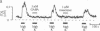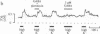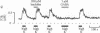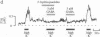Abstract
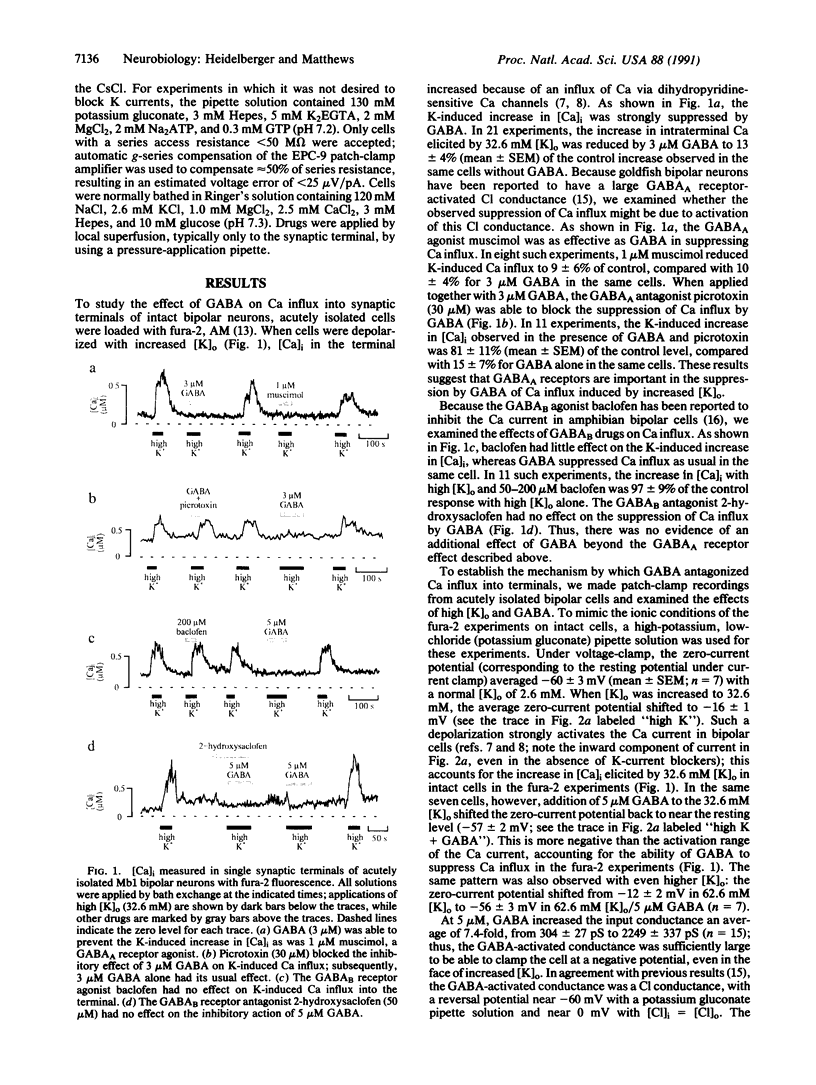
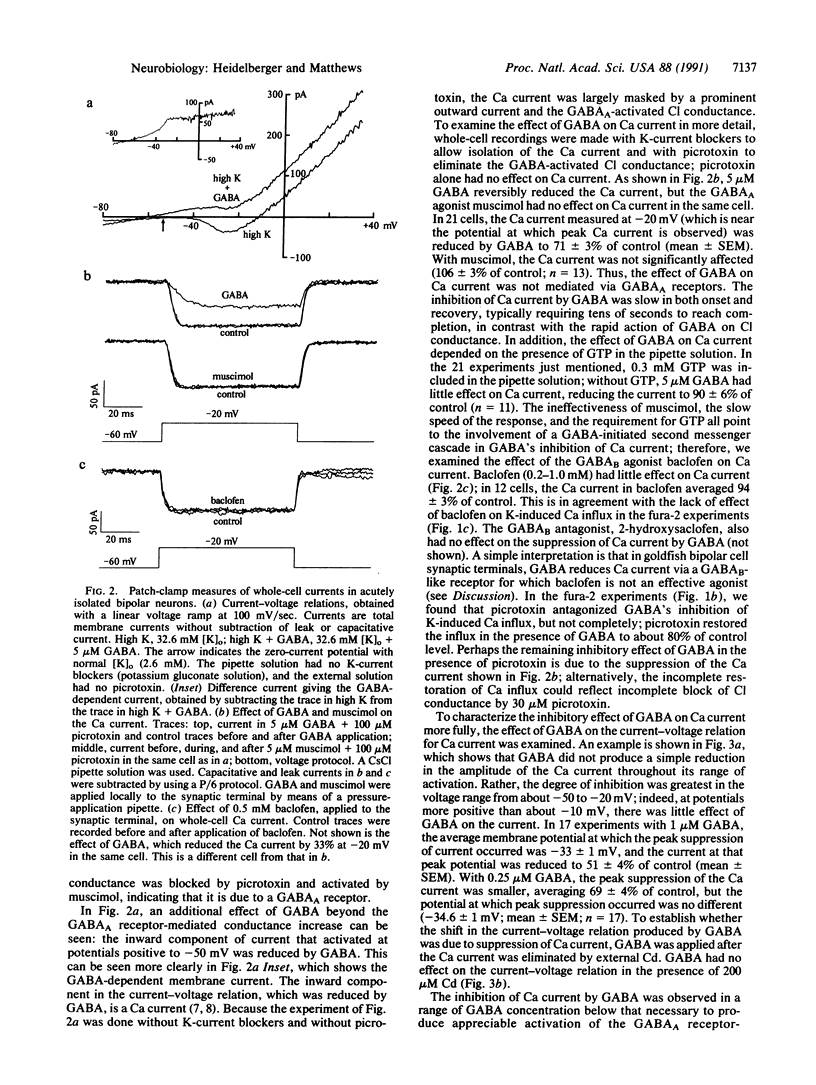
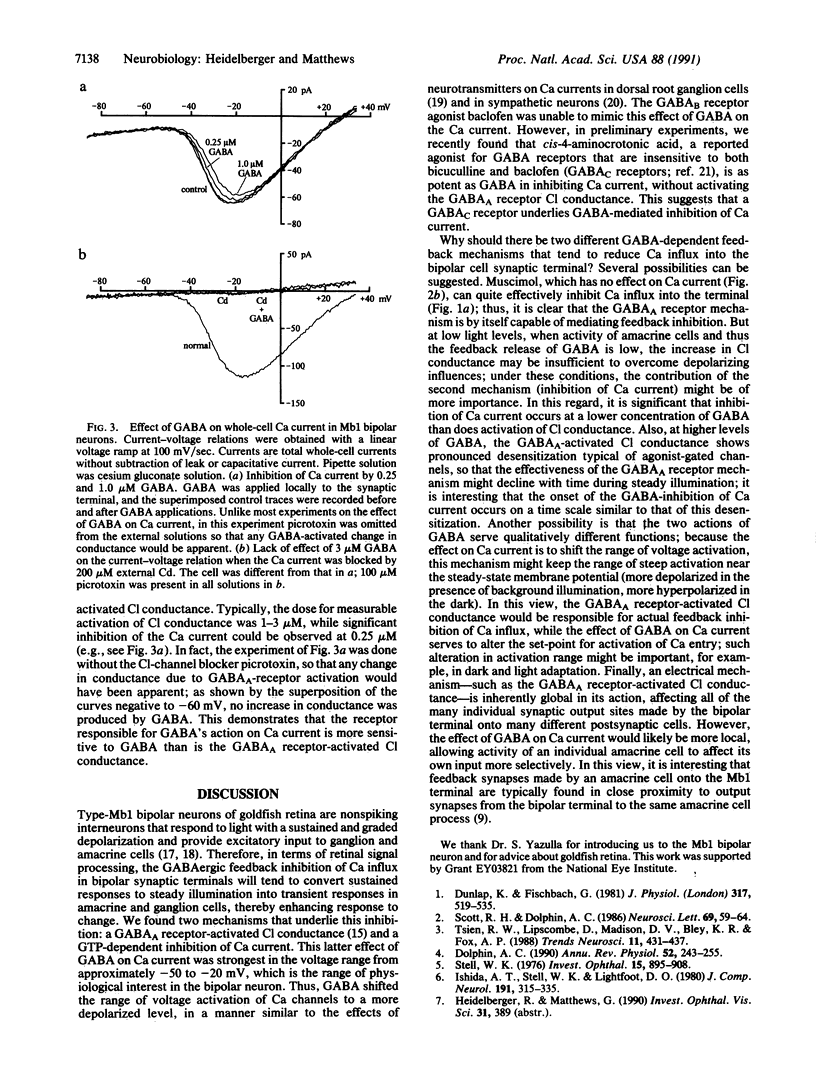
Inhibition of Ca influx and Ca current by gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was studied in single synaptic terminals of isolated retinal bipolar neurons. Measurements of intracellular Ca concentration [( Ca]i) using the fluorescent Ca indicator fura-2 showed that GABA potently inhibited Ca influx into the terminal elicited by high extracellular K concentration ([K]o). This inhibition was attributed to GABA type A (GABAA) receptor-activated chloride ion conductance that prevented bipolar neurons from depolarizing sufficiently to activate the Ca current, even in response to increased [K]o. Patch-clamp recordings of the Ca current revealed a second effect of GABA: GTP-dependent inhibition of the Ca current. This inhibition was not mediated by GABAA receptors, but baclofen, which binds to the GABA type B (GABAB) receptor and is known to inhibit the Ca current in other systems, was not able to mimic the action of GABA. This suggests the involvement of a different type of GABAB-like receptor in the inhibition of Ca current by GABA. GABA did not cause an overall suppression of the Ca current; rather, the voltage-dependence of Ca-channel activation was shifted to more depolarized potentials. Thus, maximal inhibition of the Ca current by GABA occurred in the physiological range of potential.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C. G protein modulation of calcium currents in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:243–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew C. A., Johnston G. A., Weatherby R. P. Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors: studies on the binding of (-)-baclofen to rat cerebellar membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Dec 21;52(3):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Fischbach G. D. Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium conductance activated by depolarization of embryonic chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:519–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Zhou W., Jones S. W. LHRH and GTP-gamma-S modify calcium current activation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90035-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Stell W. K., Lightfoot D. O. Rod and cone inputs to bipolar cells in goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Jun;191(3):315–335. doi: 10.1002/cne.901910302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire G., Maple B., Lukasiewicz P., Werblin F. Gamma-aminobutyrate type B receptor modulation of L-type calcium channel current at bipolar cell terminals in the retina of the tiger salamander. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10144–10147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Stell W. K., Bok D., Lam D. M. GABA-ergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 15;182(2):221–244. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Kondo H., Toyoda J. I. Ionic mechanisms of two types of on-center bipolar cells in the carp retina. I. The responses to central illumination. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Jan;73(1):73–90. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Kujiraoka T., Yonaha T. Connections between photoreceptors and horseradish peroxidase-injected bipolar cells in the carp retina. Vision Res. 1983;23(4):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(83)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Dolphin A. C. Regulation of calcium currents by a GTP analogue: potentiation of (-)-baclofen-mediated inhibition. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Aug 15;69(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90414-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Ionic currents of solitary horizontal cells isolated from goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:329–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M., Kaneko A. gamma-Aminobutyric acid exerts a local inhibitory action on the axon terminal of bipolar cells: evidence for negative feedback from amacrine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3501–3505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazulla S., Studholme K. M., Wu J. Y. GABAergic input to the synaptic terminals of mb1 bipolar cells in the goldfish retina. Brain Res. 1987 May 19;411(2):400–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]