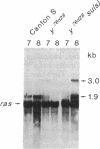
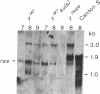
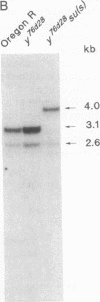
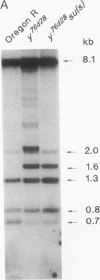
Abstract
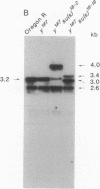
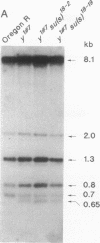
We have studied the effect of mutations in the suppressor of sable [su(s)] gene on P element-induced yellow alleles. Two independent mutations tested, y76d28 and y1#7, contain a 1.1-kilobase (kb) P element inserted in the 5' transcribed untranslated portion of the yellow gene. Sequences responsible for the y1#7 mutation are inserted in the same transcriptional orientation as yellow and cannot be processed by splicing, and this mutation is not suppressed by su(s) mutations. P element sequences are located in a transcriptional orientation opposite to that of the yellow gene in y76d28; these sequences can be spliced from a composite P element-yellow mRNA, resulting in low accumulation of a functional 1.9-kb yellow transcript. The levels of both the putative precursor P element-yellow RNA and the 1.9-kb yellow transcript increase in y76d28 su(s) flies, suggesting that mutations in su(s) do not affect the efficiency of splicing of the P element sequences. Analysis of y76d28 cDNAs isolated from flies carrying a wild-type or mutant su(s) gene demonstrates that the choice of splice junctions to process P element sequences is unchanged in these different backgrounds, suggesting that mutations in su(s) do not affect the selection of donor and acceptor splice sites. We propose that the su(s) protein functions to control the stability of unprocessed RNA during the splicing reaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. Y., Wisely B., Huang S. M., Voelker R. A. Molecular cloning of suppressor of sable, a Drosophila melanogaster transposon-mediated suppressor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1520–1528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. B., Zachar Z., Bingham P. M. Developmental expression of a regulatory gene is programmed at the level of splicing. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4095–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridell R. A., Pret A. M., Searles L. L. A retrotransposon 412 insertion within an exon of the Drosophila melanogaster vermilion gene is spliced from the precursor RNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):559–566. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Corces V. G. Separate regulatory elements are responsible for the complex pattern of tissue-specific and developmental transcription of the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):996–1004. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Richardson K. L., Corces V. G., Green M. M. Genetic instability in Drosophila melanogaster: P-element mutagenesis by gene conversion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Spana C., Corces V. G. On the molecular mechanism of gypsy-induced mutations at the yellow locus of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2657–2662. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. A., Geyer P. K., Spana C., Corces V. G. The gypsy retrotransposon of Drosophila melanogaster: mechanisms of mutagenesis and interaction with the suppressor of Hairy-wing locus. Dev Genet. 1989;10(3):239–248. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020100313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraizumi Y. Spontaneous recombination in Drosophila melanogaster males. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):268–270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes G., O'Connor M., Chia W. On the specificity and effects on transcription of P-element insertions at the yellow locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):3039–3052. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Bender W., Meselson M. Drosophila melanogaster mutations suppressible by the suppressor of Hairy-wing are insertions of a 7.3-kilobase mobile element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1678–1682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozer B., Marlor R., Parkhurst S., Corces V. Characterization and developmental expression of a Drosophila ras oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):885–889. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst S. M., Corces V. G. Interactions among the gypsy transposable element and the yellow and the suppressor of hairy-wing loci in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):47–53. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst S. M., Harrison D. A., Remington M. P., Spana C., Kelley R. L., Coyne R. S., Corces V. G. The Drosophila su(Hw) gene, which controls the phenotypic effect of the gypsy transposable element, encodes a putative DNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1205–1215. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutledge B. J., Mortin M. A., Schwarz E., Thierry-Mieg D., Meselson M. Genetic interactions of modifier genes and modifiable alleles in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Jun;119(2):391–397. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Voelker R. A. Molecular characterization of the Drosophila vermilion locus and its suppressible alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):404–408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spana C., Harrison D. A., Corces V. G. The Drosophila melanogaster suppressor of Hairy-wing protein binds to specific sequences of the gypsy retrotransposon. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1414–1423. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanda S., Corces V. G. Retrotransposon-induced overexpression of a homeobox gene causes defects in eye morphogenesis in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):407–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07962.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelker R. A., Gibson W., Graves J. P., Sterling J. F., Eisenberg M. T. The Drosophila suppressor of sable gene encodes a polypeptide with regions similar to those of RNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):894–905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelker R. A., Huang S. M., Wisely G. B., Sterling J. F., Bainbridge S. P., Hiraizumi K. Molecular and genetic organization of the suppressor of sable and minute (1) 1B region in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):625–642. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Chou T. B., Bingham P. M. Evidence that a regulatory gene autoregulates splicing of its transcript. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4105–4111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]