Abstract
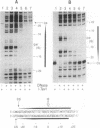
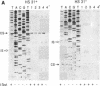
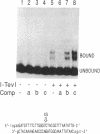
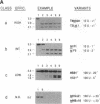
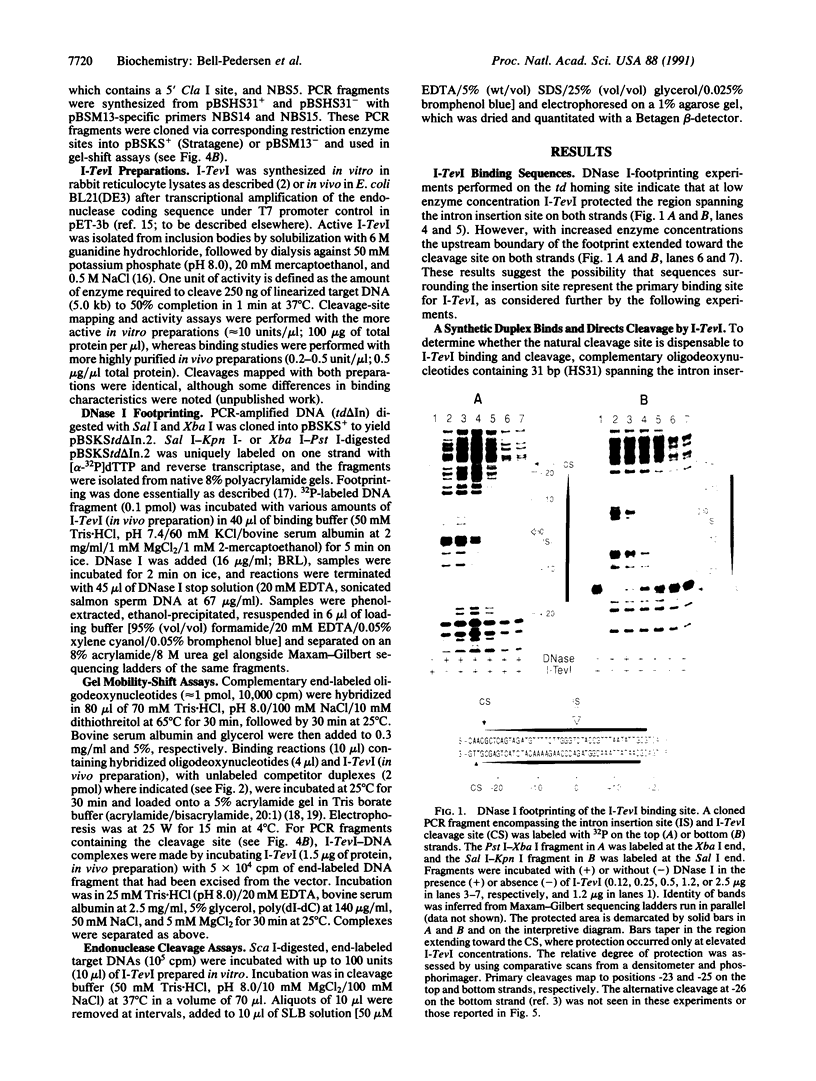
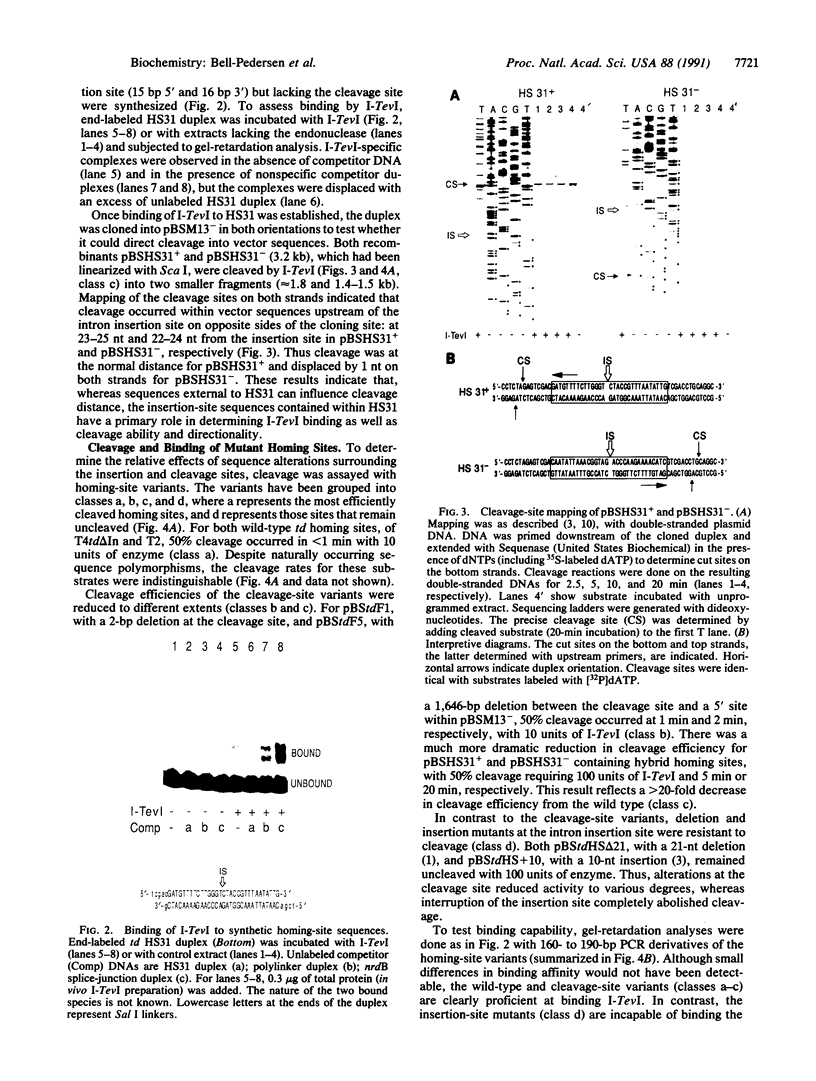
Mobility of the phage T4 td intron depends on activity of an intron-encoded endonuclease (I-TevI), which cleaves a homologous intronless (delta In) target gene. The double-strand break initiates a recombination event that leads to intron transfer. We found previously that I-TevI cleaves td delta In target DNA 23-26 nucleotides upstream of the intron insertion site. DNase I-footprinting experiments and gel-shift assays indicate that I-TevI makes primary contacts around the intron insertion site. A synthetic DNA duplex spanning the insertion site but lacking the cleavage site was shown to bind I-TevI specifically, and when cloned, to direct cleavage into vector sequences. The behavior of the cloned duplex and that of deletion and insertion mutants support a primary role for sequences surrounding the insertion site in directing I-TevI binding, conferring cleavage ability, and determining cleavage polarity. On the other hand, sequences around the cleavage site were shown to influence cleavage efficiency and cut-site selection. The role of cleavage-site sequences in determining cleavage distance argues against a strict "ruler" mechanism for cleavage by I-TevI. The complex nature of the homing site recognized by this unusual type of endonuclease is considered in the context of intron spread.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfort M. Phage T4 introns: self-splicing and mobility. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:363–385. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Galloway Salvo J. L., Belfort M. A transcription terminator in the thymidylate synthase (thyA) structural gene of Escherichia coli and construction of a viable thyA::Kmr deletion. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1193–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1193-1200.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S. M., Aubrey M., Belfort M. A site-specific endonuclease and co-conversion of flanking exons associated with the mobile td intron of phage T4. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S., Clyman J., Belfort M. Intron mobility in phage T4 is dependent upon a distinctive class of endonucleases and independent of DNA sequences encoding the intron core: mechanistic and evolutionary implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3763–3770. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Maley G., Pedersen-Lane J., Wang A. M., Maley F. Characterization of the restriction site of a prokaryotic intron-encoded endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3574–3578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., D'Auriol L., Galibert F., Dujon B. Recognition and cleavage site of the intron-encoded omega transposase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6022–6026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delahodde A., Goguel V., Becam A. M., Creusot F., Perea J., Banroques J., Jacq C. Site-specific DNA endonuclease and RNA maturase activities of two homologous intron-encoded proteins from yeast mitochondria. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Belfort M., Butow R. A., Jacq C., Lemieux C., Perlman P. S., Vogt V. M. Mobile introns: definition of terms and recommended nomenclature. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Group I introns as mobile genetic elements: facts and mechanistic speculations--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):91–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscarella D. E., Ellison E. L., Ruoff B. M., Vogt V. M. Characterization of I-Ppo, an intron-encoded endonuclease that mediates homing of a group I intron in the ribosomal DNA of Physarum polycephalum. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3386–3396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman P. S., Butow R. A. Mobile introns and intron-encoded proteins. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1106–1109. doi: 10.1126/science.2479980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirk S. M., Bell-Pedersen D., Belfort M. Intron mobility in the T-even phages: high frequency inheritance of group I introns promoted by intron open reading frames. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirk S. M., Bell-Pedersen D., Tomaschewski J., Rüger W., Belfort M. The inconsistent distribution of introns in the T-even phages indicates recent genetic exchanges. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):301–315. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revzin A. Gel electrophoresis assays for DNA-protein interactions. Biotechniques. 1989 Apr;7(4):346–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A., Kikuchi Y., Nash H. Interaction of int protein with specific sites on lambda att DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90049-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzlau J. M., Saldanha R. J., Butow R. A., Perlman P. S. A latent intron-encoded maturase is also an endonuclease needed for intron mobility. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):421–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90245-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West D. K., Changchien L. M., Maley G. F., Maley F. Evidence that the intron open reading frame of the phage T4 td gene encodes a specific endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10343–10346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]