the phenotypes associated with classic genotoxic carcinogens. We report here that the mitogenesis induced by the major PP class, the amphipathic carboxylates, and by the tetrazole-substituted acetophenones specifically requires liver fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP) in cultured rat hepatoma cells transfected with the sense cDNA of L-FABP, in contrast to L-FABP-nonexpressing cells transfected with its antisense cDNA. The mitogenic actions of L-FABP were protein-specific, inasmuch as no other protein in the nonexpressing cells could act like L-FABP. L-FABP was previously shown not only (i) to interact covalently with metabolites of the two genotoxic carcinogens 2-acetylaminofluorene and aminoazo dyes during liver carcinogenesis, but also (ii) to bind noncovalently the two classes of PP in vitro with avidities that correlate with their abilities to elicit peroxisomal enzymatic responses, and (iii) together with unsaturated fatty acids, especially linoleic acid, to promote multiplication of the transfected hepatoma cells in culture. The convergence of the two types of genotoxic carcinogens with the two classes of PP nongenotoxic carcinogens, and also with unsaturated fatty acids, at L-FABP actions in inducing mitogenesis allows the following hypothesis. During tumor promotion of carcinogenesis in vivo, these groups of genotoxic and nongenotoxic carcinogens act on the normal process by which L-FABP, functioning as a specific receptor of unsaturated fatty acids or their metabolites, promotes hepatocyte proliferation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvares K., Carrillo A., Yuan P. M., Kawano H., Morimoto R. I., Reddy J. K. Identification of cytosolic peroxisome proliferator binding protein as a member of the heat shock protein HSP70 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5293–5297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Gold L. S. Too many rodent carcinogens: mitogenesis increases mutagenesis. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):970–971. doi: 10.1126/science.2136249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal M. P., Cook R. G., Danielson K. G., Medina D. A 14-kilodalton selenium-binding protein in mouse liver is fatty acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13780–13784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardot O., Aldridge T. C., Latruffe N., Green S. PPAR-RXR heterodimer activates a peroxisome proliferator response element upstream of the bifunctional enzyme gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 15;192(1):37–45. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass N. M. The cellular fatty acid binding proteins: aspects of structure, regulation, and function. Int Rev Cytol. 1988;111:143–184. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61733-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendele A. M., Hoover D. M., van Lier R. B., Foxworthy P. S., Eacho P. I. Effects of chronic treatment with the leukotriene D4-antagonist compound LY171883 on B6C3F1 mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1990 Nov;15(4):676–682. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(90)90184-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn G. R., Schnabel S. J., Danley J. M., Hogue-Angeletti R. A., Sorof S. Principal polypeptide target of carcinogen at the beginning of liver carcinogenesis by three carcinogens. Cancer Res. 1982 Nov;42(11):4664–4672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandes R., Kaikaus R. M., Lysenko N., Ockner R. K., Bass N. M. Induction of fatty acid binding protein by peroxisome proliferators in primary hepatocyte cultures and its relationship to the induction of peroxisomal beta-oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 23;1034(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(90)90152-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrier R. E., Brecher P. Binding of lysophosphatidylcholine to the rat liver fatty acid binding protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 14;879(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. R., Eacho P. I. Interaction of LY171883 and other peroxisome proliferators with fatty-acid-binding protein isolated from rat liver. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 1;280(Pt 2):387–391. doi: 10.1042/bj2800387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattley R. C., Popp J. A. Differences between the promoting activities of the peroxisome proliferator WY-14,643 and phenobarbital in rat liver. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 15;49(12):3246–3251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Ellwein L. B. Cell proliferation in carcinogenesis. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1007–1011. doi: 10.1126/science.2204108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Custer R. P., Sorof S. Mitosis in hepatocytes is generally associated with elevated levels of the target polypeptide of a liver carcinogen. Differentiation. 1985;30(2):176–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Custer R. P., Sorof S. Target polypeptide of a carcinogen is associated with normal mitosis and carcinogen-induced hyperplasias in adult hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6738–6742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta-Roy A. K., Gopalswamy N., Trulzsch D. V. Prostaglandin E1 binds to Z protein of rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):615–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukai F., Kase T., Shidotani T., Nagai T., Katayama T. A novel role of fatty acid-binding protein as a vehicle of retinoids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):899–903. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. Peroxisome proliferators: a model for receptor mediated carcinogenesis. Cancer Surv. 1992;14:221–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlicher M., Widmark E., Li Q., Gustafsson J. A. Fatty acids activate a chimera of the clofibric acid-activated receptor and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4653–4657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins J. M., Jones W. E., Bonner F. W., Gibson G. G. The effect of peroxisome proliferators on microsomal, peroxisomal, and mitochondrial enzyme activities in the liver and kidney. Drug Metab Rev. 1987;18(4):441–515. doi: 10.3109/03602538708994130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issemann I., Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):645–650. doi: 10.1038/347645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issemann I., Prince R., Tugwood J., Green S. A role for fatty acids and liver fatty acid binding protein in peroxisome proliferation? Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Nov;20(4):824–827. doi: 10.1042/bst0200824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaikaus R. M., Bass N. M., Ockner R. K. Functions of fatty acid binding proteins. Experientia. 1990 Jun 15;46(6):617–630. doi: 10.1007/BF01939701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Ono T., Matsubara Y., Muto T. Possible role of rat fatty acid-binding proteins in the intestine as carriers of phenol and phthalate derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1053–1058. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91136-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keler T., Barker C. S., Sorof S. Specific growth stimulation by linoleic acid in hepatoma cell lines transfected with the target protein of a liver carcinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4830–4834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keler T., Sorof S. Growth promotion of transfected hepatoma cells by liver fatty acid binding protein. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Oct;157(1):33–40. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H., Dreyer C., Medin J., Mahfoudi A., Ozato K., Wahli W. Fatty acids and retinoids control lipid metabolism through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer B., Tipping E., Hackney J. F., Beale D. A low-molecular-weight protein from rat liver that resembles ligandin in its binding properties. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 1;155(3):511–521. doi: 10.1042/bj1550511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. H., Sorof S. Preferential binding of growth inhibitory prostaglandins by the target protein of a carcinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9401–9405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Noonan D. J., Heyman R. A., Evans R. M. Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):771–774. doi: 10.1038/358771a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalwani N. D., Alvares K., Reddy M. K., Reddy M. N., Parikh I., Reddy J. K. Peroxisome proliferator-binding protein: identification and partial characterization of nafenopin-, clofibric acid-, and ciprofibrate-binding proteins from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5242–5246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalwani N. D., Fahl W. E., Reddy J. K. Detection of a nafenopin-binding protein in rat liver cytosol associated with the induction of peroxisome proliferation by hypolipidemic compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):388–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem H. H., Grasso J. A., Vincent S. H., Muller-Eberhard U. Protein-mediated efflux of heme from isolated rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 16;167(2):528–534. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock E. A., Mitchell A. M., Elcombe C. R. Biochemical mechanisms of induction of hepatic peroxisome proliferation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:145–163. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsman D. S., Cattley R. C., Conway J. G., Popp J. A. Relationship of hepatic peroxisome proliferation and replicative DNA synthesis to the hepatocarcinogenicity of the peroxisome proliferators di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate and [4-chloro-6-(2,3-xylidino)-2-pyrimidinylthio]acetic acid (Wy-14,643) in rats. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 1;48(23):6739–6744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matarese V., Stone R. L., Waggoner D. W., Bernlohr D. A. Intracellular fatty acid trafficking and the role of cytosolic lipid binding proteins. Prog Lipid Res. 1989;28(4):245–272. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(89)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. M., Lhuguenot J. C., Bridges J. W., Elcombe C. R. Identification of the proximate peroxisome proliferator(s) derived from di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;80(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(85)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz de Montellano P. R., Chan W. K., Tuck S. F., Kaikaus R. M., Bass N. M., Peterson J. A. Mechanism-based probes of the topology and function of fatty acid hydroxylases. FASEB J. 1992 Jan 6;6(2):695–699. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.2.1537458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Reddy J. K. Peroxisome proliferation and hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1987 May;8(5):631–636. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.5.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raza H., Pongubala J. R., Sorof S. Specific high affinity binding of lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid by liver fatty acid binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92619-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Hermann R., Timmermann-Trosiener I., Schuppler J. Promotion of spontaneous preneoplastic cells in rat liver as a possible explanation of tumor production by nonmutagenic compounds. Cancer Res. 1983 Feb;43(2):839–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R., Lake B. G., Foster J., Gibson G. G. Microsomal cytochrome P-452 induction and peroxisome proliferation by hypolipidaemic agents in rat liver. A mechanistic inter-relationship. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 1;37(7):1193–1201. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90770-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorof S., Custer R. P. Elevated expression and cell cycle deregulation of a mitosis-associated target polypeptide of a carcinogen in hyperplastic and malignant rat hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 1987 Jan 1;47(1):210–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Birkenmeier E. H., Hoppe P. C., McKeel D. W., Gordon J. I. Mechanisms underlying generation of gradients in gene expression within the intestine: an analysis using transgenic mice containing fatty acid binding protein-human growth hormone fusion genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1318–1332. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Heuckeroth R. O., Gordon J. I. The metabolic significance of mammalian fatty-acid-binding proteins: abundant proteins in search of a function. Annu Rev Nutr. 1987;7:337–359. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.07.070187.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwood J. D., Issemann I., Anderson R. G., Bundell K. R., McPheat W. L., Green S. The mouse peroxisome proliferator activated receptor recognizes a response element in the 5' flanking sequence of the rat acyl CoA oxidase gene. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):433–439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vancura A., Haldar D. Regulation of mitochondrial and microsomal phospholipid synthesis by liver fatty acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14353–14359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerkamp J. H., Peeters R. A., Maatman R. G. Structural and functional features of different types of cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 4;1081(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90244-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]