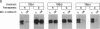Abstract
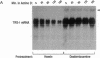
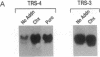
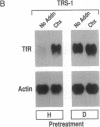
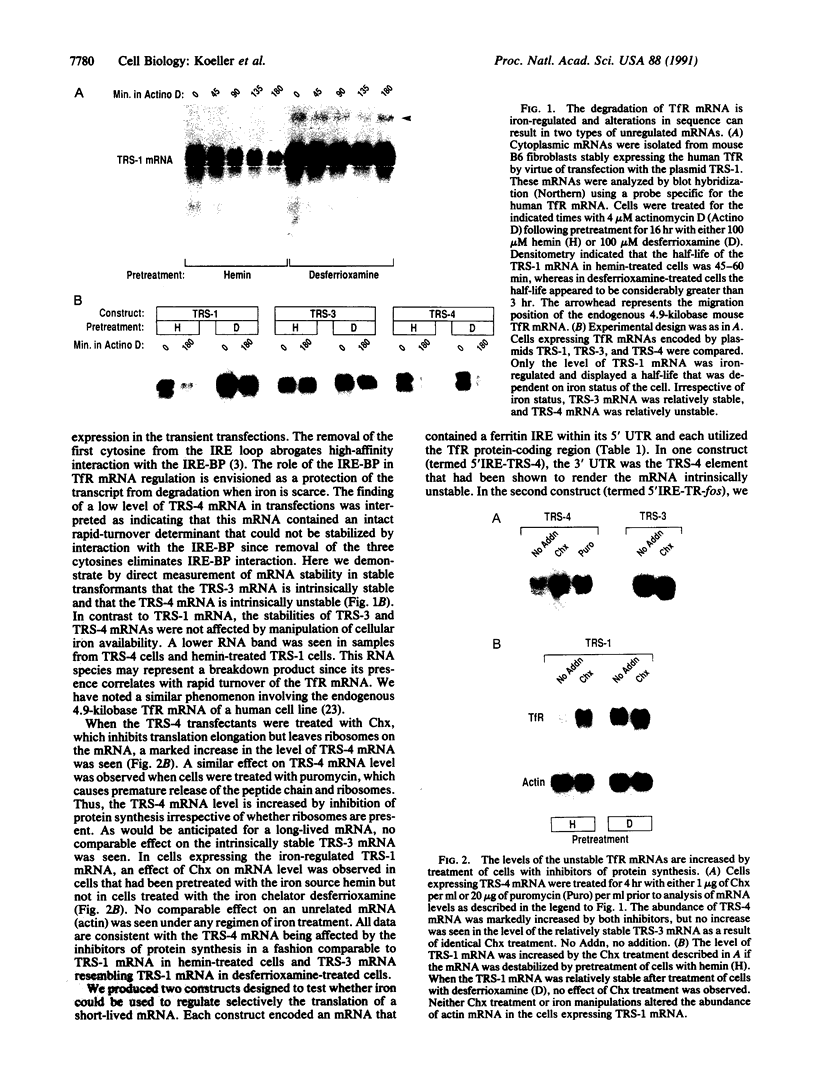
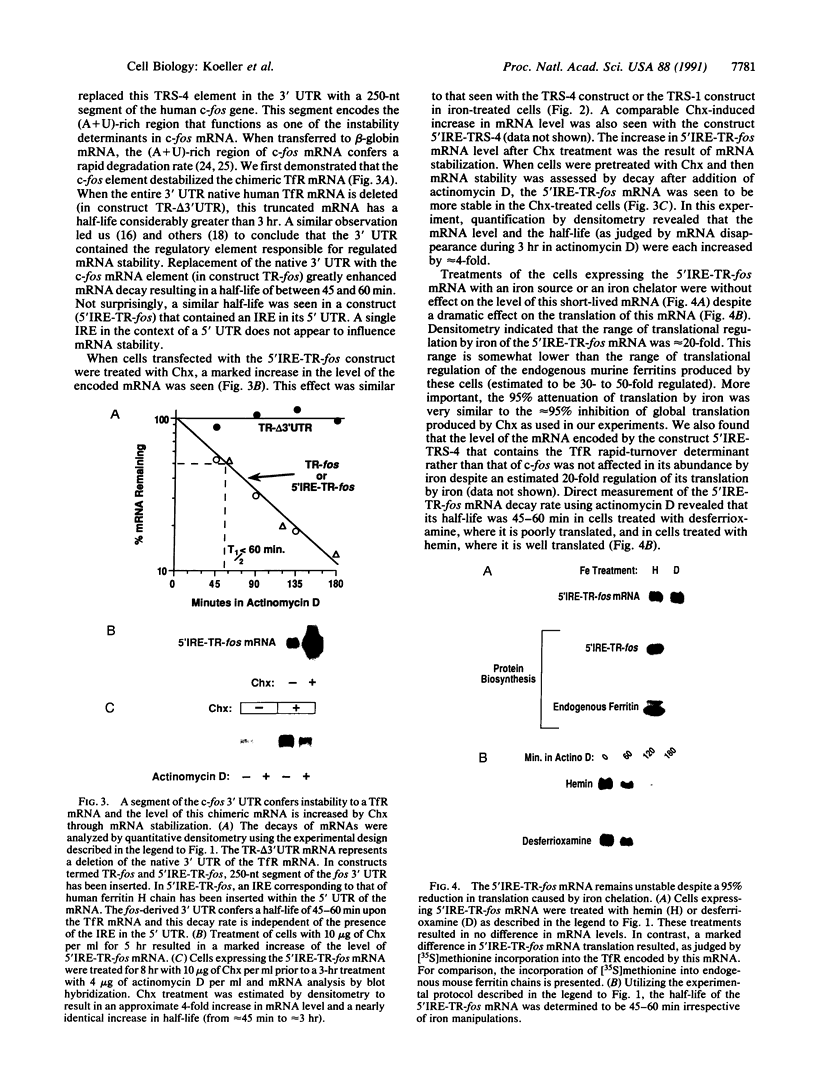
Turnover of the full-length human transferrin receptor (TfR) mRNA is regulated by iron, and this regulation is mediated by the transcript's 3' untranslated region. Alterations in the sequence of the TfR mRNA regulatory region have been identified that render the mRNA unregulated by iron and intrinsically unstable. When cells expressing this unstable mRNA are treated with inhibitors of protein synthesis (cycloheximide or puromycin), the steady-state level of the encoded human TfR mRNA is increased due to a stabilization of the transcript. A similar set of observations has been made using a chimeric mRNA in which the rapid turnover determinant of the TfR mRNA is replaced by the (A+U)-rich region from the 3' untranslated region of c-fos mRNA. To distinguish between a labile protein participant in the degradation of these mRNAs and a requirement for their translation per se, we introduced a ferritin iron-responsive element into the 5' untranslated region of each of these mRNAs. The presence of the 5' iron-responsive element allowed us to use iron availability to alter the translation of the mRNAs in question without global effects on cellular protein synthesis. Although specific translation of these mRNAs could be inhibited by iron chelation to a degree comparable to that seen with cycloheximide (approximately 95% inhibition), no effects on mRNA turnover were observed. These data support a model in which a trans-acting labile protein is necessary for the turnover of these mRNAs rather than there being a requirement for the translation of the mRNAs themselves.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein P., Ross J. Poly(A), poly(A) binding protein and the regulation of mRNA stability. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Sep;14(9):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Di Jeso B., Rao K., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Two genetic loci participate in the regulation by iron of the gene for the human transferrin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1787–1791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Koeller D. M., Ramin V. C., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA levels requires iron-responsive elements and a rapid turnover determinant in the 3' untranslated region of the mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3693–3699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Yen T. J. Multiple determinants of eukaryotic mRNA stability. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrove J. L., Schmidt F. H. The role of mRNA and protein stability in gene expression. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2360–2370. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. cis-trans models for post-transcriptional gene regulation. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):870–872. doi: 10.1126/science.2683086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn L. C., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Gene transfer, expression, and molecular cloning of the human transferrin receptor gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90304-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird-Offringa I. A., de Wit C. L., Elfferich P., van der Eb A. J. Poly(A) tail shortening is the translation-dependent step in c-myc mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6132–6140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Pandey N. B. Multiple regulatory steps control histone mRNA concentrations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N. Iron regulation of ferritin gene expression. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Oct;44(2):107–115. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240440205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D., Kühn L. C. Noncoding 3' sequences of the transferrin receptor gene are required for mRNA regulation by iron. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1287–1293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Schönthal A., Angel P., Litfin M., Rüther U., Herrlich P. Posttranscriptional regulation of c-fos mRNA expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1643–1659. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Munro H. Translation of ferritin light and heavy subunit mRNAs is regulated by intracellular chelatable iron levels in rat hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2277–2281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G., Brewer G., Peltz S. W. Properties of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9374–9381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil E. C. Regulation of ferritin and transferrin receptor mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4771–4774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene during cellular proliferation. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):374–380. doi: 10.1038/319374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]