Abstract
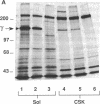
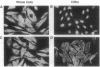
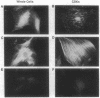
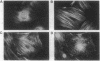
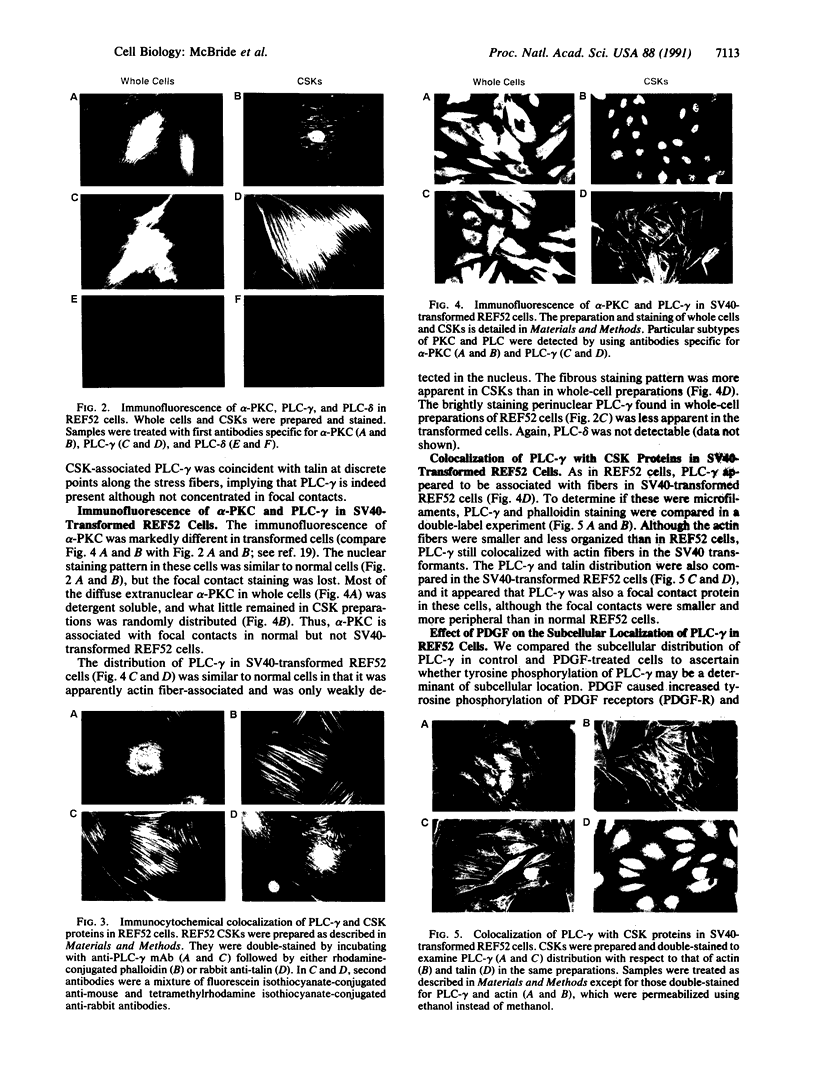
Rat embryo fibroblasts (REF52) exhibit a distinctive, transformation-sensitive distribution of alpha-protein kinase C (alpha-PKC). Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C (PLC)-gamma generates diacylglycerol, the major cellular activator of PKC. Immunofluorescence techniques were used to investigate the subcellular localization of two PLC isozymes (PLC-gamma and PLC-delta) in normal and simian virus 40-transformed REF52 cells to determine (i) if PLC colocalizes with alpha-PKC and (ii) if PLC isozyme distribution is sensitive to transformation. PLC-delta was not detected in either cell type. In REF52 cells, PLC-gamma was associated with the actin cytoskeleton and was evenly distributed along the length of the actin microfilaments. PLC-gamma was coincident with alpha-PKC at the points where the filaments are anchored to the membrane (i.e., the focal contacts). Cytoskeletal association of PLC-gamma was not transformation sensitive, although the actin cytoskeleton was more disordered in simian virus 40-transformed cells. In REF52 cells, platelet-derived growth factor induced tyrosine phosphorylation of both soluble and cytoskeletal PLC-gamma. Tyrosine phosphorylation of PLC-gamma did not seem to be a determinant of its subcellular localization, but there was a detectable increase in cytoskeleton-associated PLC-gamma in response to platelet-derived growth factor treatment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol lipids and cell proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 20;907(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Hepler J. R., Harden T. K. Hormone and growth factor receptor-mediated regulation of phospholipase C activity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):360–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi W. C., Gerfen C. R., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Immunohistochemical localization of a brain isozyme of phospholipase C (PLC III) in astroglia in rat brain. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 9;499(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Mulholland J., Zhu Z. M., Botstein D. Homology of a yeast actin-binding protein to signal transduction proteins and myosin-I. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):288–290. doi: 10.1038/343288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Choi W. C., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Phospholipase C I and II brain isozymes: immunohistochemical localization in neuronal systems in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:205–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckle W. R., Hepler J. R., Rhee S. G., Harden T. K., Earp H. S. Protein kinase C inhibits epidermal growth factor-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma and activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Endocrinology. 1990 Oct;127(4):1697–1705. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-4-1697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyatt S. L., Klauck T., Jaken S. Protein kinase C is localized in focal contacts of normal but not transformed fibroblasts. Mol Carcinog. 1990;3(2):45–53. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940030202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaken S., Leach K., Klauck T. Association of type 3 protein kinase C with focal contacts in rat embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):697–704. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P. Modulation of gelsolin function by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):362–364. doi: 10.1038/325362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Sim S. S., Kim U. H., Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Carpenter G., Rhee S. G. Tyrosine residues in bovine phospholipase C-gamma phosphorylated by the epidermal growth factor receptor in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3940–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassing I., Lindberg U. Specific interaction between phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and profilactin. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):472–474. doi: 10.1038/314472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., Powers E. A., McGuire J. C., Dong L., Kiley S. C., Jaken S. Monoclonal antibodies specific for type 3 protein kinase C recognize distinct domains of protein kinase C and inhibit in vitro functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13223–13230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leto T. L., Lomax K. J., Volpp B. D., Nunoi H., Sechler J. M., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Cloning of a 67-kD neutrophil oxidase factor with similarity to a noncatalytic region of p60c-src. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):727–730. doi: 10.1126/science.1692159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax K. J., Leto T. L., Nunoi H., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Recombinant 47-kilodalton cytosol factor restores NADPH oxidase in chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):409–412. doi: 10.1126/science.2547247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rhee S. G., Williams L. T. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-dependent association of phospholipase C-gamma with the PDGF receptor signaling complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2359–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath H. M., Fee J. A., Rhee S. G., Silbert D. F. Characterization of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C defects associated with thrombin-induced mitogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3080–3087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodaway A. R., Sternberg M. J., Bentley D. L. Similarity in membrane proteins. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):624–624. doi: 10.1038/342624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Purification and characterization of two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12511–12518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Suh P. G., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Bovine brain cytosol contains three immunologically distinct forms of inositolphospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6649–6653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Liu Y. L., Kim H., Rhee S. G., Kung H. F. Inhibition of serum- and ras-stimulated DNA synthesis by antibodies to phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1074–1077. doi: 10.1126/science.2408147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. From signal to pseudopod. How cells control cytoplasmic actin assembly. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18261–18264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Choi W. C., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Monoclonal antibodies to three phospholipase C isozymes from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14497–14504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todderud G., Wahl M. I., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Stimulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 membrane association by epidermal growth factor. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):296–298. doi: 10.1126/science.2374928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Kim J. W., Kim H., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Identification of two epidermal growth factor-sensitive tyrosine phosphorylation sites of phospholipase C-gamma in intact HSC-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3944–3948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Couchman J. R. Focal adhesions and cell-matrix interactions. Coll Relat Res. 1988 Mar;8(2):155–182. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(88)80027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa N., Nishida E., Iida K., Yahara I., Sakai H. Inhibition of the interactions of cofilin, destrin, and deoxyribonuclease I with actin by phosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8382–8386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]