Abstract
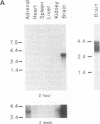
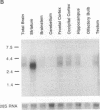
A cDNA clone encoding a neural-specific putative protein-tyrosine-phosphatase (protein-tyrosine-phosphate phosphohydrolase, EC 3.1.3.48) has been isolated from a rat striatal cDNA library. The deduced amino acid sequence predicts a protein of approximately 369 amino acids with a strong homology to other members of the family of protein-tyrosine-phosphatases. In vitro translation produces a protein with an apparent molecular mass of 46 kDa. A potential attachment mechanism to the cytoplasmic membrane is suggested by a myristoylation amino acid-consensus sequence at the N terminus of the protein. RNA analyses of various regions of rat brain reveal a 3-kilobase (kb) and a 4.4-kb mRNA. The 3-kb mRNA is highly enriched within the striatum relative to other brain areas and has been termed a "striatum enriched phosphatase" (STEP). In contrast, the 4.4-kb message is most abundant in the cerebral cortex and rare in the striatum. These two messages appear to be alternatively processed RNA transcripts of a single gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander D. R. The role of phosphatases in signal transduction. New Biol. 1990 Dec;2(12):1049–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Selective multiplication of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1357–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay A. N., Jackson D. I., Willis A. C., Williams A. F. Lymphocyte specific heterogeneity in the rat leucocyte common antigen (T200) is due to differences in polypeptide sequences near the NH2-terminus. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1259–1264. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Kumar S., Diltz C. D., Harrylock M., Cool D. E., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Human placenta protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: amino acid sequence and relationship to a family of receptor-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H. The leukocyte common antigen (CD45): a putative receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7182–7186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. cDNA isolated from a human T-cell library encodes a member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5257–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenfeldt W. H., Puskas R. S., Berger S. L. Homopolymeric tailing. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:337–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Haun R. S., Watson S. J., Geahlen R. L., Dixon J. E. Cloning and expression of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U. Second-strand cDNA synthesis: classical method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:325–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., Aswad D. W., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. II. Purification and characterization of the phosphoprotein from bovine caudate nucleus. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):99–110. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00099.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., McGuinness T. L., Huganir R. L., Greengard P. Role of protein phosphorylation in neuronal signal transduction. FASEB J. 1989 Mar;3(5):1583–1592. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.5.2493406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A. A., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. Protein tyrosine kinase activity and its endogenous substrates in rat brain: a subcellular and regional survey. J Neurochem. 1988 May;50(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirik F. R., Janzen N. M., Melhado I. G., Harder K. W. Cloning and chromosomal assignment of a widely expressed human receptor-like protein-tyrosine phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 29;273(1-2):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson R. L., Ingebritsen V. M., Ingebritsen T. S. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatases. I. Separation of multiple forms from bovine brain and purification of the major form to near homogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7747–7753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R., Morse B., Huebner K., Croce C., Howk R., Ravera M., Ricca G., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Cloning of three human tyrosine phosphatases reveals a multigene family of receptor-linked protein-tyrosine-phosphatases expressed in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. D., Ohnishi K., Lebow L. T., Bonavida B. The SJL/J T cell response to both spontaneous and transplantable syngeneic reticulum cell sarcoma is mediated predominantly by the V beta 17a+ T cell clonotype. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1553–1562. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug M. S., Berger S. L. First-strand cDNA synthesis primed with oligo(dT). Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:316–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Przybyla A. E., Chirgwin J. M. Isolation of RNA using guanidinium salts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:219–227. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. J., Cahir E. D., Thomas M. L. Identification of an additional member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family: evidence for alternative splicing in the tyrosine phosphatase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4444–4448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. Practical aspects of preparing phage and plasmid DNA: growth, maintenance, and storage of bacteria and bacteriophage. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:145–170. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., D'Eustachio P., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of a widely expressed receptor tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Tsai A. Y., Saito H. A family of receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases in humans and Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8698–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Demonstration that the leukocyte common antigen CD45 is a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8695–8701. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]