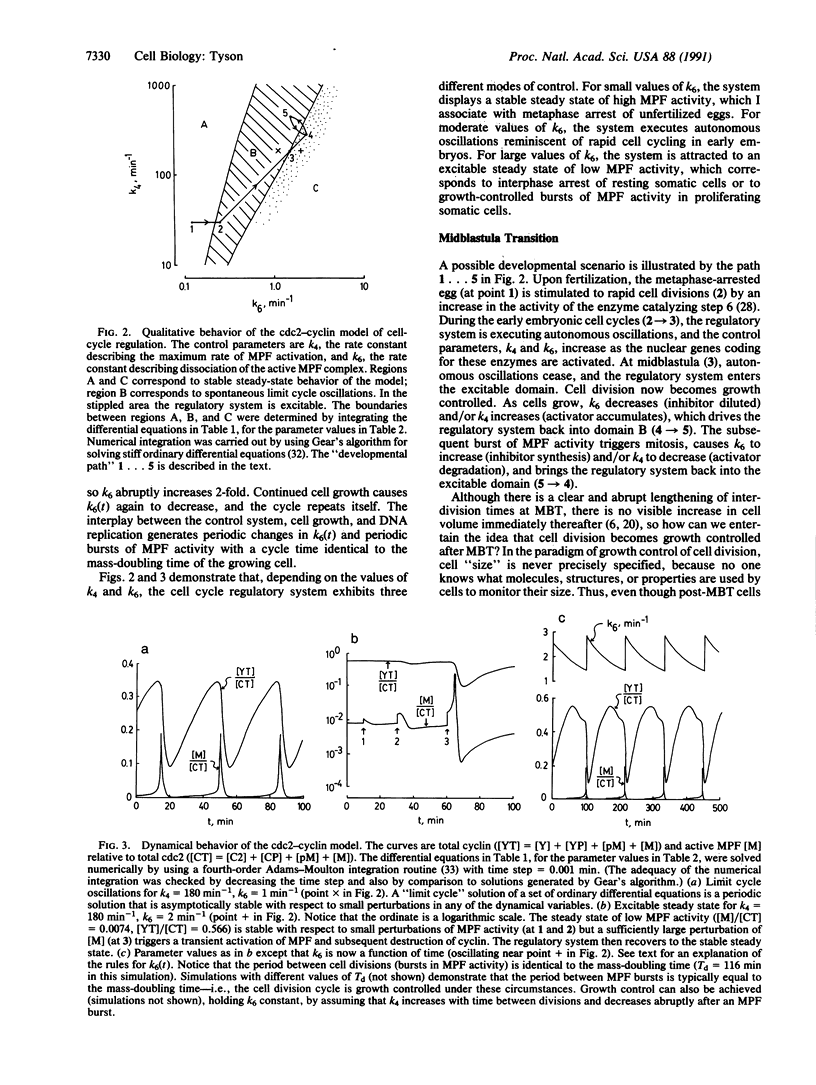
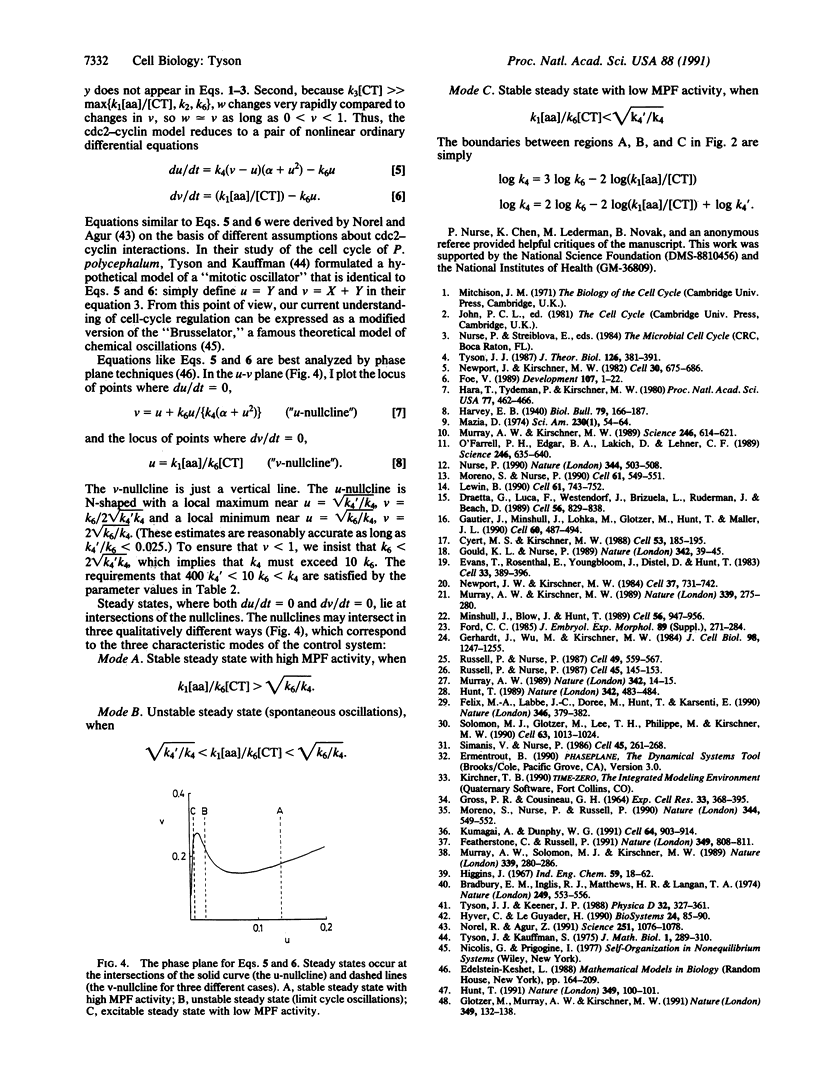
Abstract
The proteins cdc2 and cyclin form a heterodimer (maturation promoting factor) that controls the major events of the cell cycle. A mathematical model for the interactions of cdc2 and cyclin is constructed. Simulation and analysis of the model show that the control system can operate in three modes: as a steady state with high maturation promoting factor activity, as a spontaneous oscillator, or as an excitable switch. We associate the steady state with metaphase arrest in unfertilized eggs, the spontaneous oscillations with rapid division cycles in early embryos, and the excitable switch with growth-controlled division cycles typical of nonembryonic cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R., Langan T. A. Molecular basis of control of mitotic cell division in eukaryotes. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):553–556. doi: 10.1038/249553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of MPF activity in vitro. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90380-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E. Mitotic domains reveal early commitment of cells in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1989 Sep;107(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. C. Maturation promoting factor and cell cycle regulation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Nov;89 (Suppl):271–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Hunt T., Karsenti E. Triggering of cyclin degradation in interphase extracts of amphibian eggs by cdc2 kinase. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):379–382. doi: 10.1038/346379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R., COUSINEAU G. H. MACROMOLECULE SYNTHESIS AND THE INFLUENCE OF ACTINOMYCIN ON EARLY DEVELOPMENT. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Feb;33:368–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J., Wu M., Kirschner M. Cell cycle dynamics of an M-phase-specific cytoplasmic factor in Xenopus laevis oocytes and eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara K., Tydeman P., Kirschner M. A cytoplasmic clock with the same period as the division cycle in Xenopus eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):462–466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Cell biology. Destruction's our delight... Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):100–101. doi: 10.1038/349100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Embryology. Under arrest in the cell cycle. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):483–484. doi: 10.1038/342483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyver C., Le Guyader H. MPF and cyclin: modelling of the cell cycle minimum oscillator. Biosystems. 1990;24(2):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(90)90001-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. The cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):903–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90315-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Driving the cell cycle: M phase kinase, its partners, and substrates. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90181-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazia D. The cell cycle. Sci Am. 1974 Jan;230(1):53–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Blow J. J., Hunt T. Translation of cyclin mRNA is necessary for extracts of activated xenopus eggs to enter mitosis. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P., Russell P. Regulation of mitosis by cyclic accumulation of p80cdc25 mitotic inducer in fission yeast. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):549–552. doi: 10.1038/344549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P. Substrates for p34cdc2: in vivo veritas? Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):549–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90463-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. Cell biology: the cell cycle as a cdc2 cycle. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):14–15. doi: 10.1038/342014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Dominoes and clocks: the union of two views of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):614–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2683077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of the cell cycle during early Xenopus development. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norel R., Agur Z. A model for the adjustment of the mitotic clock by cyclin and MPF levels. Science. 1991 Mar 1;251(4997):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.1825521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H., Edgar B. A., Lakich D., Lehner C. F. Directing cell division during development. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2683080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson J. J. Size control of cell division. J Theor Biol. 1987 Jun 21;126(4):381–391. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(87)80146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


