Abstract
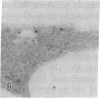
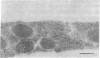
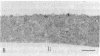
Polyclonal antibodies to the amino- or carboxyl-terminated peptide sequences of the GLUT4 transporter protein were used in immunoelectron microscopic studies to demonstrate the location and insulin-induced translocation of GLUT4 in intact isolated rat adipocytes. Labeling of untreated adipocytes with the amino-terminal antibody revealed 95% of GLUT4 was intracellular, associated with plasma membrane invaginations or vesicles contiguous with or within 75 nm of the cell membrane. Insulin treatment increased plasma membrane labeling approximately 13-fold, to 52% of the total transporters, and decreased intracellular labeling proportionately. In contrast, labeling of untreated adipocytes with the carboxyl-terminal antibody or with a monoclonal antibody (1F8) that binds to the carboxyl terminus of GLUT4 detected fewer transporters, only approximately 40% of which were intracellular. In insulin-treated cells, plasma membrane labeling increased approximately 20-fold, but the total number of labeled transporters also increased approximately 13-fold. The number of intracellular transporters was not changed. The insulin-induced increase in plasma membrane labeling was reversible. Thus, the vast majority of GLUT4 transporters in untreated adipocytes are intracellular in invaginations or vesicles attached or close to the plasma membrane. Insulin treatment causes translocation of transporters to the plasma membrane, which involves flow of transporters from invaginations to the cell surface and possible fusion of subplasma membrane vesicles with the plasma membrane. Differences in the labeling of intracellular transporters by peptide antibodies suggested the carboxyl-terminal epitope of intracellular transporters was masked. The unmasking of the carboxyl terminus during translocation to the plasma membrane may be part of the mechanism by which insulin stimulates glucose transport in rat adipocytes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blok J., Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters from post-Golgi compartments to the plasma membrane of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):69–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROFFORD O. B., RENOLD A. E. GLUCOSE UPTAKE BY INCUBATED RAT EPIDIDYMAL ADIPOSE TISSUE. RATE-LIMITING STEPS AND SITE OF INSULIN ACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:14–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Kitagawa K., Tanner L. I., Holman G. D., Lienhard G. E. Insulin regulation of the two glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13801–13808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Lienhard G. E. Labeling of glucose transporters at the cell surface in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Evidence for both translocation and a second mechanism in the insulin stimulation of transport. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12171–12174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter-Su C., Czech M. P. Reconstitution of D-glucose transport activity from cytoplasmic membranes. Evidence against recruitment of cytoplasmic membrane transporters into the plasma membrane as the sole action of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10382–10386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlapowski F. J., Bertrand B. K., Pessin J., Oka Y., Czech M. P. The relationship of microvesicles to the plasmalemma of rat adipocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;32(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Graver D. F., Smith R. M. Insulin increases the cell surface concentration of alpha 2-macroglobulin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Altered transit of the receptor among intracellular endocytic compartments. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10133–10138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W. Structure-function relationships in the adipose cell. I. Ultrastructure of the isolated adipose cell. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):326–341. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J., Simpson I. A., Karnieli E., Hissin P. J., Wheeler T. J., Hinkle P. C., Salans L. B. Insulin-induced translocation of intracellular glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cell. Fed Proc. 1984 May 15;43(8):2251–2255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Corvera S., Czech M. P. Insulin stimulates cellular iron uptake and causes the redistribution of intracellular transferrin receptors to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8708–8711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. E., Dudek R. W., Whitehead D. S., Downes D. L., Frisell W. R., Caro J. F., Dohm G. L. Immunolocalization of glucose transporter GLUT4 within human skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):150–154. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost S. C., Lane M. D., Gibbs E. M. Effect of phenylarsine oxide on fluid phase endocytosis: further evidence for activation of the glucose transporter. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Dec;141(3):467–474. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Olefsky J. M. Evidence for insulin-induced internalization and degradation of insulin receptors in rat adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):427–431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Kozka I. J., Clark A. E., Flower C. J., Saltis J., Habberfield A. D., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Cell surface labeling of glucose transporter isoform GLUT4 by bis-mannose photolabel. Correlation with stimulation of glucose transport in rat adipose cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18172–18179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurn B. A., Chantler S. M. Production of reagent antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):104–142. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M. Effect of cytochalasin B and D on groups of insulin receptors and on insulin action in rat adipocytes. Possible evidence for a structural relationship of the insulin receptor to the glucose transport system. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):571–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI109338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M. Ultrastructural localization of insulin receptors on adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Weber T. M., Cushman S. W. Qualitative and quantitative comparison of glucose transport activity and glucose transporter concentration in plasma membranes from basal and insulin-stimulated rat adipose cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):155–161. doi: 10.1042/bj2490155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Rossetti L., Lodish H. F., Charron M. J. Decreased in vivo glucose uptake but normal expression of GLUT1 and GLUT4 in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2197–2206. doi: 10.1172/JCI115254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Blevins T. L., Ezaki O. Evidence that translocation of the glucose transport activity is the major mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10942–10947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Thompson P. A., Czech M. P. Coordinate modulation of D-glucose transport activity and bilayer fluidity in plasma membranes derived from control and insulin-treated adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):915–918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavin B. G. The cytophysiology of mammalian adipose cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1972;33:297–334. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61453-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., Lienhard G. E., James D. E. Immuno-localization of the insulin regulatable glucose transporter in brown adipose tissue of the rat. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):123–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Moxley R., Geuze H. J., James D. E. No evidence for expression of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter in endothelial cells. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):369–371. doi: 10.1038/346369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Palacín M., Pilch P. F., Testar X., Zorzano A. Expression of an insulin-regulatable glucose carrier in muscle and fat endothelial cells. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):798–800. doi: 10.1038/342798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Simpson I. A., Rechler M. M., Cushman S. W. Potential mechanism of the stimulatory action of insulin on insulin-like growth factor II binding to the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent redistribution of receptors cycling between a large intracellular pool and the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8378–8383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]