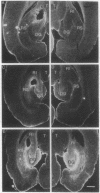
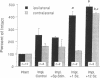
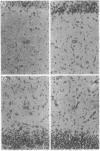
Abstract
Neuronal gene expression is known to be modulated by functional activity. This modulation is thought to play a key role in determining the differentiation of developing neurons and regulating the operation of mature neurons. Here we describe a regulation of astroglial gene expression by neuronal activity. We report that intense neuronal activity (electrically induced seizures) in rat hippocampus leads to rapid and dramatic increases in mRNA for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), an astroglia-specific intermediate filament protein. GFAP mRNA levels increased at sites of stimulation as well as in areas that were synaptically activated by the resultant seizures. When seizures were induced repetitively for many days, levels of GFAP mRNA remained chronically elevated. However, GFAP mRNA returned to control levels within a few days after the cessation of stimulation. The coupling between astroglial gene expression and neuronal activity may be a mechanism through which neuronal activity modulates the function of supporting cells that are responsible for regulating the extracellular microenvironment of the brain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertram E. H., Lothman E. W., Lenn N. J. The hippocampus in experimental chronic epilepsy: a morphometric analysis. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jan;27(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. L., Kimelberg H. K. Excitatory amino acids directly depolarize rat brain astrocytes in primary culture. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):656–659. doi: 10.1038/311656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canady K. S., Ali-Osman F., Rubel E. W. Extracellular potassium influences DNA and protein syntheses and glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in cultured glial cells. Glia. 1990;3(5):368–374. doi: 10.1002/glia.440030508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. L., Greenough W. T. Transient and enduring morphological correlates of synaptic activity and efficacy change in the rat hippocampal slice. Brain Res. 1984 Aug 20;309(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell-Bell A. H., Thomas P. G., Smith S. J. The excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate causes filopodia formation in cultured hippocampal astrocytes. Glia. 1990;3(5):322–334. doi: 10.1002/glia.440030503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmond N. L., Levy W. B. Synaptic correlates of associative potentiation/depression: an ultrastructural study in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 11;265(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragunow M., Robertson H. A. Kindling stimulation induces c-fos protein(s) in granule cells of the rat dentate gyrus. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):441–442. doi: 10.1038/329441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R. P., Heimer L. Two methods for selective silver impregnation of degenerating axons and their synaptic endings in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 1967 Apr;4(4):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(67)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin A. R. Analysis of potassium dynamics in mammalian brain tissue. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:393–426. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard G. V., McIntyre D. C., Leech C. K. A permanent change in brain function resulting from daily electrical stimulation. Exp Neurol. 1969 Nov;25(3):295–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Schottler F., Oliver M., Lynch G. Brief bursts of high-frequency stimulation produce two types of structural change in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Aug;44(2):247–258. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liuzzi F. J., Lasek R. J. Astrocytes block axonal regeneration in mammals by activating the physiological stop pathway. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):642–645. doi: 10.1126/science.3603044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothman E. W., Hatlelid J. M., Zorumski C. F. Functional mapping of limbic seizures originating in the hippocampus: a combined 2-deoxyglucose and electrophysiologic study. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 23;360(1-2):92–100. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothman E. W., Perlin J. B., Salerno R. A. Response properties of rapidly recurring hippocampal seizures in rats. Epilepsy Res. 1988 Nov-Dec;2(6):356–366. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(88)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. A., Cotman C., Lynch G. An electron microscopic study of lesion-induced synaptogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. I. Magnitude and time course of degeneration. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90819-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. O., Bonhaus D. W., Shin C., Crain B. J., Gellman R. L., Giacchino J. L. The kindling model of epilepsy: a critical review. CRC Crit Rev Clin Neurobiol. 1985;1(4):341–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Cohen D. R., Hempstead J. L., Curran T. Mapping patterns of c-fos expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):192–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3037702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler J. V., Vaca K. W., White W. F., Lynch G. S., Cotman C. W. Aspartate and glutamate as possible transmitters of excitatory hippocampal afferents. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):538–540. doi: 10.1038/260538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Sampedro M., Lewis E. R., Cotman C. W., Manthorpe M., Skaper S. D., Barbin G., Longo F. M., Varon S. Brain injury causes a time-dependent increase in neuronotrophic activity at the lesion site. Science. 1982 Aug 27;217(4562):860–861. doi: 10.1126/science.7100931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Sampedro M., Manthrope M., Barbin G., Varon S., Cotman C. W. Injury-induced neuronotrophic activity in adult rat brain: correlation with survival of delayed implants in the wound cavity. J Neurosci. 1983 Nov;3(11):2219–2229. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-11-02219.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloviter R. S. A selective loss of hippocampal mossy fiber Timm stain accompanies granule cell seizure activity induced by perforant path stimulation. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 18;330(1):150–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloviter R. S. Decreased hippocampal inhibition and a selective loss of interneurons in experimental epilepsy. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):73–76. doi: 10.1126/science.2879352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward O., Torre E. R., Phillips L. L., Trimmer P. A. The process of reinnervation in the dentate gyrus of adult rats: time course of increases in mRNA for glial fibrillary acidic protein. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2373–2384. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02373.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutula T., He X. X., Cavazos J., Scott G. Synaptic reorganization in the hippocampus induced by abnormal functional activity. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1147–1150. doi: 10.1126/science.2449733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetzlaff W., Graeber M. B., Bisby M. A., Kreutzberg G. W. Increased glial fibrillary acidic protein synthesis in astrocytes during retrograde reaction of the rat facial nucleus. Glia. 1988;1(1):90–95. doi: 10.1002/glia.440010110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. D., Gall C. M. Differential regulation of neuropeptide and proto-oncogene mRNA content in the hippocampus following recurrent seizures. Brain Res. 1987 Dec;427(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S. M., Hayward M. D., Nestler E. J., Duman R. S. Chronic electroconvulsive seizures down-regulate expression of the immediate-early genes c-fos and c-jun in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):1920–1925. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]