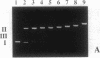
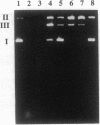
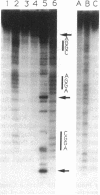
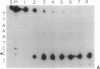
Abstract
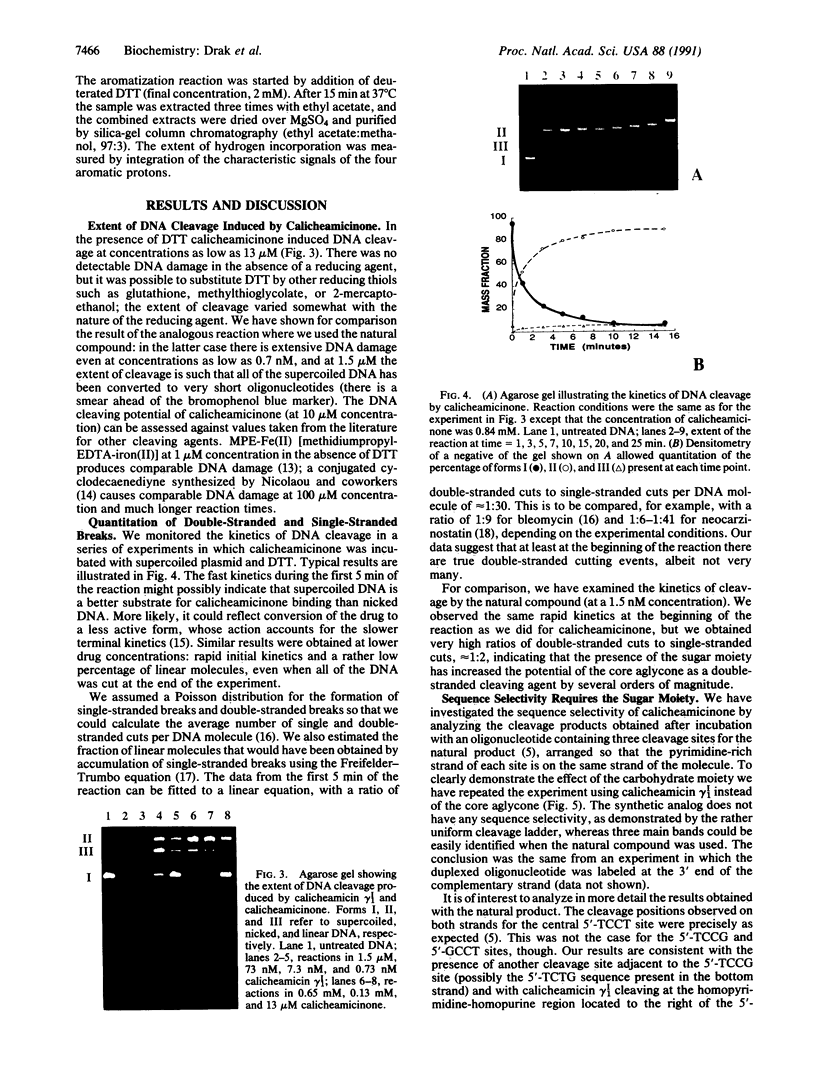
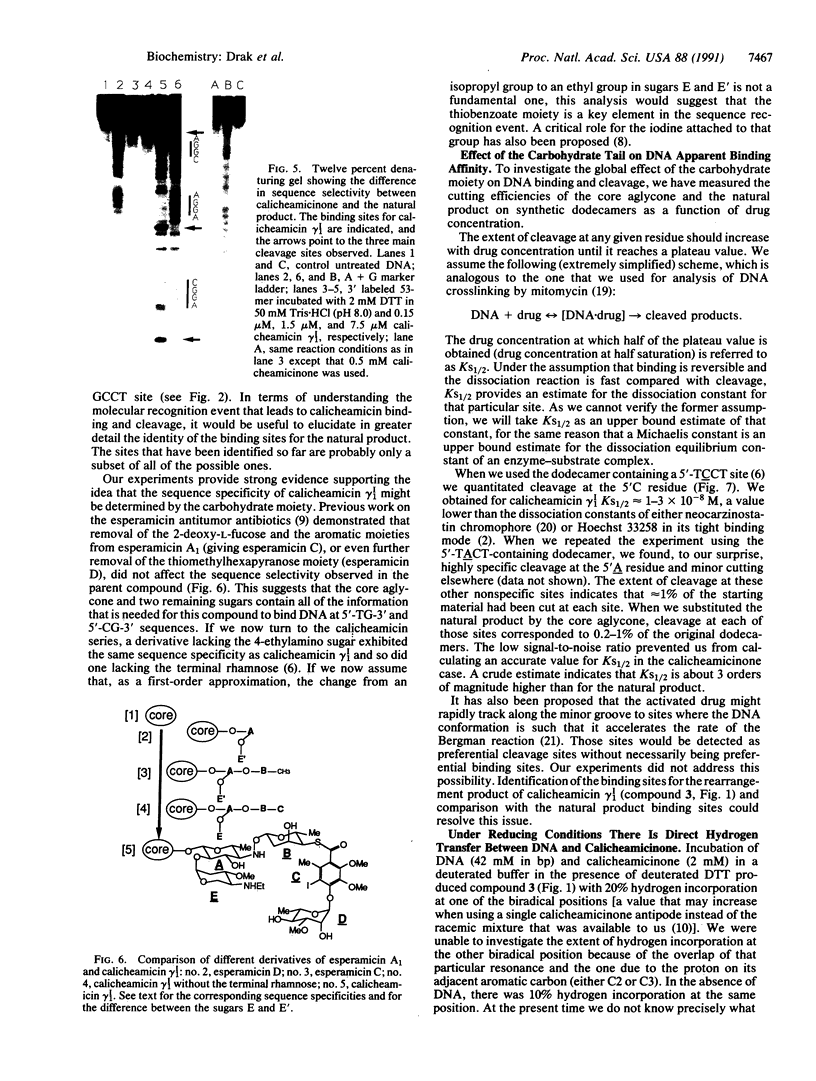
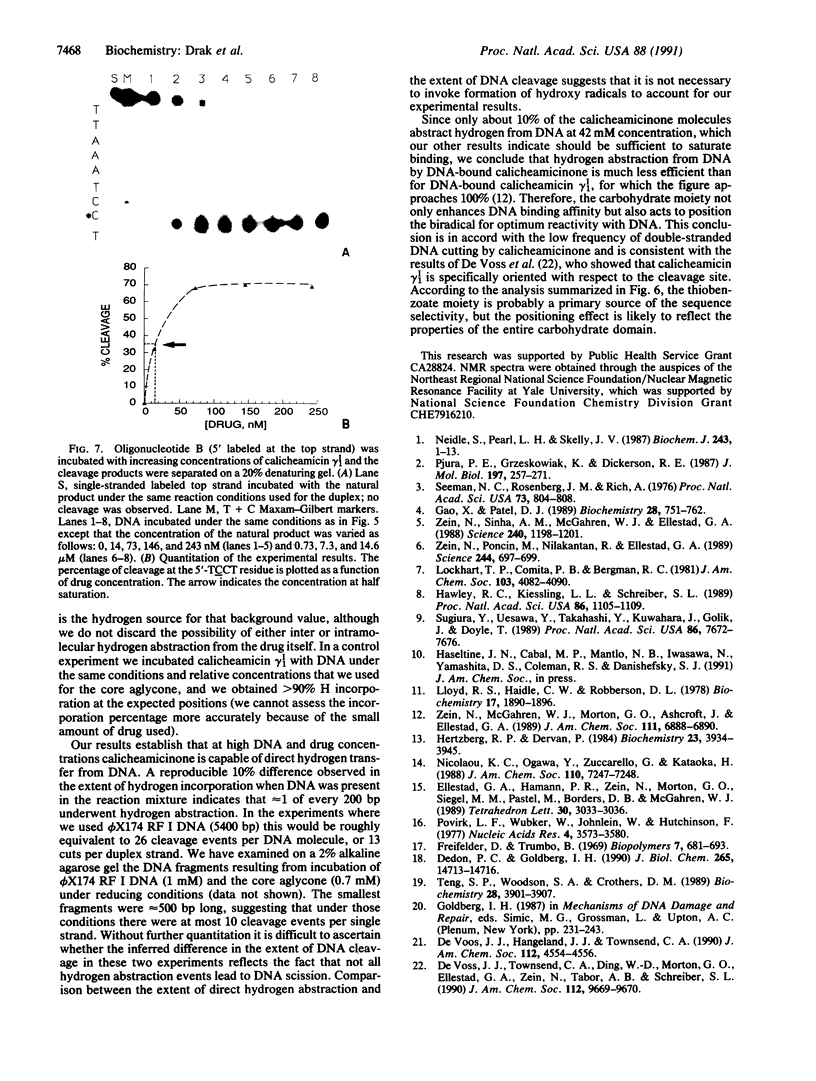
We have investigated the DNA cleaving properties of calicheamicinone, the synthetic core aglycone of calicheamicin gamma I1, a natural product with extremely potent antitumor activity. Our experiments have shown that the synthetic analog binds and cleaves DNA, albeit without any sequence selectivity and with less efficiency than the natural compound. We propose that a key element in the sequence recognition process is the thiobenzoate ring present in the natural compound. We have demonstrated by one-dimensional NMR that there is direct hydrogen abstraction from DNA by calicheamicinone, with enhanced binding affinity contributed by the carbohydrate domain. The reduced efficiency of hydrogen abstraction from DNA by bound calicheamicinone, compared with the natural compound, implicates the carbohydrate moiety in positioning the drug for hydrogen abstraction.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dedon P. C., Goldberg I. H. Sequence-specific double-strand breakage of DNA by neocarzinostatin involves different chemical mechanisms within a staggered cleavage site. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14713–14716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. L., Patel D. J. Solution structure of the chromomycin-DNA complex. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):751–762. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. C., Kiessling L. L., Schreiber S. L. Model of the interactions of calichemicin gamma 1 with a DNA fragment from pBR322. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1105–1109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. S., Haidle C. W., Robberson D. L. Bleomycin-specific fragmentation of double-stranded DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1890–1896. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle S., Pearl L. H., Skelly J. V. DNA structure and perturbation by drug binding. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2430001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pjura P. E., Grzeskowiak K., Dickerson R. E. Binding of Hoechst 33258 to the minor groove of B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povirk L. F., Wübter W., Köhnlein W., Hutchinson F. DNA double-strand breaks and alkali-labile bonds produced by bleomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3573–3580. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura Y., Uesawa Y., Takahashi Y., Kuwahara J., Golik J., Doyle T. W. Nucleotide-specific cleavage and minor-groove interaction of DNA with esperamicin antitumor antibiotics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7672–7676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng S. P., Woodson S. A., Crothers D. M. DNA sequence specificity of mitomycin cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3901–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zein N., Poncin M., Nilakantan R., Ellestad G. A. Calicheamicin gamma 1I and DNA: molecular recognition process responsible for site-specificity. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.2717946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zein N., Sinha A. M., McGahren W. J., Ellestad G. A. Calicheamicin gamma 1I: an antitumor antibiotic that cleaves double-stranded DNA site specifically. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1198–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.3240341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]