Abstract
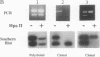
The myeloproliferative syndromes are acquired disorders of hematopoiesis that provide insights into the transition from somatic cell mutation to neoplasia. The clonal origin of specific blood cells can be assessed in patients with X chromosome-linked polymorphisms, taking advantage of random inactivation of the X chromosome. We have adapted the PCR for determination of clonality on as few as 100 cells, including individual colonies grown in culture. Amplifying a polymorphic portion of the X chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) gene after selective digestion of the active X chromosome with a methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme gave results fully concordant with standard Southern blotting of DNA samples from normal (polyclonal) polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) as well as clonal PMN from patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and polycythemia vera (PCV). We have used this technique to demonstrate heterogeneity of lineage involvement in patients with PCV. The same clinical phenotype may arise from clonal proliferation of different hematopoietic progenitors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson J. W., Singer J. W., Catalano P., Murphy S., Lin N., Steinmann L., Ernst C., Fialkow P. J. Polycythemia vera. Further in vitro studies of hematopoietic regulation. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1363–1368. doi: 10.1172/JCI109989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anger B., Janssen J. W., Schrezenmeier H., Hehlmann R., Heimpel H., Bartram C. R. Clonal analysis of chronic myeloproliferative disorders using X-linked DNA polymorphisms. Leukemia. 1990 Apr;4(4):258–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Goldberg J. D., Donovan P. B., Fruchtman S. M., Berlin N. I., Wasserman L. R. Therapeutic recommendations in polycythemia vera based on Polycythemia Vera Study Group protocols. Semin Hematol. 1986 Apr;23(2):132–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Burke P. J., Schiffer C. A., Zehnbauer B. A., Vogelstein B. Differentiation of leukemia cells to polymorphonuclear leukocytes in patients with acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 3;315(1):15–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607033150103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J. Clonal origin of human tumors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 12;458(3):283–321. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Faguet G. B., Jacobson R. J., Vaidya K., Murphy S. Evidence that essential thrombocythemia is a clonal disorder with origin in a multipotent stem cell. Blood. 1981 Nov;58(5):916–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Gartler S. M., Yoshida A. Clonal origin of chronic myelocytic leukemia in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1468–1471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson R. J., Salo A., Fialkow P. J. Agnogenic myeloid metaplasia: a clonal proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells with secondary myelofibrosis. Blood. 1978 Feb;51(2):189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., Anger B. R., Drexler H. G., Bartram C. R., Heimpel H. Essential thrombocythemia in two sisters originating from different stem cell levels. Blood. 1990 Apr 15;75(8):1633–1636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., Buschle M., Layton M., Drexler H. G., Lyons J., van den Berghe H., Heimpel H., Kubanek B., Kleihauer E., Mufti G. J. Clonal analysis of myelodysplastic syndromes: evidence of multipotent stem cell origin. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):248–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Activation of cell growth by binding of Friend spleen focus-forming virus gp55 glycoprotein to the erythropoietin receptor. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):762–764. doi: 10.1038/343762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas G. S., Padua R. A., Masters G. S., Oscier D. G., Jacobs A. The application of X-chromosome gene probes to the diagnosis of myeloproliferative disease. Br J Haematol. 1989 Aug;72(4):530–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb04318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means R. T., Jr, Krantz S. B., Sawyer S. T., Gilbert H. S. Erythropoietin receptors in polycythemia vera. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1340–1344. doi: 10.1172/JCI114303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Blake C. C., Evans S. T., Orkin S. H. Structure of the human phosphoglycerate kinase gene and the intron-mediated evolution and dispersal of the nucleotide-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6965–6969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prchal J. F., Adamson J. W., Murphy S., Steinmann L., Fialkow P. J. Polycythemia vera. The in vitro response of normal and abnormal stem cell lines to erythropoietin. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1044–1047. doi: 10.1172/JCI109003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskind W. H., Fialkow P. J. The use of cell markers in the study of human hematopoietic neoplasia. Adv Cancer Res. 1987;49:127–167. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60796-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskind W. H., Tirumali N., Jacobson R., Singer J., Fialkow P. J. Evidence for a multistep pathogenesis of a myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1318–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. M., Shetta M., Talpaz M., Kantarjian H. M., Hardikar S., Chinault A. C., McCredie K. B., Spitzer G. Myeloproliferative disorders: usefulness of X-linked probes in diagnosis. Leukemia. 1989 Jun;3(6):419–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tefferi A., Thibodeau S. N., Solberg L. A., Jr Clonal studies in the myelodysplastic syndrome using X-linked restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Blood. 1990 May 1;75(9):1770–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtieri M., Gabbianelli M., Pelosi E., Bassano E., Petti S., Russo G., Testa U., Peschle C. Erythropoietin alone induces erythroid burst formation by human embryonic but not adult BFU-E in unicellular serum-free culture. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):460–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Feinberg A. P. Use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms to determine the clonal origin of human tumors. Science. 1985 Feb 8;227(4687):642–645. doi: 10.1126/science.2982210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Willard H. F., Michelson A. M., Riggs A. D., Orkin S. H. Clonal analysis using recombinant DNA probes from the X-chromosome. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4806–4813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]