Abstract
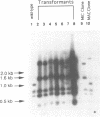
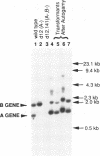
The micronuclear DNA of Paramecium contains sequences that are precisely excised during the formation of the macronuclear (somatic) genome. In this paper we show that four eliminated sequences ranging in size from 28 to 416 base pairs, are present in or near the micronuclear copy of the B surface protein gene. Each excised sequence is bounded by the dinucleotide 5'-TdA-3'. Comparison of the micronuclear B gene with the previously determined micronuclear sequence of the A surface protein gene shows that although the positions of at least three of the eliminated sequences are conserved in both genes, the sequences are highly divergent. Transformation of vegetative macronuclei with fragments of the micronuclear B gene results in replication and maintenance of the DNA, but the micronuclear specific sequences are not removed. Previous studies have shown that the correct incorporation of the B gene into the new macronucleus requires copies of the macronuclear B gene in the old macronucleus. Using macronuclear transformation, we show that the micronuclear B gene can substitute for the macronuclear B gene with regard to its role in DNA processing. This suggests that the macronuclear DNA is not acting as a guide for the excision of the micronuclear specific sequences.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar L. Chromosome end formation and internal sequence elimination as alternative genomic rearrangements in the ciliate Paramecium. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 18;236(2):421–426. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Karrer K. M. Genomic reorganization in ciliated protozoans. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:501–521. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron F. A high degree of macronuclear chromosome polymorphism is generated by variable DNA rearrangements in Paramecium primaurelia during macronuclear differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):661–678. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron F., Meyer E. Molecular basis of surface antigen variation in paramecia. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:23–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney J. D., Blackburn E. H. Developmentally controlled telomere addition in wild-type and mutant paramecia. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilley D., Preer J. R., Jr, Aufderheide K. J., Polisky B. Autonomous replication and addition of telomerelike sequences to DNA microinjected into Paramecium tetraurelia macronuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4765–4772. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., Aufderheide K. J., Gilley D., Hendrie P., Fitzwater T., Preer L. B., Polisky B., Preer J. R., Jr Transformation of Paramecium by microinjection of a cloned serotype gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7590–7594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., James C., Yao M. C. A distant 10-bp sequence specifies the boundaries of a programmed DNA deletion in Tetrahymena. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2357–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godiska R., Yao M. C. A programmed site-specific DNA rearrangement in Tetrahymena thermophila requires flanking polypurine tracts. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1237–1246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90688-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. S., Preer J. R., Jr, Polisky B. Identification of DNA segments capable of rescuing a non-mendelian mutant in paramecium. Genetics. 1994 Apr;136(4):1325–1328. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer L. B., Hamilton G., Preer J. R., Jr Micronuclear DNA from Paramecium tetraurelia: serotype 51 A gene has internally eliminated sequences. J Protozool. 1992 Nov-Dec;39(6):678–682. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb04448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott D. M. The DNA of ciliated protozoa. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Jun;58(2):233–267. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.2.233-267.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribas-Aparicio R. M., Sparkowski J. J., Proulx A. E., Mitchell J. D., Klobutcher L. A. Nucleic acid splicing events occur frequently during macronuclear development in the protozoan Oxytricha nova and involve the elimination of unique DNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):323–336. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman B., Preer L. B., Polisky B., Preer J. R., Jr Mutants affecting processing of DNA in macronuclear development in paramecium. Genetics. 1991 Sep;129(1):47–56. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. M., Mikami K., Leeck C. L., Forney J. D. Non-Mendelian inheritance of macronuclear mutations is gene specific in Paramecium tetraurelia. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2479–2484. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Leeck C., Forney J. Molecular and genetic analyses of the B type surface protein gene from Paramecium tetraurelia. Genetics. 1993 May;134(1):189–198. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldo A. T., Godoy G. A. The kinetic complexity of Paramecium macronuclear deoxyribonucleic acid. J Protozool. 1972 Nov;19(4):673–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1972.tb03558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele C. J., Barkocy-Gallagher G. A., Preer L. B., Preer J. R., Jr Developmentally excised sequences in micronuclear DNA of Paramecium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2255–2259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondravi M. M., Yao M. C. Transformation of Tetrahymena thermophila by microinjection of ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You Y., Aufderheide K., Morand J., Rodkey K., Forney J. Macronuclear transformation with specific DNA fragments controls the content of the new macronuclear genome in Paramecium tetraurelia. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1133–1137. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You Y., Scott J., Forney J. The role of macronuclear DNA sequences in the permanent rescue of a non-mendelian mutation in Paramecium tetraurelia. Genetics. 1994 Apr;136(4):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]