Abstract
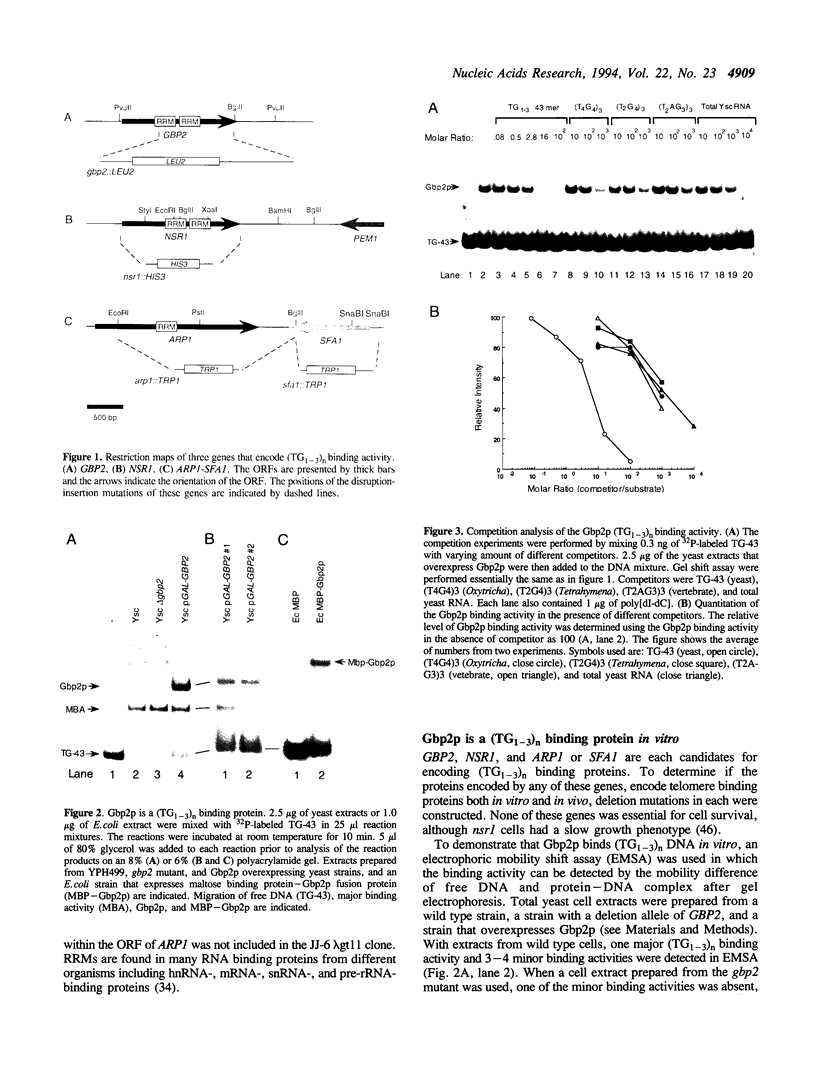
By screening lambda gt11 libraries with a radiolabeled (TG1-3)n oligonucleotide, two Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes were identified that encode polypeptides that recognize the single-stranded telomeric repeat sequence (TG1-3)n. The first gene, NSR1, a previously identified gene, encodes a protein involved in ribosomal RNA maturation and possibly in transport of proteins into the nucleus. The second gene, GBP2 (G-strand Binding Protein), is an anonymous open reading frame from chromosome III. These two genes contain RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) that are found in proteins that interact with RNA. Both Nsr1p and Gbp2p bind specifically to yeast single strand (TG1-3)n DNA in vitro. To test whether these two proteins associate with telomeres in vivo, strains were constructed in which one or both of these genes were either disrupted or overexpressed. None of these alterations affected telomere length or telomere position effect. The potential role of these two (TG1-3)n binding proteins is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudin A., Ozier-Kalogeropoulos O., Denouel A., Lacroute F., Cullin C. A simple and efficient method for direct gene deletion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3329–3330. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birney E., Kumar S., Krainer A. R. Analysis of the RNA-recognition motif and RS and RGG domains: conservation in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5803–5816. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:113–129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres: structure and synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):5919–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas M. E., Bianchi A., de Lange T. A Xenopus egg factor with DNA-binding properties characteristic of terminus-specific telomeric proteins. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):883–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang G., Cech T. R. The beta subunit of Oxytricha telomere-binding protein promotes G-quartet formation by telomeric DNA. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesman D., Best L., Tatchell K. The role of RAP1 in the regulation of the MAT alpha locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1069–1079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson E., Laroche T., Gasser S. M. Telomeres and the functional architecture of the nucleus. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;3(4):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90175-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo R., Rhodes D. The yeast telomere-binding protein RAP1 binds to and promotes the formation of DNA quadruplexes in telomeric DNA. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2411–2420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Aparicio O. M., Billington B. L., Zakian V. A. Position effect at S. cerevisiae telomeres: reversible repression of Pol II transcription. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):751–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90141-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Zakian V. A. Telomere proteins: specific recognition and protection of the natural termini of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto A., Patrick R. M., Walsh K. Nucleic acid specificity of a vertebrate telomere-binding protein: evidence for G-G base pair recognition at the core-binding site. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):815–824. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy C. F., Sussel L., Shore D. A RAP1-interacting protein involved in transcriptional silencing and telomere length regulation. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):801–814. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. R., Blackburn E. H. An overhanging 3' terminus is a conserved feature of telomeres. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):345–348. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Eghtedarzadeh M. K. Conserved arrangement of nested genes at the Drosophila Gart locus. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):711–725. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G., Cech T. R. Nuclear proteins that bind the pre-mRNA 3' splice site sequence r(UUAG/G) and the human telomeric DNA sequence d(TTAGGG)n. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4301–4310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein F., Laroche T., Cardenas M. E., Hofmann J. F., Schweizer D., Gasser S. M. Localization of RAP1 and topoisomerase II in nuclei and meiotic chromosomes of yeast. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):935–948. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Swanton M. T., Donini P., Prescott D. M. All gene-sized DNA molecules in four species of hypotrichs have the same terminal sequence and an unusual 3' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaki T., Yamashita S. Yeast phosphatidylethanolamine methylation pathway. Cloning and characterization of two distinct methyltransferase genes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15428–15435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrion G., Boakye K. A., Lustig A. J. C-terminal truncation of RAP1 results in the deregulation of telomere size, stability, and function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5159–5173. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. C., Mélèse T. Identification and characterization of a nuclear localization sequence-binding protein in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8808–8812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. C., Xue Z. X., Mélèse T. The NSR1 gene encodes a protein that specifically binds nuclear localization sequences and has two RNA recognition motifs. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):1–12. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. C., Zabetakis D., Mélèse T. NSR1 is required for pre-rRNA processing and for the proper maintenance of steady-state levels of ribosomal subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3865–3871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J. Telomeric DNA binding proteins. Bioessays. 1993 Aug;15(8):555–557. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H., Krizek J., Bretscher A. Construction of a GAL1-regulated yeast cDNA expression library and its application to the identification of genes whose overexpression causes lethality in yeast. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):665–673. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay S. J., Cooke H. A protein which specifically binds to single stranded TTAGGGn repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1387–1391. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay S. J., Cooke H. hnRNP A2/B1 binds specifically to single stranded vertebrate telomeric repeat TTAGGGn. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6461–6464. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlon C. S., Lipchitz L. R., Collins I., Deshpande A., Devenish R. J., Green R. P., Klein H. L., Palzkill T. G., Ren R. B., Synn S. Analysis of a circular derivative of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome III: a physical map and identification and location of ARS elements. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):343–357. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palladino F., Laroche T., Gilson E., Axelrod A., Pillus L., Gasser S. M. SIR3 and SIR4 proteins are required for the positioning and integrity of yeast telomeres. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):543–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petracek M. E., Konkel L. M., Kable M. L., Berman J. A Chlamydomonas protein that binds single-stranded G-strand telomere DNA. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3648–3658. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Kaine B. P., Spear B. B. The terminal organization of macronuclear DNA in Oxytricha fallax. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8145–8154. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polaina J., Adam A. C. A fast procedure for yeast DNA purification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5443–5443. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Cech T. R. Properties of the telomeric DNA-binding protein from Oxytricha nova. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):769–774. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. M., Cech T. R. Telomeric DNA-protein interactions of Oxytricha macronuclear DNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):783–793. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Assembly and self-association of oxytricha telomeric nucleoprotein complexes. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):719–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge K. W., Zakian V. A. Introduction of extra telomeric DNA sequences into Saccharomyces cerevisiae results in telomere elongation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1488–1497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoeman R. L., Traub P. The in vitro DNA-binding properties of purified nuclear lamin proteins and vimentin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9055–9061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavenhagen J. B., Zakian V. A. Internal tracts of telomeric DNA act as silencers in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 15;8(12):1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.12.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussel L., Shore D. Separation of transcriptional activation and silencing functions of the RAP1-encoded repressor/activator protein 1: isolation of viable mutants affecting both silencing and telomere length. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7749–7753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., De Camilli P., Niemann H., Jahn R. Membrane fusion machinery: insights from synaptic proteins. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehner E. P., Rao E., Brendel M. Molecular structure and genetic regulation of SFA, a gene responsible for resistance to formaldehyde in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and characterization of its protein product. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Mar;237(3):351–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00279438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellinger R. J., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. Saccharomyces telomeres acquire single-strand TG1-3 tails late in S phase. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90049-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. H., Gottschling D. E., Zakian V. A. Saccharomyces telomeres assume a non-nucleosomal chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):197–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]