Abstract
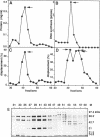
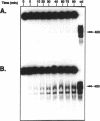
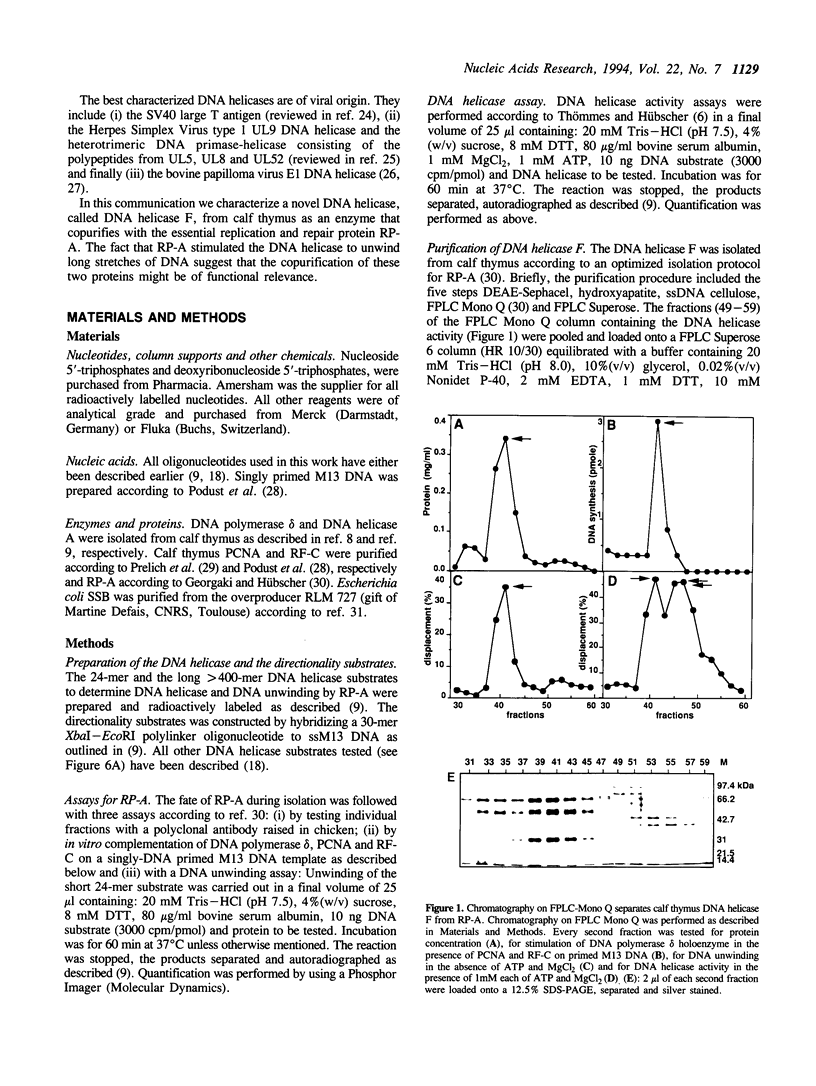
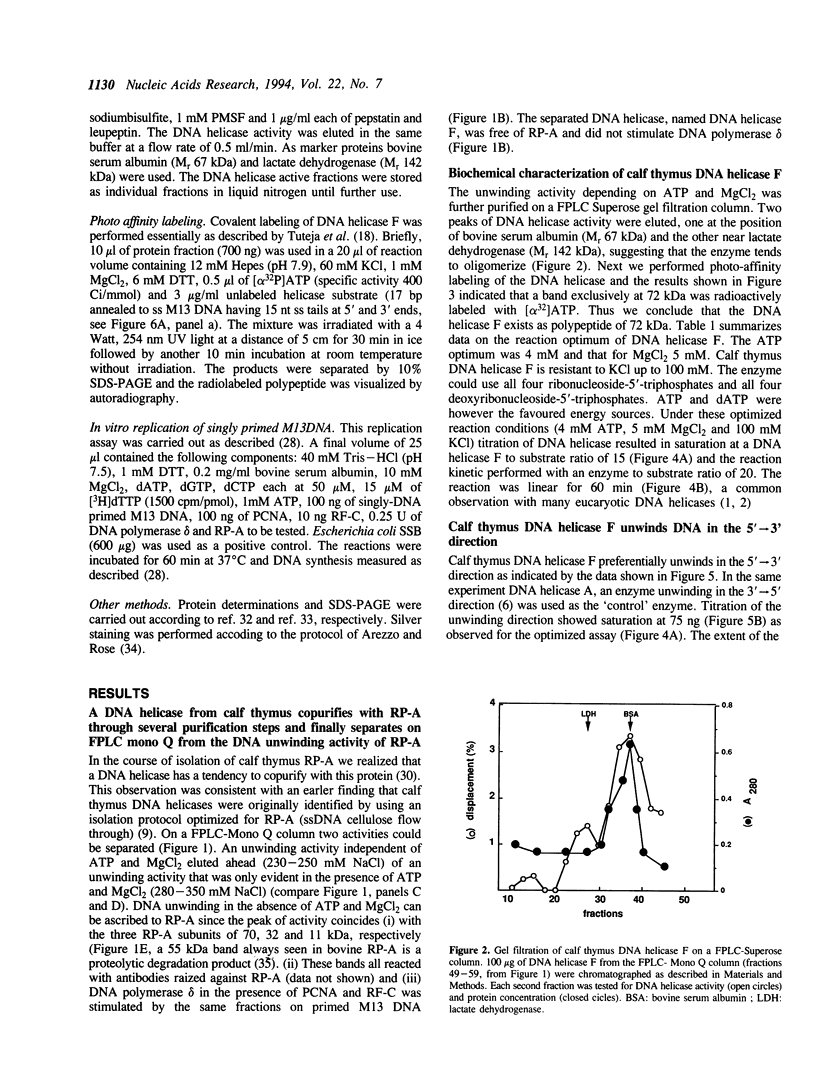
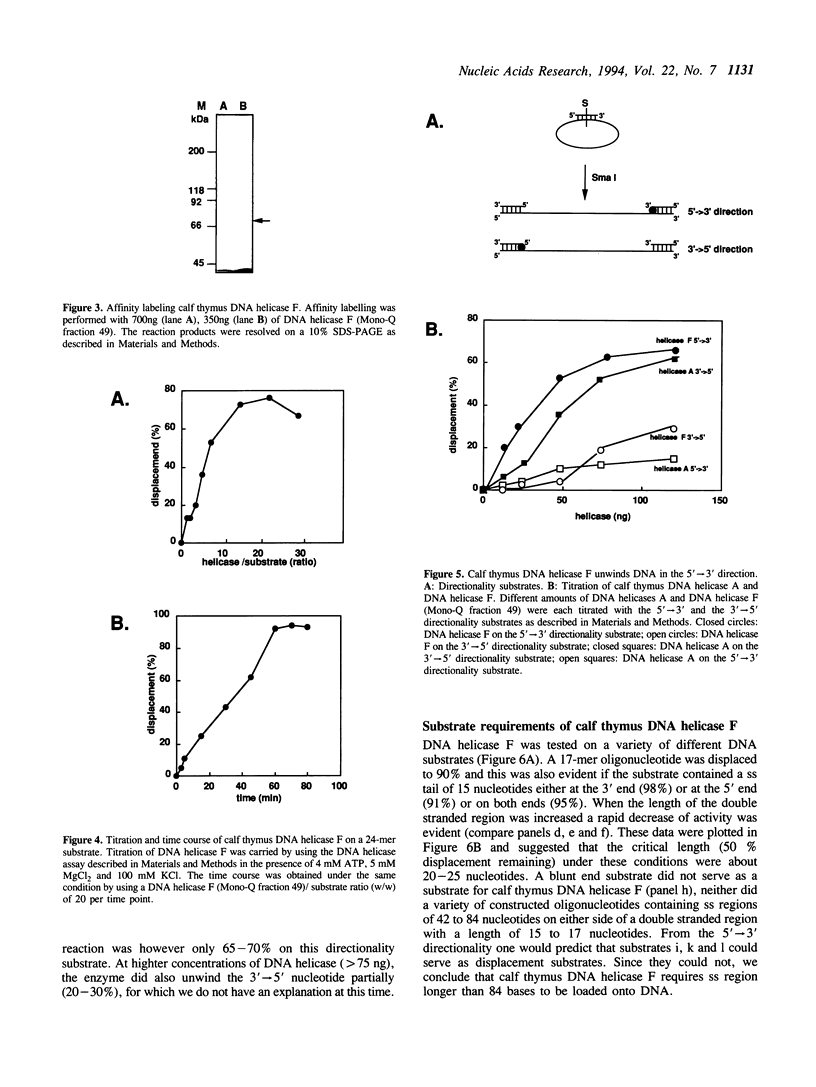
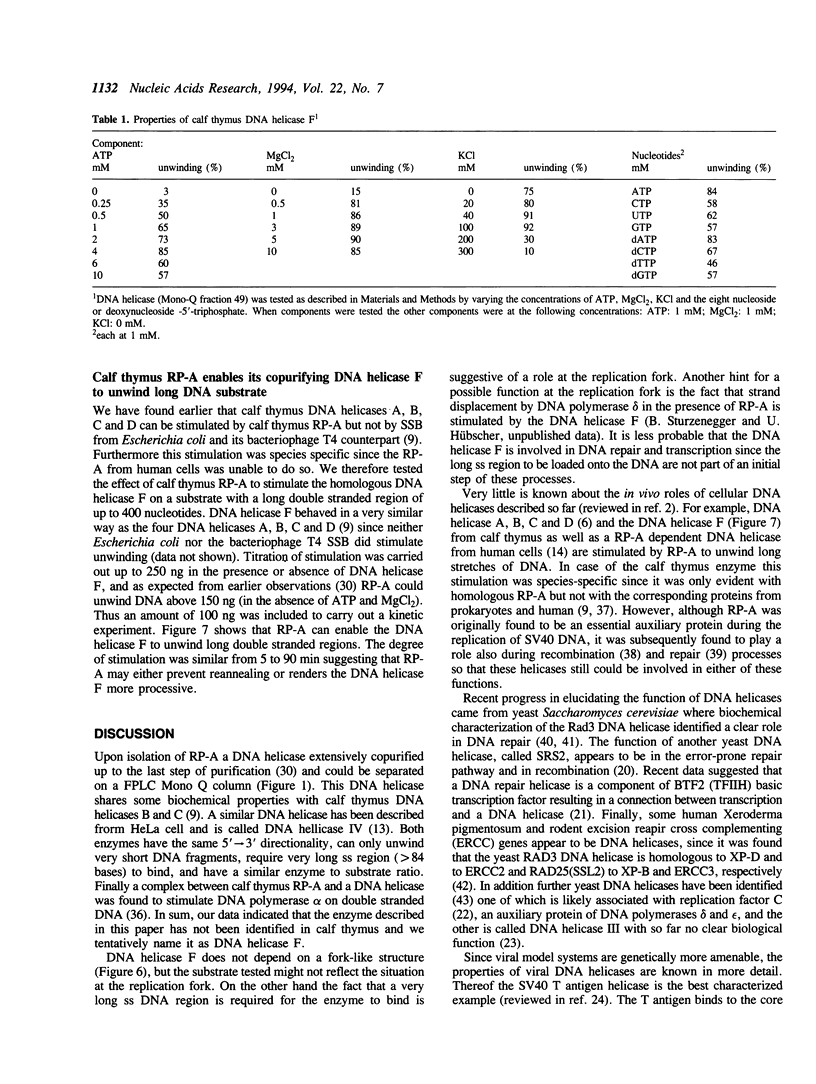
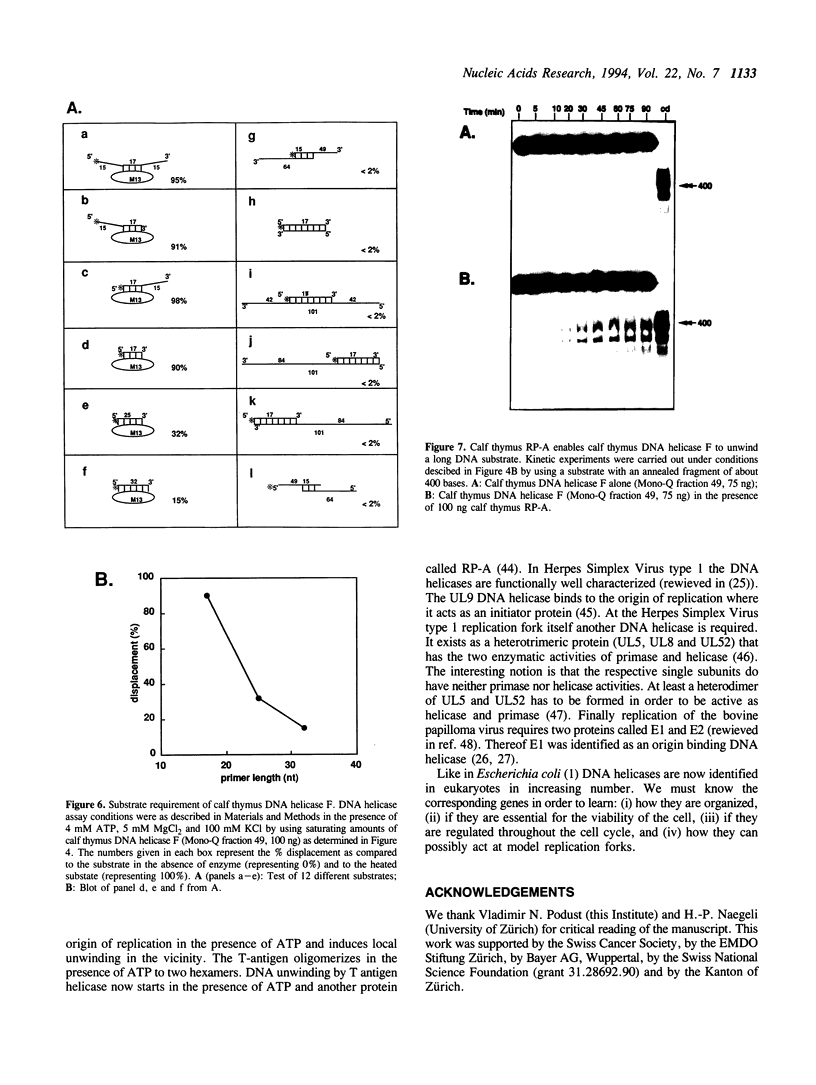
A DNA helicase from calf thymus, called DNA helicase F, copurified with replication protein A through several steps of purification including DEAE-Sephacel, hydroxyapatite and single stranded DNA cellulose. It is finally separated from replication protein A on FPLC Mono Q where the DNA helicase elutes after replication protein A. Characterization of the DNA helicase F by affinity labeling with [alpha 32P]ATP indicated that the enzyme has a catalytic subunit of 72 kDa. Gel filtration experiments suggested that DNA helicase F can exist both in a monomeric and an oligomeric form. The enzyme unwinds DNA in the 5'-->3' direction in relation to the strand it binds. All eight deoxyribonucleoside- and ribonucleosidetriphosphates could serve as an energy source. Testing a variety of DNA/DNA substrates demonstrated that the DNA helicase F preferentially unwinds very short substrates and is slightly stimulated by a single stranded 3'-tail. However, replication protein A allowed the DNA helicase to unwind much longer DNA substrates of up to 400 bases, indicating that the copurification of replication protein A with the DNA helicase F might be of functional relevance.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arezzo F., Rose K. M. Tryptic peptide analysis of nanogram quantities of proteins: radioiodination of proteins detected by silver staining in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1987 Dec;167(2):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. DNA repair. Engagement with transcription. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):114–115. doi: 10.1038/363114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner R. C., Crute J. J., Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. The herpes simplex virus 1 origin binding protein: a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2669–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. A role for the human single-stranded DNA binding protein HSSB/RPA in an early stage of nucleotide excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3873–3880. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex-1 DNA polymerase. Identification of an intrinsic 5'----3' exonuclease with ribonuclease H activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19266–19270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Caddle M. S., Heintz N., Heintz N. H. Purification of RIP60 and RIP100, mammalian proteins with origin-specific DNA-binding and ATP-dependent DNA helicase activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6225–6235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. Association of DNA helicase and primase activities with a subassembly of the herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase composed of the UL5 and UL52 gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1105–1109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Erdile L. F., Gilbert I. U., von Winkler D., Kelly T. J., Fanning E. Interaction of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with cellular replication protein A and SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):769–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E. Simian virus 40 large T antigen: the puzzle, the pieces, and the emerging picture. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1289–1293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1289-1293.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgaki A., Hübscher U. DNA unwinding by replication protein A is a property of the 70 kDa subunit and is facilitated by phosphorylation of the 32 kDa subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3659–3665. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgaki A., Strack B., Podust V., Hübscher U. DNA unwinding activity of replication protein A. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 24;308(3):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81283-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. J., Jiricny J. The purification of a human mismatch-binding protein and identification of its associated ATPase and helicase activities. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23876–23882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Stalder H. P. Mammalian DNA helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5471–5483. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessberger R., Podust V., Hübscher U., Berg P. A mammalian protein complex that repairs double-strand breaks and deletions by recombination. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15070–15079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Tan C. K., So A. G., Downey K. M. Purification and characterization of delta helicase from fetal calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3507–3513. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Yoder B. L., Burgers P. M. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA helicase associated with replication factor C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25321–25327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Green J. M., Beyer R. S. Large-scale overproduction and rapid purification of the Escherichia coli ssb gene product. Expression of the ssb gene under lambda PL control. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):21–25. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Morton B. S. Escherichia coli DNA helicase I catalyzes a site- and strand-specific nicking reaction at the F plasmid oriT. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16232–16237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Tabor S., Richardson C. C. The gene 4 protein of bacteriophage T7. Characterization of helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14017–14024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naegeli H., Bardwell L., Friedberg E. C. The DNA helicase and adenosine triphosphatase activities of yeast Rad3 protein are inhibited by DNA damage. A potential mechanism for damage-specific recognition. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):392–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naegeli H., Bardwell L., Harosh I., Freidberg E. C. Substrate specificity of the Rad3 ATPase/DNA helicase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and binding of Rad3 protein to nucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7839–7844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podust V. N., Georgaki A., Strack B., Hübscher U. Calf thymus RF-C as an essential component for DNA polymerase delta and epsilon holoenzymes function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4159–4165. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rong L., Klein H. L. Purification and characterization of the SRS2 DNA helicase of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1252–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo Y. S., Hurwitz J. Isolation of helicase alpha, a DNA helicase from HeLa cells stimulated by a fork structure and signal-stranded DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10282–10295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo Y. S., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Isolation of a DNA helicase from HeLa cells requiring the multisubunit human single-stranded DNA-binding protein for activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13161–13170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo Y. S., Müller F., Lusky M., Hurwitz J. Bovine papilloma virus (BPV)-encoded E1 protein contains multiple activities required for BPV DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):702–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Sugino A. Purification and characterization of DNA helicase III from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9578–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal G., Turchi J. J., Jessee C. B., Myers T. W., Bambara R. A. A novel DNA helicase from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13629–13635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Ferrari E., Jessberger R., Hübscher U. Four different DNA helicases from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6063–6073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. DNA helicase from calf thymus. Purification to apparent homogeneity and biochemical characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14347–14354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. Eukaryotic DNA helicases: essential enzymes for DNA transactions. Chromosoma. 1992 Jun;101(8):467–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00352468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Rahman K., Tuteja R., Falaschi A. Human DNA helicase V, a novel DNA unwinding enzyme from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2323–2329. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Rahman K., Tuteja R., Ochem A., Skopac D., Falaschi A. DNA helicase III from HeLa cells: an enzyme that acts preferentially on partially unwound DNA duplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 25;20(20):5329–5337. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.20.5329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Tuteja R., Rahman K., Kang L. Y., Falaschi A. A DNA helicase from human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6785–6792. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser T., Gassmann M., Thömmes P., Ferrari E., Hafkemeyer P., Hübscher U. Biochemical and functional comparison of DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10420–10428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Mohr I., Fouts E., Lim D. A., Nohaile M., Botchan M. The E1 protein of bovine papilloma virus 1 is an ATP-dependent DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5086–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Mohr I., Li R., Nottoli T., Sun S., Botchan M. Transcription factor E2 regulates BPV-1 DNA replication in vitro by direct protein-protein interaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:335–346. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. S., Grosse F. Purification and characterization of two DNA helicases from calf thymus nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20483–20490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S., Grosse F. A complex between replication factor A (SSB) and DNA helicase stimulates DNA synthesis of DNA polymerase alpha on double-stranded DNA. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 9;312(2-3):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80922-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]